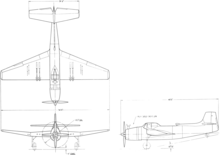
Design and development
The Vultee engineering team decided early in the design process to build the XA-41 (company Model 90) around the 3,000 hp Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major four-row, 28-cylinder radial engine. The Model 90's large tapered wing resembled that of Vultee Model 72 – a two-seat attack aircraft/dive bomber better known as the Vultee Vengeance (A-31/A-35) – including a straight leading edge, forward-swept trailing edge, and pronounced dihedral on the outer wing panels.
Designed to carry both a large internal load and external stores, the XA-41 was large for a single-engine aircraft. The single-place cockpit, set in line with the wing root, was 15 ft (4.6 m) off the ground when the airplane was parked.
As operational priorities shifted during its development phase, the original order for two XA-41 prototypes was cancelled, although the USAAF pressed for the completion of one prototype as an engine testbed for the R-4360 (the same engine used by the Boeing B-50 Superfortress).

The Douglas XTB2D Skypirate was a torpedo bomber intended for service with the United States Navy's Midway- and Essex-class aircraft carriers; it was too large for earlier decks. Two prototypes were completed, but the dedicated torpedo bomber was becoming an outdated concept, and with the end of World War II, the type was deemed unnecessary and cancelled.

The Northrop YB-35/XB-35, Northrop designation N-9 or NS-9, were experimental heavy bomber aircraft developed by the Northrop Corporation for the United States Army Air Forces during and shortly after World War II. The airplane used the radical and potentially very efficient flying wing design, in which the tail section and fuselage are eliminated and all payload is carried in a thick wing. Only prototypes and pre-production aircraft were built, although interest remained strong enough to warrant further development of the design as a jet bomber, under the designation YB-49.

The Keystone B-5 is a light bomber made by the Keystone Aircraft company for the United States Army Air Corps in the early 1930s. The B-5A was a Keystone B-3A with Wright Cyclone rather than Pratt & Whitney engines.

The Seversky XP-41 was a fighter aircraft built in the United States in 1939. A single prototype was modified from the last production Seversky P-35 by adding a new streamlined canopy, a Pratt & Whitney R-1830-19 engine with a two-speed supercharger, and revised landing gear. The XP-41 first flew in March 1939. The aircraft was developed in parallel with the P-43 Lancer, and work was stopped when the USAAC showed a preference for the latter.

The Boeing XF8B was a single-engine aircraft developed by Boeing during World War II to provide the United States Navy with a long-range shipboard fighter aircraft. The XF8B was intended for operation against the Japanese home islands from aircraft carriers outside the range of Japanese land-based aircraft. Designed for various roles including interceptor, long-range escort fighter, dive-bomber, and torpedo bomber, the final design embodied a number of innovative features in order to accomplish the various roles. Despite its formidable capabilities, the XF8B-1 never entered series production.

The Republic XP-72 was an American prototype fighter-interceptor developed by Republic Aircraft as a progression of the P-47 Thunderbolt design. The XP-72 was designed around the Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major 28-cylinder air-cooled radial engine with a supercharger mounted behind the pilot and driven by an extension shaft from the engine. The armament consisted of six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) wing-mounted Browning AN/M2 machine guns and underwing racks for two 1,000 lb bombs; Alternative armament packages included two 37 mm M4 autocannons with four .50 caliber AN/M2s, or four M4 autocannons.

The Vultee V-11 and V-12 were American stressed-skin monocoque monoplane attack aircraft of the 1930s. Developed from the Vultee V-1 single-engined airliner, the V-11 and V-12 were purchased by several nations for their armed forces, including China, who used them in combat against Japanese forces in the Second Sino-Japanese War. The United States Army Air Corps purchased seven V-11s as the YA-19 in the years before World War II, testing them to gather data to compare against twin engine light attack aircraft.

The Stearman XA-21 was a competitor in a United States Army Air Corps competition for a twin-engined attack aircraft which led to the Douglas A-20 Havoc, Martin A-22 Maryland and North American B-25 Mitchell.

The Boeing B-54 was an American strategic bomber designed by Boeing for use by the United States Air Force. Derived from the YB-50C Superfortress, construction of the prototype was canceled before completion, and the aircraft was never flown.
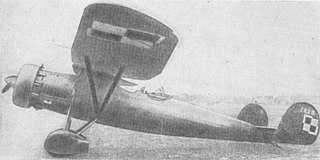
The PWS-19 was a Polish reconnaissance and bomber plane prototype of the 1930s, constructed in the PWS.

The Brewster XA-32 was an American attack aircraft, a mid-wing type with an internal bomb bay. The prototype had the R-2800 engine, but it could take the intended R-4360 powerplant. After a dismal set of test results, the XA-32 did not enter production.

The Bird Innovator was an American four-engined executive amphibious airplane modified from a Consolidated PBY Catalina by the Bird Corporation.

The SIAI-Marchetti SM.102 was a 1940s Italian light transport cabin monoplane designed and built by SIAI-Marchetti.

The Curtiss XBTC was a prototype single-seat, single-engined torpedo/dive bomber developed during World War II for the United States Navy. Four aircraft were ordered, powered by two different engines, but the two aircraft to be fitted with the Wright R-3350 radial engine were cancelled in late 1942, leaving only the pair using the Pratt & Whitney R-4360 radial. By this time, Curtiss Aircraft was overwhelmed with work and the Navy gave the XBTC-2 prototypes a low priority which delayed progress so the first flight did not take place until the beginning of 1945. One aircraft crashed in early 1947 and the other was disposed of later that year.

The Spartan C4 was an American four-seat cabin monoplane designed and built by the Spartan Aircraft Company.
The Avro 684 was a proposed British high altitude heavy bomber of the Second World War, based on Avro's successful Lancaster.

The Letov Š-50 was a 1930s prototype Czechoslovakian military general-purpose monoplane, designed and built by Letov.

The Breese-Dallas Model 1 or Breese model X was a prototype single engine airliner that rapidly changed hands throughout the 1930s. It was also known as the Michigan Aircraft Company Model 1, and the Lambert Model 1344.

The Stewart S-51D Mustang is an American aerobatic homebuilt aircraft that was designed by Jim Stewart and produced by Stewart 51 of Vero Beach, Florida, introduced in 1994. When it was available the aircraft was supplied as a kit for amateur construction.
The Vought V-326 was an American experimental aircraft used by Pratt & Whitney as a high altitude engine test bed.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.