The α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor is an ionotropic transmembrane receptor for glutamate (iGluR) that mediates fast synaptic transmission in the central nervous system (CNS). It has been traditionally classified as a non-NMDA-type receptor, along with the kainate receptor. Its name is derived from its ability to be activated by the artificial glutamate analog AMPA. The receptor was first named the "quisqualate receptor" by Watkins and colleagues after a naturally occurring agonist quisqualate and was only later given the label "AMPA receptor" after the selective agonist developed by Tage Honore and colleagues at the Royal Danish School of Pharmacy in Copenhagen. The GRIA2-encoded AMPA receptor ligand binding core was the first glutamate receptor ion channel domain to be crystallized.
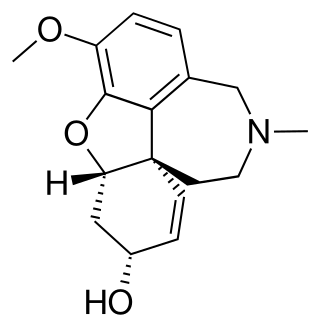
Galantamine is used for the treatment of cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and various other memory impairments. It is an alkaloid that has been isolated from the bulbs and flowers of Galanthus nivalis, Galanthus caucasicus, Galanthus woronowii, and some other members of the family Amaryllidaceae, such as Narcissus (daffodil), Leucojum aestivum (snowflake), and Lycoris including Lycoris radiata. It can also be produced synthetically.
Ampakines, also stylized as AMPAkines, are a subgroup of AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators with a benzamide or closely related chemical structure. They are also known as "CX compounds". Ampakines take their name from the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor with which the ampakines interact and act as positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of. Although all ampakines are AMPAR PAMs, not all AMPAR PAMs are ampakines.

CX717 is an ampakine compound created by Christopher Marrs and Gary Rogers in 1996 at Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It affects the neurotransmitter glutamate, with trials showing the drug improves cognitive functioning and memory.
Racetams are a class of drugs that share a pyrrolidone nucleus. Some, such as piracetam, aniracetam, oxiracetam, pramiracetam and phenylpiracetam are considered nootropics. Others such as levetiracetam, brivaracetam, and seletracetam are anticonvulsants.

CX-516 is an ampakine and nootropic that acts as an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator and had been undergoing development by a collaboration between Cortex, Shire, and Servier. It was studied as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease under the brand name Ampalex, and was also being examined as a treatment for ADHD.

Farampator is an ampakine drug. It was developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals, and licensed to Organon BioSciences for commercial development. Following the purchase of Organon by Schering-Plough in 2007, the development license to farampator was transferred. The development of farampator was eventually terminated, reportedly due to concerns about cardiac toxicity.
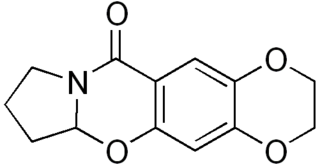
CX-614 is an ampakine drug developed by Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It has been investigated for its effect on AMPA receptors.

IDRA-21 is a positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptor and a benzothiadiazine derivative. It is a chiral molecule, with (+)-IDRA-21 being the active form.

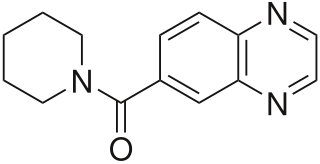
LY-503430 is an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator developed by Eli Lilly.
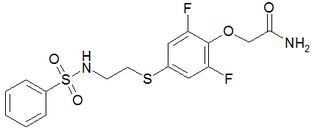
PEPA is a sulfonamide AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator, which is up to 100 times more potent than aniracetam in vitro. It produces memory-enhancing effects in rats when administered intravenously.

LY-404187 is an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator which was developed by Eli Lilly and Company. It is a member of the biarylpropylsulfonamide class of AMPA receptor potentiators.
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimulus. Some of them, like benzodiazepines, are drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind. Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands.
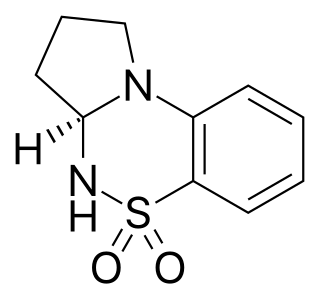
S-18986 is a positive allosteric modulator of the AMPA receptor related to cyclothiazide. It has nootropic and neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and induces both production of BDNF and AMPA-mediated release of noradrenaline and acetylcholine in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of the brain.

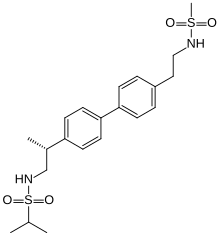
Pesampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. It was also under development for the treatment of age-related sensorineural hearing loss, but development for this indication was terminated due to insufficient effectiveness. As of July 2018, pesampator is in phase II clinical trials for cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia.

Tulrampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by RespireRx Pharmaceuticals and Servier for the treatment of major depressive disorder, Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and mild cognitive impairment. Tulrampator was in phase II clinical trial for depression, but failed to show superiority over placebo. There are also phase II clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease and phase I trials for dementia and mild cognitive impairment.

AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators are positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of the AMPA receptor (AMPR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor which mediates most fast synaptic neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
A GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator is a negative allosteric modulator (NAM), or inhibitor, of the GABAA receptor, a ligand-gated ion channel of the major inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They are closely related and similar to GABAA receptor antagonists. The effects of GABAA receptor NAMs are functionally the opposite of those of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) like the benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and ethanol (alcohol). Non-selective GABAA receptor NAMs can produce a variety of effects including convulsions, neurotoxicity, and anxiety, among others.

Mevidalen (developmental code name LY-3154207) is a dopaminergic drug which is under development for the treatment of Lewy body disease, including those with Parkinson's disease. It acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the dopamine D1 receptor. The drug is orally active and crosses the blood–brain barrier. It is a tetrahydroisoquinoline and is a close analogue of DETQ, another D1 receptor PAM. Mevidalen has been found to have wakefulness-promoting effects in sleep-deprived humans. Side effects of mevidalen have been reported to include increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, nervousness, fatigue, headaches, palpitations, and contact dermatitis, as well as falls in those with dementia. As of March 2022, mevidalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of Lewy body disease. Besides for movement disorders and dementia, D1 receptor PAMs like mevidalen might have value in the treatment of certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, excessive somnolence, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.