Burkina Faso is a landlocked Sahel country that shares borders with six nations. It lies between the Sahara desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River, mostly between latitudes 9° and 15°N, and longitudes 6°W and 3°E. The land is green in the south, with forests and fruit trees, and semi-arid in the north. Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees. Burkina Faso's game preserves – the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park—contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, common warthogs, and antelopes. Previously the endangered painted hunting dog, Lycaon pictus occurred in Burkina Faso, but, although the last sightings were made in Arli National Park, the species is considered extirpated from Burkina Faso.

Mali is a landlocked nation in West Africa, located southwest of Algeria, extending south-west from the southern Sahara Desert through the Sahel to the Sudanian savanna zone. Mali's size is 1,240,192 square kilometers.

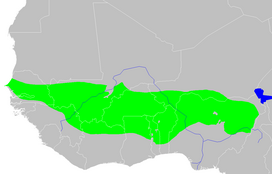
The Sahel region, or Sahelian acacia savanna, is a biogeographical region in Africa. It is the transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a hot semi-arid climate and stretches across the southernmost latitudes of North Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. Although geographically located in the tropics, the Sahel does not have a tropical climate.

The West Saharan montane xeric woodlands is an ecoregion that extends across several highland regions in the Sahara. Surrounded at lower elevations by the largely barren Sahara, the West Saharan montane xeric woodlands are isolated refuges of plants and animals that can survive in the higher humidity and lower temperatures of the highlands.

The Sudanian savanna or Sudan region is a broad belt of tropical savanna that runs east and west across the African continent, from the Ethiopian Highlands in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. It represents the central bioregion within the broader tropical savanna biome of the Afrotropical realm. The Sahel acacia savanna, a belt of drier grasslands, lies to the north, forming a transition zone between the Sudanian savanna and the Sahara Desert phytochorion. To the Sudan's south, the more humid forest-savanna mosaic forms a transition zone between the Sudanian savanna and the Guineo-Congolian forests that lie nearer the equator.

The East Sudanian savanna is a hot, seasonally dry tropical savanna ecoregion of Central and East Africa.

The Northern Congolian forest–savanna mosaic is a forest and savanna ecoregion of central Africa. It extends east and west across central Africa, covering parts of Cameroon, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Sudan, and Uganda. It is part of the belt of transitional forest-savanna mosaic that lie between Africa's moist equatorial Guineo-Congolian forests and the tropical dry forests, savannas, and grasslands to the north and south.

The Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-forests, also known as the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-forests, is an ecoregion in the eastern Mediterranean Basin. It covers portions of Turkey, Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Israel, Palestinian territories, Jordan, and Saudi Arabia.

The Mediterranean Acacia–Argania dry woodlands and succulent thickets is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion in North Africa centered mainly on Morocco but also including northwestern Western Sahara and the eastern Canary Islands.

The South Saharan steppe and woodlands, also known as the South Sahara desert, is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of northern Africa. This band is a transitional region between the Sahara's very arid center to the north, and the wetter Sahelian Acacia savanna ecoregion to the south. In pre-modern times, the grasslands were grazed by migratory gazelles and other ungulates after the rainfalls. More recently, over-grazing by domestic livestock have degraded the territory. Despite the name of the ecoregion, there are few 'woodlands' in the area; those that exist are generally acacia and shrubs along rivers and in wadis.
The Ethiopian montane grasslands and woodlands is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion in Ethiopia. It occupies the middle elevations of the Ethiopian Highlands, between the high-elevation Ethiopian montane moorlands and lowland woodlands, savannas, shrublands, and thickets.

The Ethiopian montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in Ethiopia. It covers the southwestern and southeastern portions of the Ethiopian Highlands. The ecoregion includes distinctive Afromontane evergreen forests. The ecoregion's biodiversity is threatened by deforestation, conversion to agriculture, and overgrazing.

The Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in the Armenian Highlands, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.

The Northern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets are a tropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands ecoregion in eastern Africa. The ecoregion is mostly located in Kenya, extending north into southeastern South Sudan, northeastern Uganda and southwestern Ethiopia and south into Tanzania along the Kenya-Tanzania border.

The Somali Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets is a semi-arid tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in the Horn of Africa. It is home to diverse communities of plants and animals, including several endemic species.

The Southwestern Arabian foothills savanna, also known as the Southwestern Arabian Escarpment shrublands and woodlands, is a desert and xeric shrubland ecoregion of the southern Arabian Peninsula, covering portions of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Oman.

The Victoria Basin forest–grassland mosaic is an ecoregion that lies mostly in Uganda and extends into neighboring countries. The ecoregion is centered north and west of Lake Victoria, with an outlier on the border of Ethiopia and South Sudan.

The Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in western Asia. It lies in the lowlands west of the Caspian Sea, and covers portions of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Iran.

The Mesopotamian shrub desert is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Western Asia. It extends across portions of Israel, Jordan, Syria, Iraq, and Iran.

The Nile Delta flooded savanna, ecoregion covers both the Nile Delta proper, where the Nile River enters the Mediterranean Sea, as well as the river floodplains of the Nile 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) up-river to the Aswan Dam. Since the Aswan Dam was completed in the 1970s, the Nile on this stretch has not been subject to annual flooding, leading the loss of much of the papyrus sedge swamps and other marshes along the river.