
Hephaestus is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes. Hephaestus's Roman counterpart is Vulcan. In Greek mythology, Hephaestus was either the son of Zeus and Hera or he was Hera's parthenogenous child. He was cast off Mount Olympus by his mother Hera because of his lameness, the result of a congenital impairment; or in another account, by Zeus for protecting Hera from his advances.

Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first syllable of his Roman equivalent Jupiter.

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians.

In Greek mythology, Amalthea or Amaltheia is the most-frequently mentioned foster-mother of Zeus.

In Greek mythology, the Titans were the pre-Olympian gods. According to the Theogony of Hesiod, they were the twelve children of the primordial parents Uranus (Sky) and Gaia (Earth), with six male Titans—Oceanus, Coeus, Crius, Hyperion, Iapetus, and Cronus—and six female Titans, called the Titanides or Titanesses—Theia, Rhea, Themis, Mnemosyne, Phoebe, and Tethys. Cronus mated with his older sister Rhea, who then bore the first generation of Olympians: the six siblings Zeus, Hades, Poseidon, Hestia, Demeter, and Hera. Certain descendants of the Titans, such as Prometheus, Atlas, Helios, and Leto, are sometimes also called Titans.

In Greek mythology and later Roman mythology, the Cyclopes are giant one-eyed creatures. Three groups of Cyclopes can be distinguished. In Hesiod's Theogony, the Cyclopes are the three brothers Brontes, Steropes, and Arges, who made for Zeus his weapon the thunderbolt. In Homer's Odyssey, they are an uncivilized group of shepherds, the brethren of Polyphemus encountered by Odysseus. Cyclopes were also famous as the builders of the Cyclopean walls of Mycenae and Tiryns.
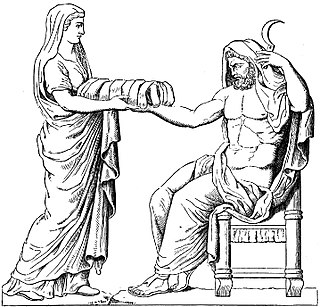
Rhea or Rheia is a mother goddess in ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Titan daughter of the earth goddess Gaia and the sky god Uranus, himself a son of Gaia. She is the older sister of Cronus, who was also her consort, and the mother of the five eldest Olympian gods and Hades, king of the underworld.

According to Greek mythology, the Korybantes or Corybantes were the armed and crested dancers who worshipped the Phrygian goddess Cybele with drumming and dancing. They are also called the Kurbantes in Phrygia.

In Greek mythology, Talos, also spelled Talus or Talon, was a giant automaton made of bronze to protect Europa in Crete from pirates and invaders. He circled the island's shores three times daily.

The Ancient Greek: δαίμων, pronounced daimon or daemon, originally referred to a lesser deity or guiding spirit such as the daimons of ancient Greek religion and mythology and of later Hellenistic religion and philosophy. The word is derived from Proto-Indo-European daimon "provider, divider ," from the root *da- "to divide". Daimons were possibly seen as the souls of men of the golden age acting as tutelary deities, according to entry δαίμων at Liddell & Scott. See also daimonic: a religious, philosophical, literary and psychological concept.
The Greek Heroic Age, in mythology, is the period between the coming of the Greeks to Thessaly and the Greek warriors' return from Troy. The poet Hesiod identified this mythological era as one of his five Ages of Man. The period spans roughly six generations; the heroes denoted by the term are superhuman, though not divine, and are celebrated in the literature of Homer and of others, such as Sophocles, Aeschylus and Euripides.

Works and Days is a didactic poem written by ancient Greek poet Hesiod around 700 BC. It is in dactylic hexameter and contains 828 lines. At its center, the Works and Days is a farmer's almanac in which Hesiod instructs his brother Perses in the agricultural arts.

In Greek mythology, Eros is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart is Cupid ('desire'). In the earliest account, he is a primordial god, while in later accounts he is described as one of the children of Aphrodite and Ares and, with some of his siblings, was one of the Erotes, a group of winged love gods.

In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, Cronus, Cronos, or Kronos was the leader and youngest of the first generation of Titans, the divine descendants of the primordial Gaia and Uranus. He overthrew his father and ruled during the mythological Golden Age, until he was overthrown by his own son Zeus and imprisoned in Tartarus. According to Plato, however, the deities Phorcys, Cronus, and Rhea were the eldest children of Oceanus and Tethys.

In Greek mythology, Gaia, also spelled Gaea, is the personification of Earth. Gaia is the ancestral mother—sometimes parthenogenic—of all life. She is the mother of Uranus (Sky), from whose sexual union she bore the Titans, the Cyclopes, and the Giants; as well as of Pontus (Sea), from whose union she bore the primordial sea gods. Her equivalent in the Roman pantheon was Terra.

In Greek mythology, Uranus, sometimes written Ouranos, is the personification of the sky and one of the Greek primordial deities. According to Hesiod, Uranus was the son and husband of Gaia (Earth), with whom he fathered the first generation of Titans. However, no cult addressed directly to Uranus survived into classical times, and Uranus does not appear among the usual themes of Greek painted pottery. Elemental Earth, Sky, and Styx might be joined, however, in solemn invocation in Homeric epic. Uranus is associated with the Roman god Caelus.

Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the origin and nature of the world; the lives and activities of deities, heroes, and mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself.

In Greek mythology, the Hecatoncheires, Hekatoncheires, or Hundred-Handers, also called the Centimanes were three monstrous giants, of enormous size and strength, each with fifty heads and one hundred arms. They were individually named Cottus, Briareus and Gyges. In the standard tradition they were the offspring of Uranus (Sky) and of Gaia (Earth), and helped Zeus and the Olympians to overthrow the Titans in the Titanomachy.

The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the Works and Days of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages, Gold being the first and the one during which the Golden Race of humanity lived. After the end of the first age was the Silver, then the Bronze, after this the Heroic age, with the fifth and current age being Iron.





















