Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Doxazosin, sold under the brand names Cardura among others, is a medication used to treat symptoms of an enlarged prostate and high blood pressure. For high blood pressure, it is a less preferred option. It is taken by mouth.
The rubiscolins are a group of opioid peptides that are formed during digestion of the ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco) protein from spinach leaves. These peptides have much in common with the better-known gluten exorphins.

Guanabenz is an alpha agonist of the alpha-2 adrenergic receptor that is used as an antihypertensive drug. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
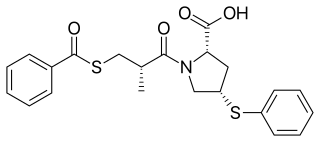
Zofenopril (INN) is a medication that protects the heart and helps reduce high blood pressure. It is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.

Manidipine is a calcium channel blocker that is used clinically as an antihypertensive.
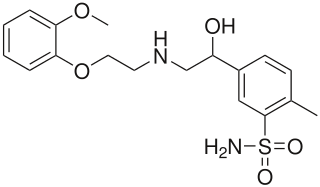
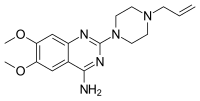
Amosulalol (INN) is an anti-hypertensive drug. It has much higher affinity for alpha-1 adrenergic receptors than for beta adrenergic receptors.

Monatepil is a calcium channel blocker and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist used as an antihypertensive.

Tolonidine is an antihypertensive.

Bietaserpine (INN), or 1-diaminoethylreserpine, is a derivative of reserpine used as an antihypertensive agent. Like reserpine, bietaserpine is a VMAT inhibitor.

Deserpidine (INN) is an antihypertensive drug related to reserpine which occurs naturally in Rauvolfia spp.
Adimolol (MEN-935) is antihypertensive agent which acts as a non-selective α1-, α2-, and β-adrenergic receptor antagonist.
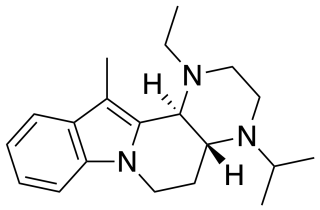
Atiprosin (AY-28,228) is an antihypertensive agent which acts as a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist. It also possesses some antihistamine activity, though it is some 15-fold weaker in this regard than as an alpha blocker. It was never marketed.

1-Phenylpiperazine is a simple chemical compound featuring a phenyl group bound to a piperazine ring. The suffix ‘-piprazole’ is sometimes used in the names of drugs to indicate they belong to this class.

Bupicomide is a chemical compound created and manufactured by Lanospharma Laboratories Company, Ltd. It is used experimentally as a beta blocker and clinically as a strong vasodilator with the noted side effects of reduced systolic, diastolic and mean arterial pressure.
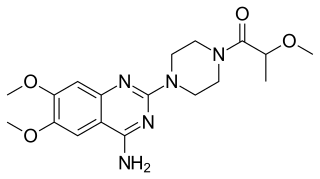
Metazosin is an antihypertensive alpha-adrenergic antagonist.
Sulfinalol is a beta adrenergic receptor antagonist.

Mexrenone is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone that was never marketed. It is the lactonic form of mexrenoic acid (mexrenoate), and mexrenoate potassium (SC-26714), the potassium salt of mexrenoic acid, also exists. In addition to the mineralocorticoid receptor, mexrenone also binds to the glucocorticoid, androgen, and progesterone receptors. Relative to spironolactone, it has markedly reduced antiandrogen activity. Eplerenone is the 9-11α-epoxy analogue of mexrenone.
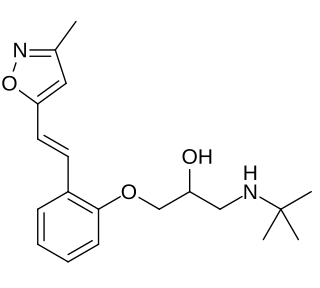
Isoxaprolol is an adrenergic antagonist with antiarrhythmic and antihypertensive properties.

Dicirenone is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent but was never marketed. It was synthesized and assayed in 1974. Similarly to other spirolactones like spironolactone, dicirenone also possesses antiandrogen activity, albeit with relatively reduced affinity.