Bruce Peninsula National Park is a national park on the Bruce Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. Located on a part of the Niagara Escarpment, the park comprises 156 square kilometres and is one of the largest protected areas in southern Ontario, forming the core of UNESCO's Niagara Escarpment World Biosphere Reserve. It was established in 1987 to protect the rock formations and shoreline of the Niagara Escarpment. The park offers opportunities for many outdoor activities, including hiking, camping, and bird watching. The park has trails ranging in difficulty from easy to expert, and connects to the Bruce Trail. Bruce Peninsula National Park is known for its crystal clear blue waters, cobblestone beaches, rocky cliffs and karst formations.
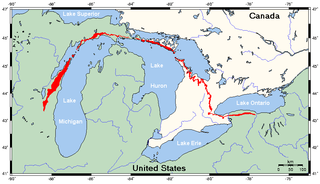
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over which the Niagara River plunges at Niagara Falls, for which it is named.

Georgian Bay is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To its northwest is the North Channel.

Tobermory is a small community located at the northern tip of the Bruce Peninsula, in the traditional territory of the Saugeen Ojibway Nation. Until European colonization in the mid-19th century, the Bruce Peninsula was home to the Saugeen Ojibway nations, with their earliest ancestors reaching the area as early as 7500 years ago. It is part of the municipality of Northern Bruce Peninsula. It is 300 kilometres northwest of Toronto. The closest city to Tobermory is Owen Sound, 100 kilometres south of Tobermory and connected by Highway 6.
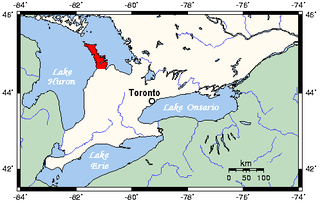
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Island, with which it forms the widest strait joining Georgian Bay to the rest of Lake Huron. The Bruce Peninsula contains part of the geological formation known as the Niagara Escarpment.

Fathom Five National Marine Park is a National Marine Conservation Area in the Georgian Bay part of Lake Huron, Ontario, Canada, that seeks to protect and display shipwrecks and lighthouses, and conserve freshwater ecosystems. The many shipwrecks make the park a popular scuba diving destination, and glass bottom boat tours leave Tobermory regularly, allowing tourists to see the shipwrecks without having to get wet.

The Scotia Sea is a sea located at the northern edge of the Southern Ocean at its boundary with the South Atlantic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Drake Passage and on the north, east, and south by the Scotia Arc, an undersea ridge and island arc system supporting various islands. The sea sits atop the Scotia Plate. It is named after the expedition ship Scotia. Many icebergs melt there.

Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation is an Anishinaabek First Nation from the Bruce Peninsula region in Ontario, Canada. Along with the Saugeen First Nation, they form the Saugeen Ojibway Nation. The Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation currently has a registered membership of 2758 individuals, as of December, 2020. Approximately 700 members live on the main reserve, Neyaashiinigmiing 27. The First Nation has 3 reserves, Neyaashiinigmiing 27, Cape Croker Hunting Ground 60B and Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1. The size of all reserves is 8083.70 hectares.
Saugeen Tract Agreement, registered as Crown Treaty Number 451⁄2, was signed August 9, 1836 between the Saugeen Ojibwa and Ottawa and the government of Upper Canada. Conducted on the Manitoulin Island, Sir Francis Bond Head used this occasion for the provincial government's annual distribution of gifts to the Ojibwa and Ottawa of the Saugeen Peninsula to negotiate the treaty. In exchange for 1.5 million acres (6,070 km²) of land, the Ojibwa and Ottawa of Saugeen received only a promise to assist and protect Indians who took up residence on the Bruce Peninsula.
Field Island is a Baffin Island offshore island located in the Arctic Archipelago in the territory of Nunavut. The island lies in Frobisher Bay, west of Waddell Bay, and southeast of Opera Glass Cape on the Hall Peninsula. Islands in the immediate vicinity include: Bruce Island to the northwest, Fletcher Island to the west, and Chase Island to the south.
Fletcher Island is a Baffin Island offshore island located in the Arctic Archipelago in the territory of Nunavut. The island lies in Frobisher Bay, north of Newell Sound. The Hall Peninsula is to the east. Islands in the immediate vicinity include: Field Island to the east; Bruce Island to the northeast; Pike and Pugh Islands to the west.
Augustus Island is one of the many uninhabited Canadian Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut. It is a Baffin Island offshore island located in inner Frobisher Bay. The island lies at the head of Ward Inlet, between Becher Peninsula and Hall Peninsula. Bruce Island is located at the mouth of the inlet. Other islands in the immediate vicinity include Algerine Island, Frobisher's Farthest, McBride Island, and Pichit Island.

Watson Peninsula is a narrow peninsula 4 km (2.5 mi) long separating Macdougal and Marr Bays on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Bruce, who named it for G.L. Watson, yacht designer and redesigner of the expedition ship Scotia.

Pirie Peninsula is a narrow peninsula extending 6 km (3.7 mi) northward from the center of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The peninsula was surveyed in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under Bruce, who named it for Dr Harvey Pirie, surgeon and geologist of the expedition.

Ferguslie Peninsula is a peninsula 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, lying between Browns Bay and Macdougal Bay on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The peninsula was charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for Ferguslie, the residence of James Coats, chief patron of the expedition.

Ferrier Peninsula is a narrow peninsula, 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, forming the eastern end of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was roughly charted in 1823 by a British sealing expedition under James Weddell. It was surveyed in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for his secretary J.G. Ferrier, who was also manager in Scotland of the expedition.
Graptolite Island is an island 0.8 km (0.50 mi) long in the north-east part of Fitchie Bay, lying off the south-east portion of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. James Weddell's chart published in 1825 shows two islands in essentially this position. Existence of a single island was determined in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who so named it because what were thought to be graptolite fossils were found there. Later analysis showed that the fossils on Graptolite Island were merely the remains of ancient plants.
Cape Robertson is a cape which marks the west side of the entrance to Jessie Bay, in the north-west part of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica.
Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1 is a First Nations reserve consisting of 89 islands in Lake Huron off the western coast of the Bruce Peninsula in Ontario. They extend north of Chief's Point 28 for 11 miles (18 km) up to Pike Bay. These islands are shared between the Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation and Saugeen First Nation.
The Pontunj, also called the Yankonyu, are a contemporary Indigenous Australian people of the eastern Cape York Peninsula in northern Queensland.