
Ulmus glabraHudson, the wych elm or Scots elm, has the widest range of the European elm species, from Ireland eastwards to the Urals, and from the Arctic Circle south to the mountains of the Peloponnese and Sicily, where the species reaches its southern limit in Europe; it is also found in Iran. A large deciduous tree, it is essentially a montane species, growing at elevations up to 1,500 m (4,900 ft), preferring sites with moist soils and high humidity. The tree can form pure forests in Scandinavia and occurs as far north as latitude 67°N at Beiarn in Norway. It has been successfully introduced as far north as Tromsø, Norway and Alta, Norway (70°N). It has also been successfully introduced to Narsarsuaq, near the southern tip of Greenland (61°N).

Aralia spinosa, commonly known as devil's walking stick, is a woody species of plant in the genus Aralia, family Araliaceae, native to eastern North America. The various names refer to the viciously sharp, spiny stems, petioles, and even leaf midribs. It has also been known as Angelica-tree.

Annona glabra is a tropical fruit tree in the family Annonaceae, in the same genus as the soursop and cherimoya. Common names include pond apple, alligator apple, swamp apple, corkwood, bobwood, and monkey apple. The tree is native to Florida in the United States, the Caribbean, Central and South America, and West Africa. It is common in the Everglades. The A. glabra tree is considered an invasive species in Sri Lanka and Australia. It grows in swamps, is tolerant of saltwater, and cannot grow in dry soil.

Eremophila is a genus of more than 260 species of plants in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae all of which are endemic to mainland Australia.. Eremophilas are widespread in the arid areas of Australia, especially Western Australia and range in size from low-growing shrubs to small trees. The petals are joined, at least at their bases, into a tube with the upper petals different in size and shape from the lower ones. Some species have common names including emu bush, poverty bush or fuchsia bush, reflecting the belief that emus eat the fruit, their arid environment or a superficial resemblance to the flowers of plants in the genus Fuchsia.

Cornus sericea, the red osier or red-osier dogwood, is a species of flowering plant in the family Cornaceae, native to much of North America. It has sometimes been considered a synonym of the Asian species Cornus alba. Other names include red brush, red willow, redstem dogwood, redtwig dogwood, red-rood, American dogwood, creek dogwood, and western dogwood.

Vaccinium corymbosum, the northern highbush blueberry, is a North American species of blueberry which has become a food crop of significant economic importance. It is native to eastern Canada and the eastern and southern United States, from Ontario east to Nova Scotia and south as far as Florida and eastern Texas. It is also naturalized in other places: Europe, Japan, New Zealand, the Pacific Northwest of North America, etc. Other common names include blue huckleberry, tall huckleberry, swamp huckleberry, high blueberry, and swamp blueberry.
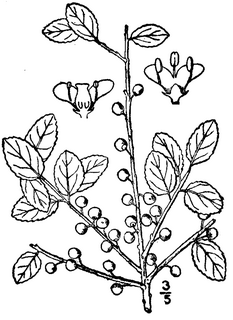
Ilex glabra, also known as Appalachian tea, dye-leaves, evergreen winterberry, gallberry, and inkberry, is a species of evergreen holly native to the coastal plain of eastern North America, from coastal Nova Scotia to Florida and west to Louisiana where it is most commonly found in sandy woods and peripheries of swamps and bogs. Ilex glabra is often found in landscapes of the middle and lower East Coast of the United States. It typically matures to 5–8 ft (1.5–2.4 m) tall, and can spread by root suckers to form colonies. It normally is cultivated as an evergreen shrub in USDA zones 6 to 10.

Bougainvillea glabra, the lesser bougainvillea or paperflower, is the most common species of bougainvillea used for bonsai. The epithet 'glabra' comes from Latin and means "bald".
Ulmus ellipticaKoch is a disputed species of elm, native to the Caucasus, where Koch reported that it formed extensive woods, and ranging north to southern Ukraine. The tree is said to be closely related to U. glabra, but to resemble U. rubra in its samara. Many authorities consider U. ellipticaKoch just a regional form of U. glabra, though Henry, Bean and Krüssman list the Caucasus tree as a species in its own right. U. ellipticaKoch is distinguished from U. scabraMill. [:U. glabra] in some Armenian and Russian plant lists.

Rhus glabra, the smooth sumac, is a species of sumac in the family Anacardiaceae, native to North America, from southern Quebec west to southern British Columbia in Canada, and south to northern Florida and Arizona in the United States and Tamaulipas in northeastern Mexico.

Cupressus stephensonii is a species of conifer known as the Cuyamaca cypress, and is endemic to Southern California. It has been classified as Hesperocyparis stephensonii. It was previously listed as Cupressus arizonica subsp. stephensonii and Cupressus arizonica var. glabra.

Conradina glabra is a rare species of shrub known by the common name Apalachicola rosemary. It is endemic to Liberty County, Florida, where it is known from about ten populations. It is found only in a small area and it is threatened by habitat destruction. It is a federally listed endangered species.

Mirabilis macfarlanei is a rare species of flowering plant in the four o'clock family known by the common name MacFarlane's four o'clock. It is native to Idaho and Oregon in the United States, where it is only known from three river canyons. It faces a number of threats and is federally listed as a threatened species of the United States.
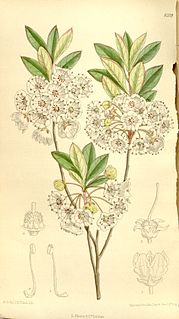
Kalmia cuneata is a species of flowering plant in the heath family known by the common name whitewicky, sometimes spelled white-wicky or white wicky. It is native to the eastern United States, where it occurs only in North Carolina and South Carolina.

Rosa stellata is a species of rose known by the common names desert rose, gooseberry rose, and star rose. In Texas this type of rose grows on dry rocky places to 6,500 feet (2,000 m), such as the Trans-Pecos. It occurs in the mountain canyons of Arizona and New Mexico. It also grows in dry, rocky places. It has trifoliate leaves, deep rose purple blossoms and yellowish white prickles on the petioles and stems. It is a perennial shrub with velvety, deciduous leaves. Some horticulturists consider it to be a browse plant.

Schisandra glabra, the bay star-vine, is the only American species of this primarily Asian genus. It is native to the southeastern United States and northern Mexico. It grows in Louisiana, eastern Arkansas, southwestern Tennessee, Mississippi, Alabama, northwestern Florida, and Georgia, with isolated populations in Kentucky, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Hidalgo. Despite its wide range, it is considered a vulnerable species. Few populations are secure due to competition from invasive species and habitat loss.

Vallesia is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1794. It is native to South America, Central America, Mexico, Florida, Galápagos, and the West Indies.
Vallesia antillana, common name pearl berry or tearshrub, is a flowering shrub that grows in The Bahamas, Greater Antilles, and Key West. A small population has also been found in Everglades National Park. The flowers do not have much fragrance. It is a perennial plant with white flowers and white fruit. It is in the family Apocynaceae.

Bauhinia glabra, also commonly referred to as the monkey step/ladder, is more often introduced with its accepted name, whereas Bauhinia cumanensis, is a synonym for the plant name. B. glabra is located in the tropical climates of countries such as Venezuela, Trinidad and Tobago, Ecuador, Brazil, Costa Rica, Colombia and Guayana, while being introduced to Sri Lanka.

The flora of Wales refers to the plant life in Wales.




















