
Linden Airport is a mile southeast of downtown Linden, in Union County, New Jersey. Also known as Linden Municipal Airport, it is next to U.S. Route 1&9. The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a general aviation reliever airport.

Troutdale Airport, also known as Troutdale-Portland Airport, is a corporate, general aviation, and flight-training airport serving the city of Troutdale, in Multnomah County, Oregon, United States. It is one of three airports in the Portland metropolitan area owned and operated by the Port of Portland. Troutdale Airport was established in 1920 as a private airfield, then purchased by the Port of Portland in 1942. It serves as a reliever airport for nearby Portland International Airport (PDX).

Hillsboro Airport, also known as Portland–Hillsboro Airport, is a corporate, general aviation and flight-training airport serving the city of Hillsboro, in Washington County, Oregon, United States as well as a large amount of private/charter and general aviation traffic into and out of the greater Portland area. It is one of three airports in the Portland, Oregon, metropolitan area owned and operated by the Port of Portland. Established in 1928, it is Oregon's second busiest airport at over 200,000 operations annually. HIO covers 900 acres and has three runways.

Adirondack Regional Airport is a public use airport located four nautical miles northwest of the central business district of Saranac Lake, in Franklin County, New York, United States. The airport is owned by the Town of Harrietstown and is situated in the north-central Adirondacks two miles (3 km) from Lake Clear. It is served by one commercial airline, subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.

Gray Army Airfield, also known as Gray AAF, is a military airfield located within Joint Base Lewis–McChord near Tacoma, in Pierce County, Washington, United States.

Cuyahoga County Airport, also known as Robert D. Shea Field, is a public use airport in northeastern Cuyahoga County, Ohio, United States. Owned and operated by Cuyahoga County since 1946, it also serves Lake County and Geauga County. The airport is located 10 nautical miles east of downtown Cleveland and sits on the border of three cities: Highland Heights, Richmond Heights and Willoughby Hills. It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015, which categorized it as a general aviation reliever airport for Cleveland Hopkins International Airport.

Manchester–Boston Regional Airport, informally referred to as Manchester Airport, is a public use airport 3 miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Manchester, New Hampshire, United States on the border of Hillsborough and Rockingham counties. It is owned by the City of Manchester, and is in the southern part of the city on the border with Londonderry, New Hampshire.

Crystal Airport is a public airport named after the city of Crystal in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States. Most of the airport is in the city of Crystal. Portions north of taxiway C are in Brooklyn Park, and the north east corner of the airport is in Brooklyn Center. It is eight miles (13 km) northwest of the central business district of Minneapolis and is owned by the Metropolitan Airports Commission. The airport covers an area of approximately 430 acres.

Brackett Field is a public airport a mile southwest of La Verne, in Los Angeles County, California, United States. It was named after astronomer Frank Parkhurst Brackett (1865–1951).
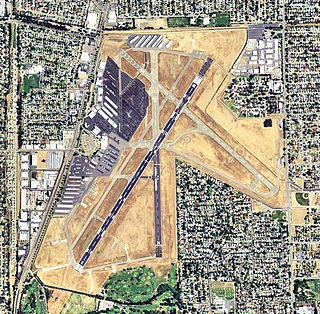
Sacramento Executive Airport is a public airport three miles (5 km) south of downtown Sacramento, in Sacramento County, California, United States. The airport covers 540 acres (219 ha) and has two lit runways and a helipad.

Edward F. Knapp State Airport is a general aviation airport located in Berlin, Vermont, United States; it is located three miles (5 km) west of the central business district of Barre. It serves both Barre and the Montpelier region. It currently has no scheduled airline service, but the airport was formerly served by Northeast Airlines and Air New England.

Schaumburg Regional Airport is a public use airport located 22 nautical miles northwest of Chicago in the village of Schaumburg in Cook and DuPage counties, Illinois, United States. The airport is owned by the Village of Schaumburg and is just south of the Schaumburg Municipal Helistop.

Lebanon-Warren County Airport is a public airport located three miles (5 km) northwest of the central business district of Lebanon, on Greentree Road, in Warren County, Ohio, United States.

Seaside Municipal Airport is a general aviation airport located one mile (1.6 km) Northeast of Seaside in Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. It is owned and operated as a public airport by the city of Seaside. The airport has one asphalt runway, a parallel taxiway, a parking apron with space for up to 20 aircraft, and a five-bay hangar building. Seaside Municipal is the closest airport to Seaside, Gearhart, and Cannon Beach.
Arthur Dunn Airpark is a public-use airport located 2 miles (3.2 km) northwest of the central business district of the city of Titusville in Brevard County, Florida, United States. The airport is publicly owned and is administered under the cognizance of the Titusville-Cocoa Airport Authority. The airport has one paved runway that is 2,961 feet in length and a turf runway that is 1,805 feet in length.

Stevens Field is a public-use, general aviation airport located three miles northwest of the central business district of Pagosa Springs in Archuleta County, Colorado, United States. It is publicly owned by Archuleta County. It has no air traffic control tower or commercial passenger services, but it does have a fixed-base operator (FBO), and it is popular among light sport and general aviation aircraft doing cross country flights, where the airport serves as a general aviation-friendly waypoint, refueling stop, and pilot rest/sleep opportunity. Its address is 61 Aviation Court, Pagosa Springs, Colorado.

Joseph A. Hardy Connellsville Airport is a public-use airport located four nautical miles southwest of Connellsville in Dunbar Township, Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is owned by the Fayette County Airport Authority and serves the south-eastern segment of the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. The airport serves the general aviation community with no scheduled commercial airline service.

Continental Airlines Flight 1883 was a Boeing 757 that mistakenly landed on a taxiway at Newark Liberty International Airport on the evening of October 28, 2006. There were no reported injuries or damage, but the narrowly averted disaster was investigated by the National Transportation Safety Board, and caused the Federal Aviation Administration to reevaluate and modify air and ground safety procedures at and around Newark Airport.

Settlers Green is an outlet shopping center in North Conway, New Hampshire, United States. The center was built on the location of the former White Mountain Airport and opened in February 1988. It has since expanded to a former industrial site and a former competing shopping center. Settlers Green is divided into four parts: the Outlet Village, which contains mostly outlet stores; Settlers Crossing, which has a combination of lifestyle and specialty retailers; Settlers Corner, which houses a Staples, Home Depot, and HomeGoods; and Streetside, which features upscale retailers. With over 500,000 square feet (46,000 m2) of retail space, it is the largest shopping center in the White Mountains Region.
The Jefferson County Airpark is a full-service general aviation public airport near Steubenville, Ohio, U.S., part of the Pittsburgh Combined Statistical Area that serves small and mid-sized private, corporate and commercial traffic. The airport serves transients traveling to and from Eastern Ohio, the Northern Panhandle of West Virginia, and Western Pennsylvania (Pittsburgh). The airport founded in January 1948 by R. G. and Pauline Pier as Pier Airport.


















