Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the seams. It is typically hard but friable. Its quality is ranked higher than lignite and sub-bituminous coal, but lesser than anthracite. It is the most abundant rank of coal, with deposits found around the world, often in rocks of Carboniferous age. Bituminous coal is formed from sub-bituminous coal that is buried deeply enough to be heated to 85 °C (185 °F) or higher.

Anthracite, also known as hard coal and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a submetallic lustre. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highest ranking of coals.

Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground or from a mine. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from iron ore and for cement production. In the United Kingdom and South Africa, a coal mine and its structures are a colliery, a coal mine is called a 'pit', and the above-ground structures are a 'pit head'. In Australia, "colliery" generally refers to an underground coal mine.
Firedamp is any flammable gas found in coal mines, typically coalbed methane. It is particularly found in areas where the coal is bituminous. The gas accumulates in pockets in the coal and adjacent strata and when they are penetrated the release can trigger explosions. Historically, if such a pocket was highly pressurized, it was termed a "bag of foulness".

A coal-seam fire is a burning of an outcrop or underground coal seam. Most coal-seam fires exhibit smouldering combustion, particularly underground coal-seam fires, because of limited atmospheric oxygen availability. Coal-seam fire instances on Earth date back several million years. Due to thermal insulation and the avoidance of rain/snow extinguishment by the crust, underground coal-seam fires are the most persistent fires on Earth and can burn for thousands of years, like Burning Mountain in Australia. Coal-seam fires can be ignited by self-heating of low-temperature oxidation, lightning, wildfires and even arson. Coal-seam fires have been slowly shaping the lithosphere and changing atmosphere, but this pace has become faster and more extensive in modern times, triggered by mining.
A mining accident is an accident that occurs during the process of mining minerals or metals. Thousands of miners die from mining accidents each year, especially from underground coal mining, although accidents also occur in hard rock mining. Coal mining is considered much more hazardous than hard rock mining due to flat-lying rock strata, generally incompetent rock, the presence of methane gas, and coal dust. Most of the deaths these days occur in developing countries, and rural parts of developed countries where safety measures are not practiced as fully. A mining disaster is an incident where there are five or more fatalities.
The history of coal mining goes back thousands of years, with early mines documented in ancient China, the Roman Empire and other early historical economies. It became important in the Industrial Revolution of the 19th and 20th centuries, when it was primarily used to power steam engines, heat buildings and generate electricity. Coal mining continues as an important economic activity today, but has begun to decline due to the strong contribution coal plays in global warming and environmental issues, which result in decreasing demand and in some geographies, peak coal.

Massey Energy Company was a coal extractor in the United States with substantial operations in West Virginia, Kentucky and Virginia. By revenue, it was the fourth largest producer of coal in the United States and the largest coal producer in Central Appalachia. By coal production weight, it was the sixth largest producer of coal in the United States.
The Westmoreland County coal strike of 1910–1911, or the Westmoreland coal miners' strike, was a strike by coal miners represented by the United Mine Workers of America. The strike is also known as the Slovak Strike because about 70 percent of the miners were Slovak immigrants. It began in Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania, on March 9, 1910, and ended on July 1, 1911. At its height, the strike encompassed 65 mines and 15,000 coal miners. Sixteen people were killed during the strike, nearly all of them striking miners or members of their families. The strike ended in defeat for the union.

The health and environmental impact of the coal industry includes issues such as land use, waste management, water and air pollution, caused by the coal mining, processing and the use of its products. In addition to atmospheric pollution, coal burning produces hundreds of millions of tons of solid waste products annually, including fly ash, bottom ash, and flue-gas desulfurization sludge, that contain mercury, uranium, thorium, arsenic, and other heavy metals. Coal is the largest contributor to the human-made increase of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere.
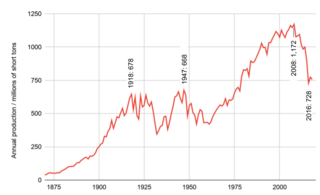
Coal mining is an industry in transition in the United States. Production in 2019 was down 40% from the peak production of 1,171.8 million short tons in 2008. Employment of 43,000 coal miners is down from a peak of 883,000 in 1923. Generation of electricity is the largest user of coal, being used to produce 50% of electric power in 2005 and 27% in 2018. The U.S. is a net exporter of coal. U.S. coal exports, for which Europe is the largest customer, peaked in 2012. In 2015, the U.S. exported 7.0 percent of mined coal.

The history of coal mining in the United States starts with the first commercial use in 1701, within the Manakin-Sabot area of Richmond, Virginia. Coal was the dominant power source in the late 1800s and early 1900s, and although in rapid decline it remains a significant source of energy in 2023.
Mining in the United States has been active since the beginning of colonial times, but became a major industry in the 19th century with a number of new mineral discoveries causing a series of mining rushes. In 2015, the value of coal, metals, and industrial minerals mined in the United States was US $109.6 billion. 158,000 workers were directly employed by the mining industry.
The Sukhodilska–Skhidna coal mine is a large underground coal mine located in Southeast Ukraine in Luhansk Oblast. Sukhodilska–Skhidna coal mine represents one of the largest coal reserves in Ukraine, having estimated reserves of 157.4 million tonnes. The annual coal production is around 712,000 tonnes.

Energy resources bring with them great social and economic promise, providing financial growth for communities and energy services for local economies. However, the infrastructure which delivers energy services can break down in an energy accident, sometimes causing considerable damage. Energy fatalities can occur, and with many systems deaths will happen often, even when the systems are working as intended.

Coal in Europe describes the use of coal as an energy fuel in Europe. Coal includes hard coal, black coal, and brown coal.
The Harwick Mine disaster was a mining accident on January 25, 1904 in Cheswick, Pennsylvania, some sixteen mi (26 km) north of Pittsburgh in the western part of the state. The blast killed an estimated 179 miners and 2 aid workers. The disaster ranks among the ten worst coal mining disasters in American history. One community especially impacted was the Hungarian community in Homestead, Pennsylvania. Fifty-eight of the members of the First Hungarian Reformed Church of Homestead—a full third of the congregation—died in the explosion.

The Mather Mine disaster refers to the events surrounding an explosion that occurred in the Mather Mine on May 19, 1928 at 4:07 PM in Mather, Pennsylvania. A report released by the United States Bureau of Mines states that a total of 195 men were killed in the catastrophe, of which two died in hospitals after being discovered by rescue crews and volunteers. The Mather Mine disaster ranks as the seventh worst mining disaster in U.S. history and the second worst in Pennsylvania history.
John J. Forbes was an American mining engineer. He served as the 9th director of the U.S. Bureau of Mines.