
Fluorometholone, also known as 6α-methyl-9α-fluoro-11β,17α-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic glucocorticoid which is used in the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases. The C17α acetate ester, fluorometholone acetate, is also a glucocorticoid and is used for similar indications.

Acebutolol, sold under the brand names Sectral among others, is a beta blocker for the treatment of hypertension and arrhythmias. Acebutolol is a cardioselective beta-1 blocker and has intrinsic sympathetic activity. It is commonly used in the treatment of angina.

Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Canrenoic acid is a synthetic steroidal antimineralocorticoid which was never marketed.

Levallorphan, also known as levallorphan tartrate (USAN), is an opioid modulator of the morphinan family used as an opioid analgesic and opioid antagonist/antidote. It acts as an antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) and as an agonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR), and as a result, blocks the effects of stronger agents with greater intrinsic activity such as morphine whilst simultaneously producing analgesia.

Formebolone, also known as formyldienolone, as well as 2-formyl-11α-hydroxy-17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone, is an orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) described as an anticatabolic and anabolic drug that is or has been marketed in Spain and Italy. As an AAS, it shows some anabolic activity, though it is inferior to testosterone in terms of potency, but is said to have virtually no androgenic activity. Formebolone counteracts the catabolic effects of potent glucocorticoids like dexamethasone phosphate. A close analogue, roxibolone, shows similar antiglucocorticoid activity to formebolone but, in contrast, is devoid of activity as an AAS.

Stenbolone is an anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was never marketed. A C17β ester prodrug of stenbolone, stenbolone acetate, is used as an AAS for depot intramuscular injection under the brand names Anatrofin and Stenobolone.

Moxestrol, sold under the brand name Surestryl, is an estrogen medication which has been used in Europe for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and menstrual disorders. It is taken by mouth. In addition to its use as a medication, moxestrol has been used in scientific research as a radioligand of the estrogen receptor.

Chloral betaine, also known as cloral betaine (INN), is a sedative-hypnotic drug. It was introduced by Mead Johnson in the United States in 1963. It is a betaine complex with chloral hydrate, which acts as an extended-acting formulation of chloral hydrate which is then metabolized into trichloroethanol, which is responsible for most or all of its effects.

Cinnamedrine, also known as N-cinnamylephedrine, is a sympathomimetic drug with similar effects relative to those of ephedrine. It also has some local anesthetic activity. Cinnamedrine was previously used, in combination with analgesics, as an antispasmodic to treat dysmenorrhea in the over-the-counter drug Midol in the 1980s. There is a case report of the drug being abused as a psychostimulant.
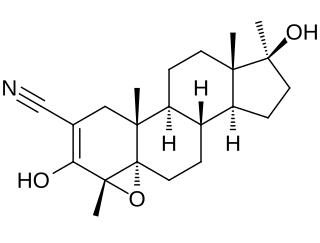
Epostane is an inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) that was developed as a contraceptive, abortifacient, and oxytocic drug but was never marketed. By inhibiting 3β-HSD, epostane blocks the biosynthesis of progesterone from pregnenolone, thereby functioning as an antiprogestogen and terminating pregnancy. The drug was trialed and in a study was found to be slightly more effective at inducing abortion relative to mifepristone.
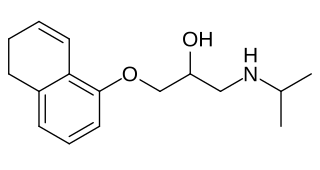
Idropranolol is a beta blocker that was never marketed.

Testosterone furoate, also referred to as testosterone furanate in some publications, is an androgen and anabolic steroid and a testosterone ester which is no longer marketed.

Algestone acetonide, also known as algestone 16α,17α-acetonide or 16α,17α-isopropylidenedioxyprogesterone, is a progestin which was never marketed. It is the acetonide cyclic ketal of algestone. Another progestin, algestone acetophenide, in contrast, has been marketed.

Clostebol acetate (BAN), also known as 4-chlorotestosterone 17β-acetate (4-CLTA) or as 4-chloroandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one 17β-acetate, is a synthetic, injected anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of testosterone that is marketed in Germany and Italy. It is an androgen ester – specifically, the C17β acetate ester of clostebol (4-chlorotestosterone) – and acts as a prodrug of clostebol in the body. Clostebol acetate is administered via intramuscular injection.

Androstenediol dipropionate, or 5-androstenediol 3β,17β-dipropionate, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-dipropionate, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid and an androgen ester – specifically, the dipropionate diester of 5-androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol) – which has been marketed in Europe, including in Spain, Italy, and Austria.

Endrisone (INN), or endrysone (USAN), is a synthetic, steroidal glucocorticoid which is or has been marketed in Italy by SIFI. It is used as a topical and ophthalmic anti-inflammatory drug in the treatment of skin and eye conditions, respectively.
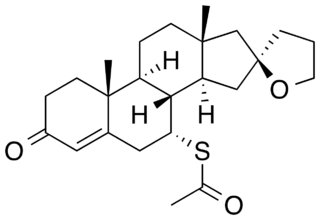
Spiroxasone is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed as a diuretic and antihypertensive agent but was never marketed. It was synthesized and assayed in 1963. The drug is 7α-acetylthiospirolactone with the ketone group removed from the C17α spirolactone ring. Similarly to other spirolactones like spironolactone, spiroxasone also possesses antiandrogen activity.

Dacuronium bromide is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent which was never marketed. It acts as a competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR).

Pirenperone (INN, USAN, BAN; developmental code names R-47456, R-50656) is a serotonin receptor antagonist described as an antipsychotic and tranquilizer which was never marketed. It is a relatively selective antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors and has been used in scientific research to study the serotonin system. In the 1980s, the drug was found to block the effects of the lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) in animals, and along with ketanserin, led to the elucidation of the 5-HT2A receptor as the biological mediator of the effects of serotonergic psychedelics.




















