Women's Football Australia (WFA) was the governing body for the sport of Women's Australian rules football in Australia between 1991 and its dissolution in 2015. [1] The organisation coordinated the Women's National Championship throughout its existence.
In 2010, the AFL gained control over women's Australian rules football, and took over the operations of Women's Football Australia.
After the 2015 edition, the AFL arranged the 2016 Exhibition Series and announced the formation of the AFLW in September 2016, along with other associated competitions including the AFL Women's Under 18 Championships and the NAB League Girls: with this, the raison d'etre for Women's Football Australia and the Championship ceased to exist, and they were both dissolved.
Consequently, the leagues it ran were either dissolved and replaced by AFL-sanctioned leagues, or are now operated by the AFL or its state/territory level bodies.

Australian football, also called Australian rules football or Aussie rules, or more simply football or footy, is a contact sport played between two teams of 18 players on an oval field, often a modified cricket ground. Points are scored by kicking the oval ball between the central goal posts, or between a central and outer post.

Football in Australia refers to numerous codes which each have major shares of the mainstream sports market, media, broadcasting, professional athletes, financial performance and grassroots participation: Australian rules football, rugby league, rugby union and association football. There are four pre-eminent professional football competitions played in Australia: the Australian Football League, the National Rugby League, Super Rugby and the A-League (soccer). By most measures, including attendance, television audience and media presence across the most states, Australian football is the most popular nationally. However, in the states of New South Wales and Queensland, rugby football is overall the most watched and receives the most media coverage, especially the Rugby League State of Origin contested between the two states referred to as “Australian sport's greatest rivalry”. In recent times there has been an increase in popularity in Australian football and corresponding decrease in popularity of Rugby union in New South Wales and Queensland. Soccer, while extending its lead in participation rate particularly in the large cities and improving its performance at the FIFA World Cup, continues to attract the overall lowest attendance as well as media and public interest of the four codes.

Representative matches in Australian rules football are matches between representative teams played under the Australian rules, most notably of the colonies and later Australian states and territories that have been held since 1879. For most of the 20th century, the absence of a national club competition in Australia and international matches meant that intercolonial and later interstate matches were regarded with great importance.

The Geography of Australian rules football describes the sport of Australian rules football played in more than 60 countries around the world. By 2017 more than 26 nations had contested the Australian Football International Cup the highest level of worldwide competition.

Australian rules football in Queensland was the first official football code played in 1866. The Colony of Queensland was the second after Victoria to adopt Australian rules football, just days after there rules were widely published. For two decades it was the most popular football code, however a strong desire for representative football success saw Queenslanders favour British football variants for more than a century. 120 years later in 1986 Queensland was the first state awarded a licence to have a club, the Brisbane Bears, in the national competition, also its first privately owned club. However the Gold Coast based Bears had a detrimental effect until the 1993 redevelopment of the Brisbane Cricket Ground (Gabba). In contrast the Bears transformation into a Brisbane and traditional membership based club resulted in enormous growth, and a tripling of average AFL attendances by 1996.

Women's Australian rules football, is the female-only form of Australian rules football, generally with some modification to the laws of the game.

Australian rules football in South East Queensland has a varied history and many changes were made especially in the 21st century. Ruled and organised by the AFL Queensland, the region had a total of 46 teams playing in different divisions.

The Queensland Australian Football League (QAFL) is an Australian rules football competition organised by the AFL Queensland, contested by clubs from South East Queensland.

Australian rules football in England is a team sport and spectator sport with a long history. The current competitions originated in 1989 and have grown to a number of local and regional leagues coordinated by AFL England. In 2018, these regional divisions were the AFL London, AFL Central & Northern England and Southern England AFL.

AFL South Africa is the governing body and federation for Australian rules football in South Africa. Its name is due to its formal affiliation in 2004 to the AFL Commission the game's world governing body.

Australian rules football in Tasmania, has been played since the late 1870s and draws the largest audience for a football code in the state.

Australian Football in the Northern Territory is the most popular sport, particularly with indigenous Australian communities in Darwin, Alice Springs and the Tiwi Islands. It is governed by AFL Northern Territory.

Australian rules football in Victoria is the most watched code of football. Victoria has more than double the number of Australian rules football players of any other state in Australia.

Australian rules football is the most watched and attended sport and the second most participated code of football in Australia.
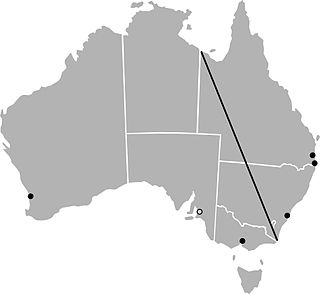
The "Barassi Line" is an imaginary line in Australia which approximately divides areas where Australian rules football and rugby league is the most popular football code. It was first used by historian Ian Turner in his "1978 Ron Barassi Memorial Lecture". Crowd figures, media coverage, and participation rates are heavily skewed in favour of the dominant code on both sides of the line.
The AFL Under-19 Championships is an annual Australian national underage representative championship in Australian rules football tournament. It is seen as one of the main pathways towards being drafted into a team in the fully professional Australian Football League (AFL).

The sport of Australian football has been called by a number of different names throughout its history. Since 1905, with the formation of the Australasian Football Council, the game has been called "Australian football". The name has been codified by the AFL Commission, as the game's name in the "Laws of Australian football". Historically, the sport has been referred to as "Victorian rules", the "Victorian game", "Australasian rules", the "Australian game" and "Australian national football", "national football", the "bouncing game" and, derisively, "aerial ping pong" as well as several other names. Today, the common names for the sport are "Australian Football" and "Australian rules football" and it is referred to as "football", "footy", "Aussie rules" or sometimes, mistakenly, as "AFL".
The NAB AFL Women's Under-18 Championships are the annual national Australian rules football championships for women players aged 18 years or younger. The competition is seen as one of the main pathways towards being drafted into a team in the professional AFL Women's competition (AFLW). Originally known as the AFL Youth Girls National Championship, the competition has teams of players representing their states and territories in a round robin tournament. The tournament is currently sponsored by the National Australia Bank. The winner of the 2019 tournament was Vic Metro.
Jordan Zanchetta is an Australian rules footballer who played for the Brisbane Lions in the AFL Women's.