Related Research Articles

Papua, formerly Irian Jaya, is the largest and easternmost province of Indonesia, comprising most of Western New Guinea. The province is located on the island of New Guinea. It is bordered by the state of Papua New Guinea to the east, the province of West Papua to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the north, and the Arafura Sea to the south. The province also shares maritime boundaries with Palau to the north. The province is divided into twenty-eight regencies and one city. Its capital and largest city is Jayapura. The province has a large potential in natural resources, such as gold, nickel, petroleum, etc. Puncak Jaya is the province's highest mountain and the highest point in Indonesia. Papua, along with West Papua, has a higher degree of autonomy level compared to other Indonesian provinces.

Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. It is the world's third largest island country with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Port Moresby, also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea and the largest city in the South Pacific outside of Australia and New Zealand. It is located on the shores of the Gulf of Papua, on the south-western coast of the Papuan Peninsula of the island of New Guinea. The city emerged as a trade centre in the second half of the 19th century. During World War II it was a prime objective for conquest by the Imperial Japanese forces during 1942–43 as a staging point and air base to cut off Australia from Southeast Asia and the Americas.

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from the island of New Guinea in the west to Tonga in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
Provinces of Indonesia are the 34 administrative division of Indonesia and the highest tier of the local government. Provinces are further divided into regencies and cities, which are in turn subdivided into districts (kecamatan).

Bougainville, officially the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, is an autonomous region in Papua New Guinea. The largest island is Bougainville Island, while the region also includes Buka Island and a number of outlying islands and atolls. The interim capital is Buka, although this is considered temporary, with the capital likely to move. One potential location is Arawa, the previous capital.

Bougainville Island is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. It was previously the main landmass in the German Empire-associated North Solomons. Its land area is 9,300 km2 (3,600 sq mi). The population of the whole province, including nearby islets such as the Carterets, is approximately 300,000. The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at 2,715 m (8,907 ft). The much-smaller Buka Island, c. 500 km2 (190 sq mi), lies to the north, across the 400–500 m (1,300–1,600 ft) wide Buka Strait. Even though the strait is narrow, there is no bridge across it, but there is a regular ferry service between the key settlements on either side. The main airport in the north is in the town of Buka.

The Papuan languages are the non-Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea, and neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan peoples as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892.

The Free Papua Movement is an umbrella term for the independence movement established during 1965 in the West Papuan or West New Guinea territory which is currently being administrated by Indonesia as the provinces of Papua and West Papua, also formerly known as Papua, Irian Jaya and West Irian.

West Papua, formerly Irian Jaya Barat or Irian Barat, is a province of Indonesia. It covers the two western peninsulas of the island of New Guinea, Bird's Head Peninsula and Bomberai Peninsula, along with nearby islands. The province is bordered to the north by the Pacific Ocean, to the west by the Halmahera Sea and the Ceram Sea, to the south by the Banda Sea, and to the east by the province of Papua and the Cenderawasih Bay. Manokwari is the province's capital, while Sorong is its largest city. West Papua is the second-least populous province in Indonesia, with a population of 1,134,068 at the 2020 Census.

The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the annexation but in 1884 a Protectorate was proclaimed over the territory, then called "British New Guinea". There is a certain ambiguity about the exact date on which the entire territory was annexed by the British. The Papua Act 1905 recites that this happened "on or about" 4 September 1888. On 18 March 1902, the Territory was placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia. Resolutions of acceptance were passed by the Commonwealth Parliament, who accepted the territory under the name of Papua.

The indigenous peoples of New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Australo-Melanesians.

Western New Guinea, also known as Papua or Indonesian New Guinea, is the western portion of the island of New Guinea controlled by Indonesia since 1962. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region is also called West Papua. Lying to the west of Papua New Guinea, it is the only Indonesian territory situated in Oceania. Considered part of the Australian continent, the territory is mostly in the Southern Hemisphere and includes the Schouten and Raja Ampat archipelagoes. The region is predominantly covered with ancient rainforest where numerous traditional tribes live such as the Dani of the Baliem Valley although a large proportion of the population live in or near coastal areas with the largest city being Jayapura.

The Papua New Guinea national cricket team, nicknamed the Barramundis, is the team that represents the country of Papua New Guinea in international cricket. The team is organised by Cricket PNG, which has been an Associate Member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) since 1973. Papua New Guinea previously had One-Day International (ODI) status, which it gained by finishing fourth in 2014 World Cup Qualifier. Papua New Guinea lost both their ODI and T20I status in March 2018 after losing a playoff match against Nepal during the 2018 Cricket World Cup Qualifier, a result that earned ODI and T20I status for their opponents. On 26 April 2019, at the final World Cricket League 2 fixture; PNG defeated Oman to finish at the fourth position and reclaim their ODI status.

This page is a list of local-level governments (LLGs) of Papua New Guinea. There are 326 LLGs comprising 6,112 wards as of 2018.

Papua New Guinea, a sovereign state in Oceania, is the most linguistically diverse country in the world. According to Ethnologue, there are 839 living languages spoken in the country. In 2006, Papua New Guinea Prime Minister Sir Michael Somare stated that "Papua New Guinea has 832 living languages ." Languages with statutory recognition are Tok Pisin, English, Hiri Motu, and Papua New Guinean Sign Language. Tok Pisin, an English-based creole, is the most widely spoken, serving as the country's lingua franca. Papua New Guinean Sign Language became the fourth officially recognised language in May 2015, and is used by the deaf population throughout the country.

The monarchy of Papua New Guinea is a system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Papua New Guinea. The current monarch, since 16 September 1975, is Queen Elizabeth II. Although the person of the sovereign is equally shared with 15 other independent countries within the Commonwealth of Nations, each country's monarchy is separate and legally distinct. As a result, the current monarch is officially titled the Queen of Papua New Guinea and, in this capacity, she and other members of the Royal Family undertake public and private functions domestically and abroad as representatives of the Papua New Guinean state. However, the Queen is the only member of the Royal Family with any constitutional role. The Queen lives predominantly in the United Kingdom and, while several powers are the sovereign's alone, most of the royal governmental and ceremonial duties in Papua New Guinea are carried out by the Queen's representative, the governor-general.
The Northern Adelbert or Pihom–Isumrud languages are a family of two dozen languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. The occupy the coastal northern Adelbert Range of mountains, vs. the Southern Adelbert languages, another branch of Madang.
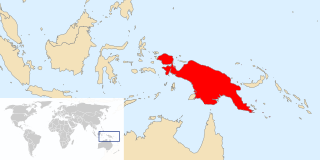
New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, and with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi), the largest island in the Southern Hemisphere. Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, it is separated by the 150 km wide Torres Strait from Australia. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea or West Papua, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua and West Papua.

The Papua conflict is an ongoing conflict in Western New Guinea between Indonesia and the Free Papua Movement. Subsequent to the withdrawal of the Dutch administration from the Netherlands New Guinea in 1962 and implementation of Indonesian administration in 1963, the Free Papua Movement has conducted a low-intensity guerrilla war against Indonesia through the targeting of its military, police, and civilians.
References
- ↑ Wanambre at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)