
Lithops is a genus of succulent plants in the ice plant family, Aizoaceae. Members of the genus are native to southern Africa. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek words λίθος (lithos), meaning "stone," and ὄψ (ops), meaning "face," referring to the stone-like appearance of the plants. They avoid being eaten by blending in with surrounding rocks and are often known as pebble plants or living stones. The formation of the name from the Greek "-ops" means that even a single plant is called a Lithops.

Aptenia is a small genus of flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae. They are native to southern Africa. The genus name is from the Greek a- (not) and ptenos (winged), and refers to the wingless fruit capsules.

Conophytum is a genus of South African and Namibian succulent plants that belong to the family Aizoaceae. The name is derived from the Latin conus (cone) and Greek phytum (plant). The plants are also known as knopies (buttons), waterblasies, sphaeroids, conos, cone plants, dumplings, or button plants.

Mesembryanthemum cordifolium formerly known as Aptenia cordifolia is a species of succulent plant in the iceplant family. The common names of the plant include baby sun rose,. heart-leaf, red aptenia or aptenia in English, as well as rooi brakvygie or brakvygie in Afrikaans, and umjuluka, ibohlololo, or uncolozi omncane in isiZulu in South Africa. It is known as heartleaf iceplant in the USA British names may be heart-leaved aptenia or heart-leaved midday flower because, like many other representatives of the Aizoaceae, it opens its flowers only during the sunshine of the day. It is a creeping plant that forms a carpet of flat-growing perennial herbs in groups on the ground from a base. Genus name means middle-embryo flower in reference to the position of the ovary in the flower. The specific epithet is derived from Latin for heart-shaped leaves.

Trichodiadema is a genus of succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae.

Pelargonium cucullatum is a hairy, upright, branching, perennial shrub, of 1–2 m (3.3–6.6 ft) high, that has been assigned to the cranesbill family. It sprouts new stems from the underground rootstock and becomes woody at its base. It has alternately set, sometimes slightly succulent leaves crowded near the top of the branches, with leaf stalks and flat to hood-shaped leaf blades, with a rounded broad triangular to kidney-shaped outline of about 4–5.5 cm long and 5–9 cm wide, often somewhat incised, the margin with irregular teeth. The white to purplish red, 5-merous, somewhat mirror symmetrical flowers grow in umbel-like clusters, and each contain mostly 7 fertile stamens and 3 infertile staminodes of different length. P. cucullatum has been cultivated as a garden ornamental and house plant since the 17th century. It has been used to breed many modern pelargonium hybrids, notably the Regal pelargoniums. It is called hooded-leaf pelargonium or herba althaea in English and wildemalva in Afrikaans.

Lithops francisci, commonly known as one of the living stones or pebble plants, is in the family Aizoaceae. It is endemic to the arid desert environments of Namibia. It is a succulent with a natural habitat in rocky areas. L. francisci was assessed by Nicholas Edward Brown in 1925. It is one of the Lithops plants and shares the characteristic bi-leaf head pattern separated by a deep fissure, the bottom of which houses and protects the stunted stem.

Lapidaria is a monotypic genus of dwarf succulent plants in the family Aizoaceae. The only species it contains is Lapidaria margaretae, also known as the Karoo rose.

Mitrophyllum is a genus of succulent plants of the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to the arid region around the Richtersveld, on the border of South Africa and Namibia.

Muiria hortenseae ("mouse-head") is a rare dwarf species of succulent plant of the family Aizoaceae, indigenous to a very small area in the Little Karoo, Western Cape, South Africa. It is the only species in the monophyletic genus Muiria.

Astroloba spiralis is a small succulent plant of the Astroloba genus, endemic to the southern Karoo regions of the Western and Eastern Cape Provinces, South Africa.

Gasteria rawlinsonii is succulent plant of the genus Gasteria native to South Africa.
Gunniopsis tenuifolia, commonly known as the narrow-leaf pigface, is a succulent plant in the iceplant family, Aizoaceae. It is endemic to Australia.
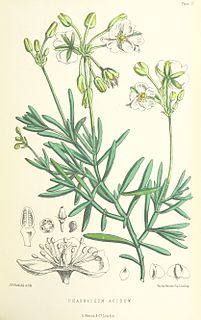
Kewa acida is one of the eight species currently recognized in the genus Kewa, the sole genus in the family Kewaceae. It is a bushy grey-leaved annual or short-lived perennial plant, with white flowers, endemic to St Helena, where it has been called the "salad plant". It is regarded as Critically Endangered. The succulent leaves are high in Vitamin C and were used by sailors in the past as a scurvy preventative.
Vlokia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae. The first description of the genus was published in 1994 by Steven A. Hammer. The generic name honors the discoverer of Vlokia ater, South African botanist, Jan H. J. Vlok (1957-). The pronunciation "Flow-key-a" has been recommended based on the pronunciation of his name.

Persoonia hindii is a plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to a small area of New South Wales near Lithgow. It is a shrub with an underground stolon from which new stems arise and has succulent, linear to oblong leaves and deep yellow flowers.

Glottiphyllum depressum is a common species of succulent plant, of the family Aizoaceae, native to South Africa.
Hartmanthus is a genus of tropical, succulent flowering plants in the family Aizoaceae, native to the lower Orange River in ǁKaras, Namibia and Northern Cape, South Africa.

Trichodiadema gracile is succulent plant of the genus Trichodiadema, native to the Western Cape Province, South Africa, where it is common on dry, rocky hillsides in the Overberg region.

Carpobrotus modestus, commonly known as inland pigface, is a succulent perennial of the family Aizoaceae, native to the coasts of Australia. It produces purple flowers which mature into fruits and is mainly used as a groundcover succulent or as a drought tolerant plant.
















