
Kangaroo Island, also known as Karta Pintingga, is Australia's third-largest island, after Tasmania and Melville Island. It lies in the state of South Australia, 112 km (70 mi) southwest of Adelaide. Its closest point to the mainland is Snapper Point in Backstairs Passage, which is 13.5 km (8.4 mi) from the Fleurieu Peninsula.

The Tasmanian pygmy possum, also known as the little pygmy possum or tiny pygmy possum, is the world's smallest possum. It was first described by Oldfield Thomas in 1888, after he identified that a museum specimen labelled as an eastern pygmy possum in fact represented a species then unknown to science. The holotype resides in the Natural History Museum in London.

The Kangaroo Island emu or dwarf emu is an extinct subspecies of emu. It was restricted to Kangaroo Island, South Australia, which was known as Ile Decrés by the members of the Baudin expedition. It differed from the mainland emu mainly in its smaller size. The species became extinct by about 1827.

The King Island emu is an extinct subspecies of emu that was endemic to King Island, in the Bass Strait between mainland Australia and Tasmania. Its closest relative may be the extinct Tasmanian emu, as they belonged to a single population until less than 14,000 years ago when Tasmania and King Island were still connected. The small size of the King Island emu may be an example of insular dwarfism. The King Island emu was the smallest of all known emus and had darker plumage than the mainland emu. It was black and brown and had naked blue skin on the neck, and its chicks were striped like those on the mainland. The subspecies was distinct from the likewise small and extinct Kangaroo Island emu in a number of osteological details, including size. The behaviour of the King Island emu probably did not differ much from that of the mainland emu. The birds gathered in flocks to forage and during breeding time. They fed on berries, grass and seaweed. They ran swiftly and could defend themselves by kicking. The nest was shallow and consisted of dead leaves and moss. Seven to nine eggs were laid, which were incubated by both parents.

The Kangaroo Island dunnart is a dark sooty-grey coloured dunnart species first described in 1969, with paler underparts of its body. It has an average body length of 170–198 mm, a snout to anus length of 80–93 mm, a tail measurement of 90–105 mm, a hind foot of 17.5 mm, ear length of 18 mm and a weight of 20–25 grams. The thin tail is also gray, but lighter on the bottom. The tail is longer than the body. Kangaroo Island dunnarts are dimorphic, with males larger than females.
Short-range endemic (SRE) invertebrates are animals that display restricted geographic distributions, nominally less than 10,000 km2, that may also be disjunct and highly localised. The most appropriate analogy is that of an island, where the movement of fauna is restricted by the surrounding marine waters, therefore isolating the fauna from other terrestrial populations. Isolating mechanisms and features such as roads, urban infrastructure, large creek lines and ridges can act to prevent the dispersal and gene flow of the less mobile invertebrate species. Subterranean fauna, which include stygofauna and troglofauna, typically comprise short-range endemics.

Zephyrarchaea is a genus of Australian assassin spiders first described by Michael Gordon Rix & Mark Harvey in 2012 for nine new species and two that were formerly placed in the genus Austrarchaea. The name is based on the Latin zephyrus, meaning "west wind", referring to the western distribution in Australia and a preference for windy, coastal habitats by some species. It has been encountered in Western Australia, Victoria and South Australia.

Zephyrarchaea janineae is a species of spider of the family Archaeidae. The Latin species name was chosen to honor Janine Wojcieszek who helped in discovering the first live specimens of the species in 2006. Zephyrarchaea janineae is endemic to the South West Region in Western Australia.

Zephyrarchaea barrettae is a species of spider of the family Archaeidae. The Latin species name was chosen to honor Sarah Barrett, who first discovered assassin spiders in the Stirling Range National Park.
Michael Gordon Rix is an Australian arachnologist, whose publications mainly concern spiders.
Moggridgea rainbowi, also called the Australian trapdoor spider, is a small spider endemic to Kangaroo Island in South Australia. The spider was first recorded in 1919.

Gaius is a genus of large mygalomorph spiders in the family Idiopidae. Erected in 1914 by William Joseph Rainbow, for much of its history the genus contained only one species, Gaius villosus. More species were added in 2018. All are endemic to Western Australia.

Zephyrarchaea mainae is a species of spider, informally known as Main's assassin spider, Albany assassin spider, and the Western archaeid spider. The first of the assassin spider family found in Western Australia, the species was unknown until its collection at Torndirrup National Park near Albany was published in 1987.
Austrarchaea mcguiganae is a species of spider in the family Archaeidae. It is endemic to Monga National Park in New South Wales, Australia.
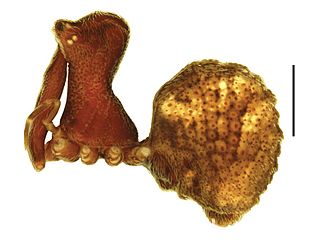
Zephyrarchaea grayi, also known as the Grampians Assassin Spider, is a species of spider in the family Archaeidae. It is endemic to Grampians National Park in Australia.
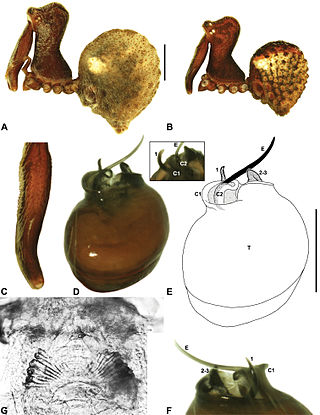
Zephyrarchaea marae, the West Gippsland assassin spider, is a spider in the family Archaeidae. The species was first described by Michael G. Rix and Mark Harvey in 2012. It is endemic to Victoria in Australia.

Zephyrarchaea marki, the Cape Le Grand assassin spider, is a spider in the family Archaeidae. The species was first described by Michael G. Rix and Mark Harvey in 2012. It is endemic to Cape Le Grand National Park in Australia.
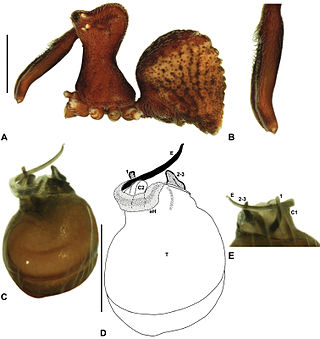
The Otway Range Assassin Spider(Zephyrarchaea porchi) is a species of spider in the family Archaeidae. It is endemic to Victoria, Australia.

Zephyrarchaea vichickmani, the Central Highlands assassin spider, is a spider in the family Archaeidae. The species was first described by Michael G. Rix and Mark Harvey in 2012. It is endemic to Victoria, Australia.
















