
The tufted puffin, also known as crested puffin, is a relatively abundant medium-sized pelagic seabird in the auk family (Alcidae) found throughout the North Pacific Ocean. It is one of three species of puffin that make up the genus Fratercula and is easily recognizable by its thick red bill and yellow tufts.

Auks or alcids are a group of birds of the family Alcidae in the order Charadriiformes. The alcid family includes the murres, guillemots, auklets, puffins, and murrelets. The family contains 25 extant or recently extinct species that are divided into 11 genera. Auks are found throughout the Northern Hemisphere.

The Atlantic puffin, also known as the common puffin, is a species of seabird in the auk family. It is the only puffin native to the Atlantic Ocean; two related species, the tufted puffin and the horned puffin being found in the northeastern Pacific. The Atlantic puffin breeds in Russia, Iceland, Ireland, Britain, Norway, Greenland, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and the Faroe Islands, and as far south as Maine in the west and France in the east. It is most commonly found in the Westman Islands, Iceland. Although it has a large population and a wide range, the species has declined rapidly, at least in parts of its range, resulting in it being rated as vulnerable by the IUCN. On land, it has the typical upright stance of an auk. At sea, it swims on the surface and feeds on zooplankton, small fish, and crabs, which it catches by diving underwater, using its wings for propulsion.

The razorbill, razor-billed auk, or lesser auk is a North Atlantic colonial seabird and the only extant member of the genus Alca of the family Alcidae, the auks. It is the closest living relative of the extinct great auk. Historically, it has also been known as "auk", "razor-billed auk" and "lesser auk".

The common murre or common guillemot is a large auk. It has a circumpolar distribution, occurring in low-Arctic and boreal waters in the North Atlantic and North Pacific. It spends most of its time at sea, only coming to land to breed on rocky cliff shores or islands.

The roseate tern is a species of tern in the family Laridae. The genus name Sterna is derived from Old English "stearn", "tern", and the specific dougallii refers to Scottish physician and collector Dr Peter McDougall (1777–1814). "Roseate" refers to the bird's pink breast in breeding plumage.

The thick-billed murre or Brünnich's guillemot is a bird in the auk family (Alcidae). This bird is named after the Danish zoologist Morten Thrane Brünnich. The very deeply black North Pacific subspecies Uria lomvia arra is also called Pallas' murre after its describer.

The horned puffin is an auk found in the North Pacific Ocean, including the coasts of Alaska, Siberia and British Columbia. It is a pelagic seabird that feeds primarily by diving for fish. It nests in colonies, often with other auks.

Skomer or Skomer Island is an island off the coast of Pembrokeshire, in the community of Marloes and St Brides in west Wales. It is well known for its wildlife: around half the world's population of Manx shearwaters nest on the island, the Atlantic puffin colony is the largest in southern Britain, and the Skomer vole is unique to the island. Skomer is a national nature reserve, a Site of Special Scientific Interest and a Special Protection Area. It is surrounded by a marine nature reserve and is managed by the Wildlife Trust of South and West Wales.

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.

Baccalieu Island or Bacalhoo Island is a 5 km2 uninhabited island at the northern extremities of Conception Bay in Subdivision 1G, near the community of Red Head Cove, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. It is separated from the island of Newfoundland by Baccalieu Tickle, a small strait and an abundant fishing ground. The island has some trees but is mostly rocky.

Fowlsheugh is a coastal nature reserve in Kincardineshire, northeast Scotland, known for its 70-metre-high (230 ft) cliff formations and habitat supporting prolific seabird nesting colonies. Designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) by Scottish Natural Heritage, the property is owned by the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds. Fowlsheugh can be accessed by a public clifftop trail, or by boats which usually emanate from the nearby harbour at the town of Stonehaven. Tens of thousands of pelagic birds return to the site every spring to breed, after wintering at sea or in more southern climates, principal species being puffins, razorbills, kittiwakes, fulmars and guillemots.

A bird colony is a large congregation of individuals of one or more species of bird that nest or roost in proximity at a particular location. Many kinds of birds are known to congregate in groups of varying size; a congregation of nesting birds is called a breeding colony. Colonial nesting birds include seabirds such as auks and albatrosses; wetland species such as herons; and a few passerines such as weaverbirds, certain blackbirds, and some swallows. A group of birds congregating for rest is called a communal roost. Evidence of colonial nesting has been found in non-neornithine birds (Enantiornithes), in sediments from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) of Romania.
Baccalieu Island Ecological Reserve is a wildlife reserve located on an island off the northeastern tip of Bay de Verde Peninsula of Newfoundland.

The Cape Shore is a region on the southwestern portion of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland, Canada.

Witless Bay is a town on the Avalon Peninsula in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. Located on the Irish Loop, 35 km south of the provincial capital, St. John's, Witless Bay is a small, scenic, traditional Newfoundland outport community. The town had a population of 1640 in the Canada 2021 Census. It is connected to the Witless Bay Ecological Reserve.
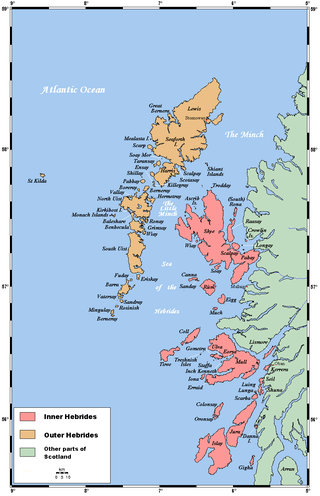
The flora and fauna of the Outer Hebrides in northwest Scotland comprises a unique and diverse ecosystem. A long archipelago, set on the eastern shores of the Atlantic Ocean, it attracts a wide variety of seabirds, and thanks to the Gulf Stream a climate more mild than might be expected at this latitude. Because it is on the Gulf Stream, it also occasionally gets exotic visitors.

Bird cliffs, or nesting cliffs, are steep cliffs with numerous small shelves which serve as nesting locations for bird colonies. Bird cliffs are found on islands in the North Atlantic and Arctic, such as the Faroe Islands, Iceland, the Svalbard archipelago and on islands off Northern Norway. Among species that nest in large numbers on bird cliffs are common murre, thick-billed murre, razorbill, kittiwake, little auk and Atlantic puffin. The number of breeding couples may exhibit large variations depending on available food. Bird cliffs have often been exploited as a food resource by the local population, as well as being used by hunters and egg collectors.

Gjesværstappan is a group of high, steep-sided, grass-covered islands which are located north of the island village of Gjesvær in Nordkapp Municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. The three main islands are Storstappen, Kjerkestappen, and Bukkstappen.

Pee Pee Island is a small island located in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador in the far east of Canada. It is the smallest of the four islands in the Witless Bay Ecological Reserve, which it became a part of in 1983. It serves as a breeding place for Atlantic puffins.























