
L1, also known as L1CAM, is a transmembrane protein member of the L1 protein family, encoded by the L1CAM gene. This protein, of 200 to 220 kDa, is a neuronal cell adhesion molecule with a strong implication in cell migration, adhesion, neurite outgrowth, myelination and neuronal differentiation. It also plays a key role in treatment-resistant cancers due to its function. It was first identified in 1984 by M. Schachner who found the protein in post-mitotic mice neurons.

T-box transcription factor T, also known as Brachyury protein, is encoded for in humans by the TBXT gene. Brachyury functions as a transcription factor within the T-box family of genes. Brachyury homologs have been found in all bilaterian animals that have been screened, as well as the freshwater cnidarian Hydra.

SMAD4, also called SMAD family member 4, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, or DPC4 is a highly conserved protein present in all metazoans. It belongs to the SMAD family of transcription factor proteins, which act as mediators of TGF-β signal transduction. The TGFβ family of cytokines regulates critical processes during the lifecycle of metazoans, with important roles during embryo development, tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and immune regulation.

Transcription factor Jun is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUN gene. c-Jun, in combination with protein c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the JUN gene. c-jun was the first oncogenic transcription factor discovered. The proto-oncogene c-Jun is the cellular homolog of the viral oncoprotein v-jun. The viral homolog v-jun was discovered in avian sarcoma virus 17 and was named for ju-nana, the Japanese word for 17. The human JUN encodes a protein that is highly similar to the viral protein, which interacts directly with specific target DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. This gene is intronless and is mapped to 1p32-p31, a chromosomal region involved in both translocations and deletions in human malignancies.

High-mobility group AT-hook 2, also known as HMGA2, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the HMGA2 gene.
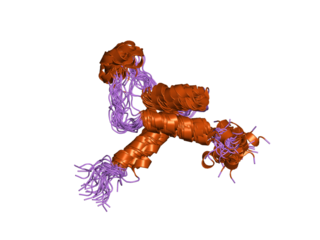
TEAD2, together with TEAD1, defines a novel family of transcription factors, the TEAD family, highly conserved through evolution. TEAD proteins were notably found in Drosophila (Scalloped), C. elegans, S. cerevisiae and A. nidulans. TEAD2 has been less studied than TEAD1 but a few studies revealed its role during development.

Runt-related transcription factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUNX3 gene.

Metastasis-associated protein MTA1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTA1 gene. MTA1 is the founding member of the MTA family of genes. MTA1 is primarily localized in the nucleus but also found to be distributed in the extra-nuclear compartments. MTA1 is a component of several chromatin remodeling complexes including the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylation complex (NuRD). MTA1 regulates gene expression by functioning as a coregulator to integrate DNA-interacting factors to gene activity. MTA1 participates in physiological functions in the normal and cancer cells. MTA1 is one of the most upregulated proteins in human cancer and associates with cancer progression, aggressive phenotypes, and poor prognosis of cancer patients.
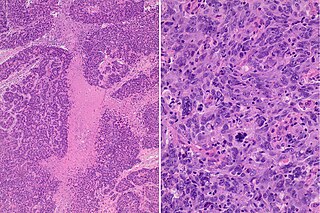
The basal-like carcinoma is a recently proposed subtype of breast cancer defined by its gene expression and protein expression profile.

GATA3 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the GATA3 gene. Studies in animal models and humans indicate that it controls the expression of a wide range of biologically and clinically important genes.
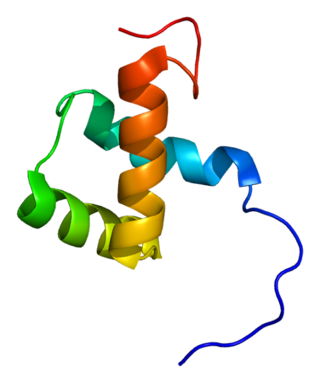
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZEB1 gene.

Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-1 also known as TEA domain family member 1 (TEAD1) and transcription factor 13 (TCF-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEAD1 gene. TEAD1 was the first member of the TEAD family of transcription factors to be identified.

Protein UXT also known as androgen receptor trapped clone 27 (ART-27) protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UXT gene.

SAM pointed domain-containing Ets transcription factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPDEF gene.

Zinc transporter SLC39A7 (ZIP7), also known as solute carrier family 39 member 7, is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC39A7 gene. It belongs to the ZIP family, which consists of 14 proteins that transport zinc into the cytoplasm. Its primary role is to control the transport of zinc from the ER and Golgi apparatus to the cytoplasm. It also plays a role in glucose metabolism. Its structure consists of helices that bind to zinc in a binuclear metal center. Its fruit fly orthologue is Catsup.

ETS homologous factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EHF gene. This gene encodes a protein that belongs to an ETS transcription factor subfamily characterized by epithelial-specific expression (ESEs). The encoded protein acts as a transcriptional repressor and may be associated with asthma susceptibility. This protein may be involved in epithelial differentiation and carcinogenesis.

Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEAD3 gene.

Transcription factor AP-2 gamma also known as AP2-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2C gene. AP2-gamma is a member of the activating protein 2 family of transcription factors.

Forkhead box protein J1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXJ1 gene. It is a member of the Forkhead/winged helix (FOX) family of transcription factors that is involved in ciliogenesis. FOXJ1 is expressed in ciliated cells of the lung, choroid plexus, reproductive tract, embryonic kidney and pre-somite embryo stage.

Vestigial like family member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VGLL4 gene.






















