The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824 and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.
The 1818–19 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1818 and August 12, 1819. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 16th United States Congress convened on December 6, 1819. They occurred during President James Monroe's first term. Also, newly admitted Alabama elected its first representatives in September 1819, increasing the size of the House to 186 seats.
The 1816–17 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 30, 1816 and August 14, 1817. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 15th United States Congress convened on December 1, 1817. The size of the House increased to 184 after Indiana and Mississippi achieved statehood.
The 1814–15 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1814 and August 10, 1815. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 14th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1815. They occurred during President James Madison's second term. Elections were held for all 182 seats, representing 18 states.
The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810 and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
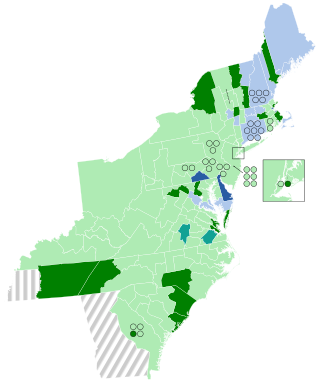
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804 and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1790–91 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 27, 1790 and October 11, 1791. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 2nd United States Congress convened on October 24, 1791. This was the first midterm election cycle, which took place in the middle of President George Washington's first term. The size of the House increased to 67 seats after the new state of Vermont elected its first representatives.
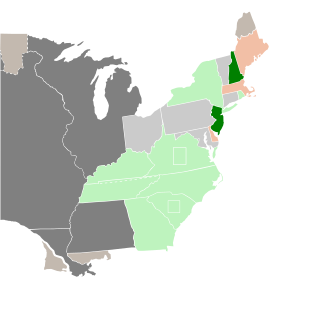
The 1804–05 United States Senate elections were elections that expanded the Democratic-Republican Party's overwhelming control over the United States Senate. The Federalists went into the elections with such a small share of Senate seats that even if they had won every election, they would have still remained a minority caucus.
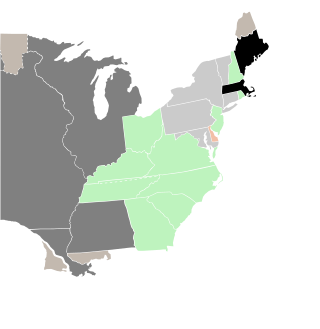
The 1810–11 United States Senate elections were elections that had the Democratic-Republican Party maintain their majority in the United States Senate. The minority Federalists had gone into the elections with such a small share of Senate seats that, had they won all of the elections, they would still not have reached a majority.
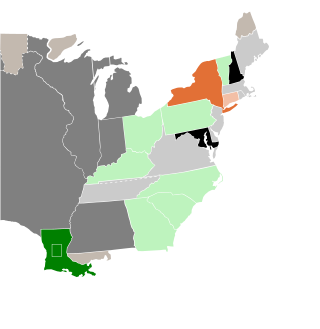
The 1812–13 United States Senate elections were elections that, coinciding with President James Madison's re-election, had the Democratic-Republican Party lose two seats but still retain an overwhelming majority in the United States Senate. As in recent elections, the minority Federalists had gone into the elections with such a small share of Senate seats that if they had won every one of the elections, they would still not have controlled a majority.
The 1814–15 United States Senate elections were elections that had the Democratic-Republican Party lose a seat but still retain an overwhelming majority in the United States Senate. Unlike in recent elections, the minority Federalists had gone into the elections with a chance of regaining their long-lost majority had they swept almost all the seats. However, only one seat switched parties. Two seats held by Democratic-Republicans were left unfilled until long after the next Congress began.

The 1802–03 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate which resulted in the Democratic-Republican Party maintaining and greatly expanding their majority of seats to over two-thirds of the Senate.
The 1800–01 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that, coinciding with their election to the White House, also led to the Democratic-Republican Party taking control of the United States Senate. Although the Federalists began the next 7th Congress with a slim majority, they lost their majority shortly thereafter due to mid-year special elections.

The 1798–99 United States Senate elections were held at the middle of President John Adams's administration and had no net change in political control of the Senate.

The 1792–93 United States Senate elections were elections of United States senators that coincided with President George Washington's unanimous re-election. In these elections, terms were up for the ten senators in class 2.

The 1794–95 United States Senate elections were elections that had the formation of organized political parties in the United States, with the Federalist Party emerging from the Pro Administration coalition, and the Democratic-Republican Party emerging from the Anti-Administration coalition.

On January 1, 1818, a special election was held in North Carolina's 7th district to fill a vacancy left by the death of Representative-elect Alexander McMillan (F) before the 15th Congress had assembled.

On November 7, 1818, a special election was held in North Carolina's 11th district to fill a vacancy caused by Daniel M. Forney (DR)'s resignation earlier that year.

On March 23, 1824, Hutchins G. Burton (DR), who had represented North Carolina's 2nd district, resigned upon being elected Governor. A special election was held to fill the resulting vacancy on January 6, 1825













