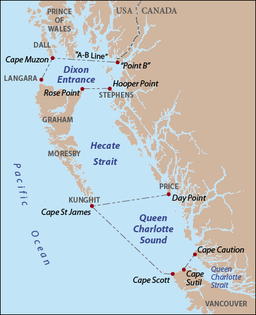
Haida Gwaii, formerly known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago located between 55–125 km (34–78 mi) off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Hecate Strait. Queen Charlotte Sound lies to the south, with Vancouver Island beyond. To the north, the disputed Dixon Entrance separates Haida Gwaii from the Alexander Archipelago in the U.S. state of Alaska.

Graham Island is the largest island in the Haida Gwaii archipelago, lying off the mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada. It is separated by the narrow Skidegate Channel from the other principal island of the group to the south, Moresby Island. It has a population of 3,858, an area of 6,361 km2 (2,456 sq mi), and is the 101st largest island in the world and Canada's 22nd largest island.
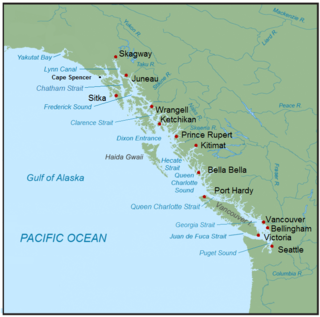
The Inside Passage is a coastal route for ships and boats along a network of passages which weave through the islands on the Pacific Northwest coast of the North American Fjordland. The route extends from southeastern Alaska in the United States, through western British Columbia in Canada, to northwestern Washington state in the United States. Ships using the route can avoid some of the bad weather in the open ocean and may visit some of the many isolated communities along the route. The Inside Passage is heavily travelled by cruise ships, freighters, tugs with tows, fishing craft, pleasure craft, and ships of the Alaska Marine Highway, BC Ferries, and Washington State Ferries systems. Coast Guard vessels of both Canada and the United States patrol and transit in the Passage.

The Dixon Entrance is a strait about 80 kilometers (50 mi) long and wide in the Pacific Ocean at the Canada–United States border, between the U.S. state of Alaska and the province of British Columbia in Canada. The Dixon Entrance is part of the Inside Passage shipping route. It forms part of the maritime boundary between the U.S. and Canada, although the location of that boundary here is disputed.

Hecate Strait is a wide but shallow strait between Haida Gwaii and the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It merges with Queen Charlotte Sound to the south and Dixon Entrance to the north. About 140 kilometres (87 mi) wide at its southern end, Hecate Strait narrows in the north to about 48 kilometres (30 mi). It is about 260 kilometres (160 mi) in length.

Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve, National Marine Conservation Area, and Haida Heritage Site, usually referred to simply as Gwaii Haanas, is located in southernmost Haida Gwaii, 130 kilometres off the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. Gwaii Haanas protects an archipelago of 138 islands, the largest being Moresby Island and the southernmost being Kunghit Island. "Gwaii Haanas" means "Islands of Beauty" in X̱aayda kíl, the language of the Haida people.

Queen Charlotte Strait is a strait between Vancouver Island and the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It connects Queen Charlotte Sound with Johnstone Strait and Discovery Passage and via them to the Strait of Georgia and Puget Sound. It forms part of the Inside Passage from Washington to Alaska. The term Queen Charlotte Strait is also used to refer to the general region and its many communities, notably of the Kwakwakaʼwakw peoples. Despite its name, Queen Charlotte Strait does not lie between Haida Gwaii and the mainland; that body of water is named Hecate Strait.

The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada along the Pacific Ocean is in the province, it is synonymous with being the West Coast of Canada.

Johnstone Strait is a 110 km (68 mi) channel along the north east coast of Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada. Opposite the Vancouver Island coast, running north to south, are Hanson Island, West Cracroft Island, the mainland British Columbia Coast, Hardwicke Island, West Thurlow Island and East Thurlow Island. At that point, the strait meets Discovery Passage which connects to Georgia Strait.

Milbanke Sound is a sound on the coast of the Canadian province of British Columbia.
The Queen Charlottes Gold Rush was a gold rush in southern Haida Gwaii of what is now the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada, in 1851.
Kunghit Island is an island in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the southernmost island in the Haida Gwaii archipelago, located to the south of Moresby Island. The southernmost point of Kunghit Island, called Cape St James, is used to delineate the boundary between Hecate Strait and Queen Charlotte Sound. The only habitation on Kunghit Island is Rose Harbour, on its north shore.

SG̱ang Gwaay Llnagaay, commonly known by its English name Ninstints, is a village site of the Haida people and part of the Gwaii Haanas National Park Reserve and Haida Heritage Site on Haida Gwaii on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada.
Cartwright Sound is a sound on the southwest coast of Graham Island in the Queen Charlotte Islands of the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. It was named by Captain George Vancouver in honour of John Cartwright, then serving in the Royal Navy under Admiral Howe and later a noted political and social reformer in Britain. The sound is located in the area of Kano Inlet, and lies between Tcenakum and Hunter Points. In the center is a tiny island called Marble Island. Listed by the BC Geographical Names Information System, the sound is entirely missing from Google Maps. Adding to the confusion, Cartwright Sound Charters, which runs fishing expeditions to the sound, is based in Sandspit, British Columbia, on the far east coast of Graham island Queen Charlotte Islands is also now known as the Haida Gwaii archipelago
Queen Charlotte was the consort of George III.

Skidegate Inlet is a broad inlet on the east coast of the Haida Gwaii archipelago of the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. It is the easternmost of a series of waterways separating Graham Island to the north from Moresby Island to the south.
Parry Passage is a strait and marine waterway between Langara Island (N) and Graham Island (S) in Haida Gwaii, formerly known as the Queen Charlotte Islands, in British Columbia, Canada.

James Charles Stuart Strange was a British officer of the East India Company, one of the first maritime fur traders, a banker, and a Member of Parliament.
Union was an American sloop built in Somerset, Massachusetts in 1792. It is best known for its circumnavigation of the world, 1794–1796, under the maritime fur trader John Boit.
John Boit Jr was one of the first Americans involved in the maritime fur trade. He sailed as fifth mate under Captain Robert Gray on the second voyage of the Columbia Rediviva, 1790–1793. During the voyage he wrote a short but important journal in which he described the discovery of the Columbia River.