
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Lunar impact craters range from microscopic craters on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo program and small, simple, bowl-shaped depressions in the lunar regolith to large, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth.

A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or moon. When the original object enters the atmosphere, various factors such as friction, pressure, and chemical interactions with the atmospheric gases cause it to heat up and radiate energy. It then becomes a meteor and forms a fireball, also known as a shooting star; astronomers call the brightest examples "bolides". Once it settles on the larger body's surface, the meteor becomes a meteorite. Meteorites vary greatly in size. For geologists, a bolide is a meteorite large enough to create an impact crater.

Ida, minor planet designation 243 Ida, is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 September 1884 by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at Vienna Observatory and named after a nymph from Greek mythology. Later telescopic observations categorized Ida as an S-type asteroid, the most numerous type in the inner asteroid belt. On 28 August 1993, Ida was visited by the uncrewed Galileo spacecraft while en route to Jupiter. It was the second asteroid visited by a spacecraft and the first found to have a natural satellite.

Meteor Crater or Barringer Crater is an impact crater about 37 mi (60 km) east of Flagstaff and 18 mi (29 km) west of Winslow in the desert of northern Arizona, United States. The site had several earlier names, and fragments of the meteorite are officially called the Canyon Diablo Meteorite, after the adjacent Canyon Diablo.

An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale.

A Martian meteorite is a rock that formed on Mars, was ejected from the planet by an impact event, and traversed interplanetary space before landing on Earth as a meteorite. As of September 2020, 277 meteorites had been classified as Martian, less than half a percent of the 72,000 meteorites that have been classified. The largest complete, uncut Martian meteorite, Taoudenni 002, was recovered in Mali in early 2021. It weighs 14.5 kilograms and is on display at the Maine Mineral & Gem Museum.

The Nördlinger Ries is an impact crater and large circular depression in western Bavaria and eastern Baden-Württemberg. It is located north of the Danube in the district of Donau-Ries. The city of Nördlingen is located within the depression, about 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) south-west of its centre.

Tektites are gravel-sized bodies composed of black, green, brown or grey natural glass formed from terrestrial debris ejected during meteorite impacts. The term was coined by Austrian geologist Franz Eduard Suess (1867–1941), son of Eduard Suess. They generally range in size from millimetres to centimetres. Millimetre-scale tektites are known as microtektites.
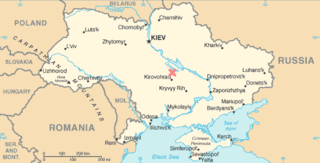
The Boltysh crater or Bovtyshka crater is a buried impact crater in the Kirovohrad Oblast of Ukraine, near the village of Bovtyshka. The crater is 24 kilometres (15 mi) in diameter and its age of 65.39 ± 0.14/0.16 million years, based on argon-argon dating techniques, less than 1 million years younger than Chicxulub crater in Mexico and the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The Chicxulub impact is believed to have caused the mass extinction at the end of the Cretaceous period, which included the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs. The Boltysh crater is currently thought to be unrelated to the Chicxulub impact, and to have not generated major global environmental effects.
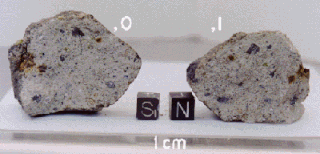
HED meteorites are a clan (subgroup) of achondrite meteorites. HED stands for "howardite–eucrite–diogenite". These achondrites came from a differentiated parent body and experienced extensive igneous processing not much different from the magmatic rocks found on Earth and for this reason they closely resemble terrestrial igneous rocks.

An ejecta blanket is a generally symmetrical apron of ejecta that surrounds an impact crater; it is layered thickly at the crater's rim and thin to discontinuous at the blanket's outer edge. The impact cratering is one of the basic surface formation mechanisms of the solar system bodies and the formation and emplacement of ejecta blankets are the fundamental characteristics associated with impact cratering event. The ejecta materials are considered as the transported materials beyond the transient cavity formed during impact cratering regardless of the state of the target materials.

Tooting is an impact crater with volcanic features at 23.1°N, 207.1°E, in Amazonis Planitia, due west of the volcano Olympus Mons, on Mars. It was identified by planetary geologist Peter Mouginis-Mark in September 2004. Scientists estimate that its age is on the order of hundreds of thousands of years, which is relatively young for a Martian crater. A later study confirms this order of magnitude estimate. A preliminary paper describing the geology and geometry of Tooting was published in 2007 by the journal Meteoritics and Planetary Science, vol. 42, pages 1615–1625. Further papers have been published, including a 2010 analysis of flows on the walls of Tooting crater by A. R. Morris et al., and a 2012 review paper by P.J. Mouginis-Mark and J.M. Boyce in Chemie der Erde Geochemistry, vol. 72, p. 1–23. A geologic map has also been submitted in 2012 to the U.S. Geological Survey for consideration and future publication.

Zunil is an impact crater near the Cerberus Fossae on Mars, with a diameter of 10.26 kilometres. It is named after the town of Zunil in Guatemala. The crater is located in the Elysium quadrangle. Visible in images from the Viking 1 and Viking 2 Mars orbiters in the 1970s, Zunil was subsequently imaged at higher resolution for the first time by the Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) in 2000.

Suevite is a rock consisting partly of melted material, typically forming a breccia containing glass and crystal or lithic fragments, formed during an impact event. It forms part of a group of rock types and structures that are known as impactites.

Whitecourt crater is a meteorite impact crater in central Alberta, Canada, located approximately 10 km (6.2 mi) southeast of the Town of Whitecourt within Woodlands County. It is remarkable for being unusually well-preserved for a crater of small size and relatively young age.

Nakhlites are a group of Martian meteorites, named after the first one, Nakhla meteorite.

Northwest Africa 7034 is a Martian meteorite believed to be the second oldest yet discovered. It is estimated to be two billion years old and contains the most water of any Martian meteorite found on Earth. Although it is from Mars it does not fit into any of the three SNC meteorite categories, and forms a new Martian meteorite group named "Martian ". Nicknamed "Black Beauty", it was purchased in Morocco and a slice of it was donated to the University of New Mexico by its American owner. The image of the original NWA 7034 was photographed in 2012 by Carl Agee, University of New Mexico.

The Braunschweig meteorite is a 1.3 kilograms meteorite that hit Melverode, a suburb in Braunschweig, Germany, at around 2:05 AM on 23 April 2013. It hit the concrete pavement in front of the home of Erhard Seemann, breaking into hundreds of fragments on impact, the largest of which is 214 grams. The meteorite created a small impact crater in the concrete, with a diameter of 7 cm (2.8 in) and a depth of 3 cm (1.2 in).

Karratha is an impact crater in the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. It was named after the town of Karratha, Western Australia, in 2021.



















