
The DFS Olympia Meise was a German sailplane designed by the Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug (DFS) for Olympic competition, based on the DFS Meise.
The Slingsby T.25 Gull 4 is a British glider designed and built by Slingsby that first flew in 1947.

The Eon Olympia was a glider produced from 1947 by Elliotts of Newbury.

The DFS Weihe is a German single-seat, high-wing, 18 metre wingspan, high-performance glider that was designed by Hans Jacobs in 1937-38.
The Gehrlein GP-1 is an American mid-wing, single seat FAI Standard Class glider that was designed by Jay and Rod Gehrlein and first flown in July 1968.

The Zögling is a German high-wing, cable-braced, single seat primary glider that was designed by Alexander Lippisch in 1926 and produced with many variations by a variety of manufacturers.
The Moore SS-1 is an American high-wing, single seat, FAI Standard Class glider that was designed and constructed by Arien C. Moore of Sweet Home, Oregon.

The Crown City Glider Club Screaming Wiener is an American mid-wing, single-seat glider that was designed and built by members of the Crown City Glider Club in 1938.

The CVV-4 Pellicano was a single seat Italian glider designed for a competition to select an aircraft for the 1940 Olympic Games. The DFS Olympia Meise was preferred to it after the trials in Italy in 1939.

The DFS Rhönsperber, otherwise known as the Schweyer Rhönsperber or Jacobs Rhönsperber was a single seat competition glider designed in Germany by Hans Jacobs and first flown in 1935. For several years it was regarded as the best German sailplane and about one hundred were built.

The Schleicher Rhönadler, DFS Rhönadler or Jacobs Rhönadler is a high performance, single seat competition sailplane built in Germany in the 1930s. More than 65 were built.

The Rotondi R.2 Tobia was built as a student group project in an Italian technical institute, begun in 1958. The sole example of this single seat, wooden glider first flew in 1962.

The Zlín Šohaj series of club gliders began as a post World War II development of the DFS Olympia Meise. A large number were built in the 1940s and '50s.
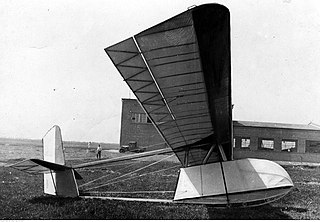
The Czajka (transl. Lapwing) or Kocjan Czajka after its designer was a Polish secondary training glider which was in continuous production from 1931 to the start of World War II. More than 160 were completed in Warsztaty Szybowcowe in Warsaw.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe Wrona, or Kocjan Wrona after its designer, was the most numerous and widely used Polish pre-war primary glider.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe Sroka, or Kocjan Sroka after its designer, was a Polish intermediate training glider. About sixty were built between 1934 and 1939.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe Sokół was a 1930s Polish aerobatic sailplane. Ten were built and flown by Polish aeroclubs, participating in national and international events, until the outbreak of the Second World War.
The Warsztaty Szybowcowe Mewa was a Polish, high performance, two seat sailplane flown in 1936 and built in small numbers.

The Warsztaty Szybowcowe SG-7 was a Polish high performance, single seat sailplane. Two prototypes flew in 1937 but, outperformed by their contemporaries, no more were built.

The single-seat Kocjan Komar (Gnat) intermediate trainer, designed in 1932, was the leading and most produced sailplane in pre-war Poland. Production was resumed after World War II as the IS-B Komar and it remained in use until 1965.


















