
Monmouth is a market town and community in Monmouthshire, Wales, situated on where the River Monnow joins the River Wye, two miles from the Wales–England border. The population in the 2011 census was 10,508, rising from 8,877 in 2001. Monmouth was the county town of historic Monmouthshire, although Abergavenny is the largest settlement and Monmouthshire County Council has its main offices at Rhadyr, just outside Usk. Monmouth is in the UK Parliament constituency of Monmouthshire and the Senedd constituency of Monmouth.

The River Wye is the fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some 250 kilometres from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn Estuary. The lower reaches of the river forms part of the border between England and Wales. The Wye Valley is designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The Wye is important for nature conservation and recreation, but is affected by pollution.

The historic counties of Wales were the thirteen sub-divisions used in Wales from either 1282 and 1535, up to their abolition in 1974, being replaced by eight counties. They were used for various functions for several hundred years, but for administrative purposes have been superseded by contemporary sub-national divisions, some of which bear some limited similarity to the historic entities in name and extent. They are alternatively known as ancient counties.

Monmouthshire is a county in the south east of Wales. It borders Powys to the north; the English counties of Herefordshire and Gloucestershire to the north and east; the Severn Estuary to the south, and Torfaen, Newport and Blaenau Gwent to the west. The largest town is Abergavenny, and the administrative centre is Usk. The county is administered by Monmouthshire County Council. It sends two directly-elected members to the Senedd at Cardiff and one elected member to the UK parliament at Westminster. The county name is identical to that of the historic county, of which the current local authority covers the eastern three-fifths. Between 1974 and 1996, the county was known as Gwent, recalling the medieval kingdom which covered a similar area. The present county was formed under the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994, which came into effect in 1996. In his essay 'Changes in local government', in the fifth and final volume of the Gwent County History, Robert McCloy writes, "the local government of no county in the United Kingdom in the twentieth century was so transformed as that of Monmouthshire".
Monmouthshire, also formerly known as the County of Monmouth, was one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales in the south-east of Wales, on the border with England. Its area now corresponds approximately to the present principal areas of Monmouthshire, Blaenau Gwent, Newport and Torfaen, and those parts of Caerphilly and Cardiff east of the Rhymney River.

Goodrich is a village and civil parish in south Herefordshire, England close to Gloucestershire and the Forest of Dean, situated near the River Wye at grid reference SO574193. It is known for its Norman and mediaeval castle built with Old Red Sandstone.

Welsh Newton is a small village and civil parish in the county of Herefordshire, England. It is located close to the border with Wales to which the parish extends towards Monmouthshire. It should not be confused with Newton, a township-chapelry in Clodock Parish and near Longtown, or with Newton Leominister. Its postal address is in Wales, with Monmouth as its post town.

Walford is a village and civil parish in south Herefordshire, England, two miles south of the market town of Ross-on-Wye. It includes the settlements of Bishopswood, Coughton, Deep Dean, Hom Green and Walford.

Ganarew is a village and small civil parish in south Herefordshire, England near the River Wye and the border with Wales. The village is located 0.62 miles (1.00 km) southwest of the village of Whitchurch on the main A40 road, and lies within the electoral ward of Kerne Bridge. The village is about 2 miles (3.2 km) from Monmouth and 8 miles (13 km) from Ross-on-Wye. It contains the Church of St Swithin and Ganarew Manor.
Kerne Bridge is a hamlet in south Herefordshire, England, about 3.5 miles (6 km) south of the market town of Ross-on-Wye on the B4234 Ross-on-Wye to Coleford road adjacent to Bishopswood. Situated on the left bank of the River Wye, it takes its modern name from the nineteenth century bridge over the river. It was once a significant stop on the now disused and abandoned Monmouth to Ross-on-Wye railway, and is now known for a popular canoe-launching site. It marks the northern start of the Upper Wye Gorge and is situated in the heart of the Wye Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.

The Wye Valley is a valley in Wales and England. The River Wye is the fourth-longest river in the United Kingdom.

Lydbrook is a civil parish in the Forest of Dean, a local government district in the English county of Gloucestershire and is located in the Wye Valley. It is on the north west edge of the Forest of Dean's present legal boundary proper. It comprises the districts of Lower Lydbrook, Upper Lydbrook, Joys Green and Worrall Hill. It has a mile and a half long high street, reputed to be the longest high street of any village in England.

Coppet Hill or Coppett Hill is a local nature reserve in the parish of Goodrich near Ross-on-Wye in Herefordshire.
Maud Francis, Countess of Salisbury was daughter of Sir Adam Francis, born c. 1326, Lord Mayor of London, and Agnes Champnes. She was married and widowed three times. Her first husband was John Aubrey and her second Sir Alan Buxhull, KG in 1372.
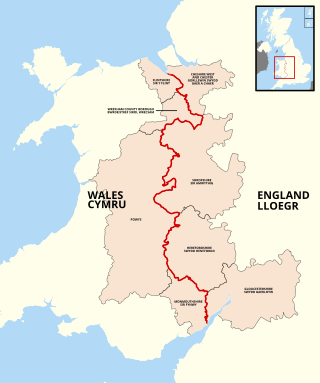
The England–Wales border, sometimes referred to as the Wales–England border or the Anglo-Welsh border, runs for 160 miles (260 km) from the Dee estuary, in the north, to the Severn estuary in the south, separating England and Wales.

The Ross and Monmouth Railway was a standard gauge railway of 13 miles (21 km) which ran between Ross-on-Wye, in Herefordshire, England and Monmouth, Wales.
Walford Halt railway station is a disused halt on the Ross and Monmouth Railway constructed near the Herefordshire village of Walford. It also served the surrounding settlements. Nothing remains of the station. It was located approximately 3 miles and 12 chains along the railway from Ross-on-Wye station.

Kerne Bridge was built over the River Wye in the County of Herefordshire, England in 1825–28, on the site of an ancient ford crossing known as Flanesford. It is designated as a Scheduled Monument. Carrying the B4229 road, it connects the parishes of Walford on the river's left bank and Goodrich on the right. It is situated in the heart of the Wye Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and marks the northern end of the Upper Wye Gorge.

Courtfield, Welsh Bicknor, Herefordshire, England is a country house dating from the early 19th century. The present building stands on the site of a much older mansion which, according to tradition, was home to Henry V for the early years of his life. This house was originally called Greenfield or Greyfield but was renamed Courtfield at that time. Nothing now remains of that building and the present house was erected in the very early 19th century by William Michael Vaughan. The Vaughans had purchased the estate in the 16th century. Staunchly Roman Catholic, and much persecuted in the 17th and 18th centuries; in the mid-19th century Herbert Vaughan, later a cardinal and Archbishop of Westminster, was brought up at the house, born into a large family, an unusually high number of whom entered the church. In 1950 Courtfield was sold by Patrick Vaughan to the Mill Hill Missionaries who ran a House of Formation at the house. In 2010, the mission was closed and the house sold back to the Vaughan family, who had retained ownership of the wider estate. Courtfield is a Grade II listed building. The house is not open to the public.

Dry Arch Bridge in Goodrich, Herefordshire, England, built in 1828, is one of the earliest examples of a bridge built specifically to carry a minor road across a more major one without the need for a road junction. It was constructed to carry the existing old road between Goodrich and Welsh Bicknor over a cutting for a new-built road connecting Kerne Bridge with Goodrich. It was built with a single span, using local sandstone, at least some of which came from the cutting beneath the bridge. It was also constructed to allow pedestrians to cross from one road to the other three-dimensionally without a lengthy diversion.



















