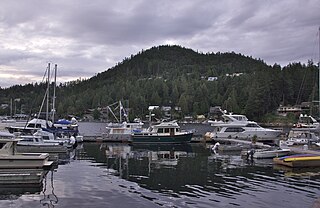The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a body of water about 96 miles long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait.

The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada, and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately 240 kilometres (150 mi) long and varies in width from 20 to 58 kilometres. Along with the Strait of Juan de Fuca and Puget Sound, it is a constituent part of the Salish Sea.
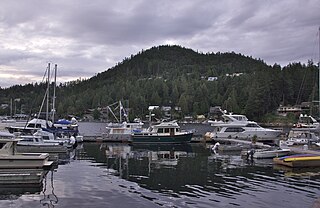
The Sunshine Coast is a geographic subregion of the British Columbia Coast that generally comprises the regional districts of qathet and Sunshine Coast.

The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada along the Pacific Ocean is in the province, it is synonymous with being the West Coast of Canada.

Toba Inlet is one of the lesser, but still principal, inlets of the British Columbia Coast. It is fourth in the series north from the 49th parallel which begins with Burrard Inlet, which is the harbour for the city of Vancouver. Between it and Jervis Inlet to its east, however, there is a freshwater fjord, Powell Lake, which has been augmented by a small hydro project to supply power to the large pulp mill at Powell River, the principal town of the Malaspina Peninsula of the upper Sunshine Coast. Klahoose 1 Reserve, of the Klahoose First Nation is at the mouth of Toba River at the Head of Toba Inlet. Toba Inlet and the Toba Valley is home to many grizzly bears.

Knight Inlet is one of the principal inlets of the British Columbia Coast, and the largest of the major inlets in the southern part of the Coast. It is fifth in sequence of the great saltwater inlets north from the 49th parallel near Vancouver, but it is the first whose outflow points away from the Strait of Georgia, opening into Queen Charlotte Strait at the Kwakwakaʼwakw community of Memkumlis on Village Island.

Desolation Sound is a deep water sound at the northern end of the Salish Sea and of the Sunshine Coast in British Columbia, Canada.

Desolation Sound Marine Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. The park is distinguished by its many picturesque sheltered coves and anchorages, frequented by yachts and pleasure craft. The scenery consists of waterfalls, rugged glaciated peaks, and steep forested slopes that fall into the ocean.
Saanich Peninsula is located north of Victoria, British Columbia, Canada. It is bounded by Saanich Inlet on the west, Satellite Channel on the north, the small Colburne Passage on the northeast, and Haro Strait on the east. The exact southern boundary of what is referred to as the "Saanich Peninsula" is somewhat fluid in local parlance.

The Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Puget Sound, and an intricate network of connecting channels and adjoining waterways.
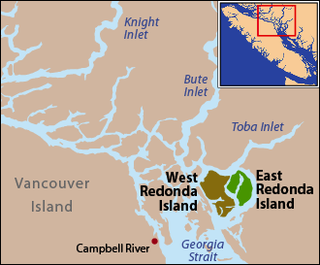
East Redonda Island is a coastal island in British Columbia, Canada, part of the Discovery Islands archipelago. It lies just to the north of Desolation Sound Marine Park, which is located off the north end of the Malaspina Peninsula at the mouth of Toba Inlet within Electoral Area C of the Strathcona Regional District.

Cortes Island is an island in the Discovery Islands archipelago on the coast of British Columbia, Canada. The island is 25 km (16 mi) long, 13 km (8 mi) wide, and 130 km2 (50 sq mi) in area. It has a population of 1,035 permanent residents. Cortes Island lies within Electoral Area B of the Strathcona Regional District, which provides water and sewerage systems, fire protection, land use planning, parks, recreation, and emergency response.

Broughton Archipelago is a group of islands located at the eastern end of Queen Charlotte Strait in Mount Waddington Regional District, British Columbia. The archipelago is the traditional territory of the Musgamagw Dzawada'enuxw, Namgis, Ma'amtagila and Tlowitsis nations of the Kwakwaka'wakw peoples.

The ƛoʔos Klahoose are one of the three groups comprising the ʔayʔaǰuθəm Tla'Amin or Mainland Comox. The other two divisions of this once-populous group are the χʷɛmaɬku Homalco and Sliammon. The Klahoose, Homalco and Sliammon are, according to oral tradition, the descendants of the survivors of the Great Flood. The three groups were split by colonialism into different band councils but united historically as the Tla A'min, known as the Mainland Comox, and K’ómoks, the larger grouping of the Comox people, also known as the Island Comox and before the merger with the Laich-kwil-tach culture. Historically both groups are a subgroup of the Coast Salish though the K’ómoks name is from, and their language today, is the Lik'wala dialect of Kwak'wala. The ancestral tongue is the Comox language, though the Sahtloot/Island dialect is extinct.

West Redonda Island is an island in British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Discovery Islands, an archipelago between Vancouver Island and the mainland, and between the Strait of Georgia and Johnstone Strait.

Sutil Channel is a broad strait located in the Discovery Islands of British Columbia, Canada.

Chatham Sound is a sound on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada, bordering on Alaska, United States. It is located between the Dundas and Stephens Islands and the Tsimpsean Peninsula, it is part of the Inside Passage and extends from Portland Inlet in the north to Porcher Island in the south.

Lewis Channel is a strait located between Cortes Island and West Redonda Island in the Discovery Islands of British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the northern Salish Sea.
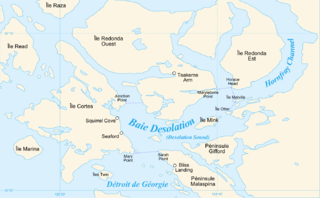
Waddington Channel is a strait located between East Redonda and West Redonda Island of the Discovery Islands in British Columbia, Canada.

Calm Channel is a channel located between several major islands of the Discovery Islands in British Columbia, Canada. The channel is an important waterway for boats transiting the archipelago.