Related Research Articles

Malayalam, the lingua franca of the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puduchery, is one of the six classical languages of India. Malayalam literature comprises those literary texts written in Malayalam, a South-Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala. The first travelogue in any Indian language is the Malayalam Varthamanappusthakam, written by Paremmakkal Thoma Kathanar in 1785. Malayalam literature has been presented with 6 Jnanapith awards, the second-most for any Dravidian language and the third-highest for any Indian language.

Sree Narayana Guru was a philosopher, spiritual leader and social reformer in India. He led a reform movement against the injustice in the caste-ridden society of Kerala in order to promote spiritual enlightenment and social equality. A quote of his that defined his movement was "one caste, one religion, and one god for all human beings." He is the author of the Advaita poem Daiva Dasakam, which is one of the most used poem in Kerala for community prayer.

Panikkassery Keshavan "P.K." Balakrishnan was an Indian novelist and critic. A doyen of Malayalam literature, he is best known for his novel, Ini Njan Urangatte, a novel based on Mahabharata as well as a number of critical studies which include Chandu Menon Oru Padanam, Novel Siddhiyum Sadhanayum, Kavyakala Kumaranasaniloode, and Ezhuthachante Kala: Chila Vyasabharatha Patanangalum. His Jathivyavasthayum Kerala Charitravum is a work in social history.

Mahakavi Kumaran Asan was a poet of Malayalam literature, Indian social reformer and a philosopher.He is known to have initiated a revolution in Malayalam poetry during the first quarter of the 20th century, transforming it from the metaphysical to the lyrical and his poetry is characterised by its moral and spiritual content, poetic concentration and dramatic contextualisation. He is one of the triumvirate poets of Kerala and a disciple of Sree Narayana Guru. He was awarded the prefix "Mahakavi" in 1922 by the Madras university which means "great poet".
Nitya Chaitanya Yati was an Indian philosopher, psychologist, author and poet, best known for his commentaries on Advaita Vedanta as well as his literary criticisms. He was a disciple of Nataraja Guru, the successor to Narayana Guru. Yati published over 140 books in English and Malayalam including a commentary on Darsana Mala of Narayana Guru, titled, Psychology of Darsana Mala. Kerala Sahitya Akademi honoured him with their annual award for literary criticism in 1977.

Vallathol Narayana Menon was a Malayalam poet and one of the triumvirate of modern Malayalam poetry, along with Asan and Ulloor. The honorific Mahakavi was applied to him in 1913 after the publication of his MahakavyaChitrayogam. He was a nationalist poet and wrote a series of poems on various aspects of the Indian freedom movement. He founded the Kerala Kalamandalam and is credited with revitalising the traditional Keralite dance form known as Kathakali.
Kumbalathuparambu Ayyappan, better identified as Sahodaran Ayyappan, was a social reformer, thinker, rationalist, journalist, and politician from Kerala, India. As a vocal follower of Sree Narayana Guru, he was associated with a number of events related to the Kerala reformation movement and was the organizer of Misra Bhojanam in Cherai in 1917. He founded Sahodara Sangam, and the journal Sahodaran and was the founder editor of the magazine Yukthivadi.
Kanakku Chembakaraman Kesava Pillai (1868–1914) was an Indian composer of Carnatic music and a poet of Malayalam literature. He was the Poet Laureate of Travancore and was known for Kesaveeyam, a mahakavya in Malayalam, two attakathas and several bhajans and kirtans. He also translated the Sanskrit text, Narayaniyam, into Malayalam under the title, Bhashanarayaniyam.

Ulloor S. Parameswara Iyer, born Sambasivan but popularly known as Ulloor, was an Indian poet of Malayalam literature and a historian. He was one of the modern triumvirate poets of Kerala in the first half of the 20th century, along with Kumaran Asan and Vallathol Narayana Menon. Umakeralam, a mahakavya, and Kerala Sahitya Charitram, a comprehensive history of the Malayalam language are two of his most important works.

The Ezhavas are a community with origins in the region of India presently known as Kerala, where in the 2010s they constituted about 23% of the population and were reported to be the largest Hindu community. The Malabar Ezhava group have claimed a higher ranking in the Hindu caste system than do the others, although from the perspective of the colonial and subsequent administrations they were treated as being of similar rank.

T. K. Madhavan Alias Deshabhimani Madhavan, was an Indian social reformer, journalist and revolutionary, who was involved with the Sree Narayana Dharma Paripalana Yogam. He hailed from Kerala and led the struggle against Social discrimination which was known as Vaikom Satyagraha.

Moorkoth Kumaran (1874–1941) was a social reformer, a teacher and a writer in Malayalam. He came from a Thiyya family of Telicherry. He was a disciple of Narayana Guru and wrote the first biography of Guru. He also published some of the earliest short stories and novels in Malayalam.

C. V. Kunhiraman was an Indian social reformer, journalist and the founder of Kerala Kaumudi daily. A follower of Sree Narayana Guru, Kunhiraman was the author of a number of books covering the genres of novels, short story, poetry, biographies and essays. He was one of the leaders involved in the Vaikom Satyagraha of Reformation movement in Kerala which led to the Temple Entry Proclamation.
Karimpumannil Mathai George (1914–2002), popularly known as Dr. K. M. George, was an eminent Malayalam writer and educator. An erudite scholar and literary critic with astute organisational capabilities, he is best known as a pioneer of Comparative Indian Studies and Literatures. He was a recipient of the fourth highest Indian civilian honour, the Padma Shri, the highest literary award of the Government of Kerala, the Ezhuthachan Puraskaram and the third highest Indian civilian award, the Padma Bhushan, besides other honours.

Kerala Varma, most commonly known as Mahakavi Pandalam Kerala Varma, was an Indian poet, scholar, and publisher. He was born in Pandalam, and belonged to the Pandalam Royal Family. He wrote two mahakavyas, more than a hundred narrative poems, translations, and children's poetry. He is widely regarded as the author of the first complete mahakavya in Malayalam. He was the owner and Chief Editor of Kavana Kaumudi, the first Malayalam periodical, which was also the first to introduce special issues in Malayalam.

N. Krishna Pillai was an Indian dramatist, literary critic, translator and historian of Malayalam language. Known for his realism and dramatic portrayal of psycho-social tensions, Pillai's plays earned him the moniker, Kerala Ibsen. He was a recipient of the Sahitya Akademi Award, Kerala Sahitya Akademi Award for Drama, Odakkuzhal Award, Vayalar Award and Kerala Sangeetha Nataka Akademi Award, besides other honours. The Kerala Sahitya Akademi inducted him as a distinguished fellow in 1979.

Puthussery Ramachandran Pillai was an Indian poet of the Malayalam language. He was a scholar of Dravidian linguistics and a professor of Malayalam for more than three decades. On 14 March 2020, he died of age-related illnesses.

Malappurath Raman Chandrasekharan, popularly known as M.R. Chandrasekharan or simply M. R. C., is a Malayalam literary critic and author from Kerala, India. Chandrasekharan has published more than 50 books in different literary sections like literary criticism, translations, politics, social etc. He also works in the field of journalism and education. He won the 2010 Kerala Sahitya Akademi Award for Literary Criticism.
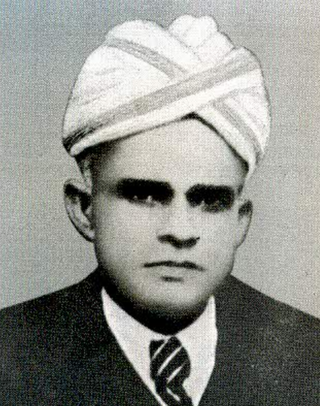
P. K. Narayana Pillai, better identified as Sahitya Panchanan P. K. Narayana Pillai, was an Indian literary critic, essayist, scholar, grammarian and poet of Malayalam language. One of the pioneers of literary criticism in Malayalam, he wrote more than 25 books which include Panchananante Vimarssthrayam, a critique of the writings of Thunchaththu Ezhuthachan, Cherusseri Namboothiri and Kunchan Nambiar and two books on Malayalam grammar, Leghuvyakaranam and Vyakarana Pravesika. He was a judge of the High Court of Kerala, a member of the Sree Moolam Popular Assembly and the founder president of the Samastha Kerala Sahithya Parishad.

Prayar Prabhakaran is a literary critic, academic and orator from Kerala, India. He won several noted awards including Kerala Sahitya Akademi Award for Overall Contributions and the Thayatt Award for Literary Criticism.
References
- ↑ George 1972, p. 22.
- ↑ Das 1991, p. 257.
- 1 2 3 Sadasivan 2000, p. 600.
- ↑ George 1972, pp. 22, 66–67.
- ↑ Kesavan 1988, p. 19.
- ↑ "Publications". Kumaran Asan National Institute of Culture. Archived from the original on 18 November 2010. Retrieved 15 September 2013.
- ↑ George 1972, pp. 66–67.
- ↑ George 1972, pp. 68–69.
- ↑ George 1972, p. 70.
- ↑ Basu, Shankari Prasad (1989). "Vivekananda and social movements in Kerala". Prabuddha Bharata . 94 (2): 103.
