A motte-and-bailey castle is a fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised earthwork called a motte, accompanied by an enclosed courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy to build with unskilled, often forced, labour, but still militarily formidable, these castles were built across northern Europe from the 10th century onwards, spreading from Normandy and Anjou in France, into the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. The Normans introduced the design into England and Wales following their invasion in 1066. Motte-and-bailey castles were adopted in Scotland, Ireland, the Low Countries and Denmark in the 12th and 13th centuries. By the end of the 13th century, the design was largely superseded by alternative forms of fortification, but the earthworks remain a prominent feature in many countries.

Aberdyfi Castle is a castle located near Glandyfi, Ceredigion, in Wales. All that now remains is the motte, which is referred to as Domen Las.

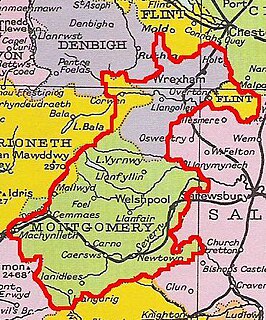
Sycharth is a motte and bailey castle and town in Llansilin, Powys, Wales. Until 1996 Sycharth was in the historic county of Denbighshire, but was then transferred to the Shire area of Montgomeryshire within Powys. Sycharth Castle was the birthplace of Owain Glyndŵr.

The remains of Aberedw Castle, also known as 'Castle in Elfael Uwch Mynydd', are located at the small village of Aberedw in the county of Powys, Mid-Wales. It was built in the late twelfth century and probably replaced the motte and bailey castle a few hundred metres away.

Hen Domen Welsh, meaning "old mound", is the site of a medieval timber motte-and-bailey castle in Powys, Wales. It is the site of the original Montgomery Castle, and was built by Roger de Montgomery in 1070. From 1105 the castle was the home of the de Boulers (Bowdler) family, and it is from Baldwin de Boulers that Montgomery gets its Welsh name, Trefaldwyn "The Town of Baldwin". When the castle was rebuilt in stone (1223–1234), it was decided to rebuild it on a rocky promontory a mile to the south-east – the location of the current town of Montgomery, Powys. The Hen Domen site has been extensively excavated.

Thetford Castle is a medieval motte and bailey castle in the market town of Thetford in the Breckland area of Norfolk, England. The first castle in Thetford, a probable 11th century Norman ringwork called Red Castle, was replaced in the 12th century by a much larger motte and bailey castle on the other side of the town. This new castle was largely destroyed in 1173 by Henry II, although the huge motte, the second largest man-made mound in England, remained intact. The motte, recognised as a scheduled monument, now forms part of a local park, and the remains are known variously as Castle Hill, Castle Mound and Military Parade.

Castell Gwallter, also known as Walter's Castle and sometimes Castell Penweddig, is the remains of a Norman motte-and-bailey castle situated on a large hill above the old village of Llandre in northern Ceredigion, Wales, four miles northeast of Aberystwyth.
Pen y Clawdd Castle is a ditched mound with a double moat, roughly circular in shape, with a diameter of approximately 28m to 30m and about 2.4m high. The castle is in Llanvihangel Crucorney, about five miles to the north of Abergavenny, Monmouthshire, in south east Wales and lies between the Usk and Monnow rivers. The mound was designated a scheduled monument in 1950 and described as a defensive medieval motte.
Bleddfa Castle was a motte and bailey structure near Llangunllo in modern-day Powys, Wales. It is believed to have been built before 1195 and abandoned by 1304. What remains today is described as a "mutilated oval mound" of 46 by 36 metres, containing some traces of masonry. It is surrounded by a rectangular bailey measuring 100 by 60 metres, with a hedge on its northern border.
Prestatyn Castle is a motte and bailey castle built in 1157 on land granted to the Norman lord Robert Banastre by King Henry II of England. It was built on level ground on the coastal plain and commanded an extensive view. Nowadays the mound and slight remnants of a causeway are all that is visible.

Barland Castle, also known as Bishopston Old Castle, was a motte-and-bailey castle located near the village of Old Radnor, in Radnorshire, Wales. It is believed to have been described in the Domesday Book under the ownership of Hugh L'Asne, who owned the nearby lands. An excavation took place in 1898, which found pottery shards and other artefacts dated to the late 12th/early 13th century. The name is suspected to have slowly changed over time, from "Bernoldune", to "Beraldon", "Barlondon" and finally "Barlonde". All that remains is a ditch and a stepped bank, which may contain tumbled remains of masonry, while 19th century excavations showed evidence of a wooden palisade.
Castle Nimble was a motte and bailey defensive fortification near Old Radnor, in Radnorshire, Wales. Castle Nimble appears to have had an oval-shaped ditched motte, with a semi-rectangular bailey, and some other enclosures, including possibly a pond.

Castle Batch was a fortification at Worle that once stood overlooking the town of Weston-super-Mare in Somerset, England.

Castle Caereinion is a small village and community in Montgomeryshire, Powys, Wales upon the River Banwy, around 8 miles west of Welshpool, and 4 miles east of Llanfair Caereinion.

Tomen yr Allt was a Medieval motte and bailey defensive castle near Llanfyllin in Powys, Wales.
Banc y Betws or Betws Castle, is a motte and scheduled ancient monument in Wales. It is located in Llangyndeyrn, in the Gwendraith Valley in Carmarthenshire, Wales; map grid SN458154. All that is visible of the structure nowadays is a mound capped with trees and the remains of the ditch that surrounded it.

Rhayader Castle is the remains of a motte-and-bailey castle in the town of Rhayader, Powys, Wales. The available documentary sources are not clear enough to distinguish between this site and the castle mound across the river and one or the other was probably built by Rhys ap Gruffydd, Prince of Deheubarth, in 1177. At that time the river formed the border between Gwrtheyrnion and the independent state of Buellt; the town of Rhayader is on the Gwrtheyrnion side of the river.