
Acetazolamide, sold under the trade name Diamox among others, is a medication used to treat glaucoma, epilepsy, acute mountain sickness, periodic paralysis, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, heart failure and to alkalinize urine. It may be used long term for the treatment of open angle glaucoma and short term for acute angle closure glaucoma until surgery can be carried out. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Acetazolamide is a first generation carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and it decreases the ocular fluid and osmolality in the eye to decrease intraocular pressure.

Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat edema due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It has had many trade names including Discoid, Frusemide, Lasix and Uremide. Furosemide may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken intravenously or orally. When given intravenously, furosemide typically takes effect within five minutes; when taken orally, it typically metabolizes within an hour.

Sulfonamide is a functional group that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides.
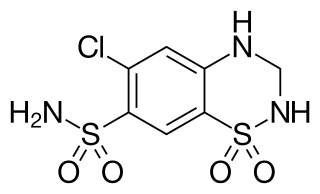
Hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Hydrodiuril among others, is a diuretic medication used to treat hypertension and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide medication which inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions from the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys, causing a natriuresis. This initially increases urine volume and lowers blood volume. It is believed to reduce peripheral vascular resistance.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Loop diuretics are diuretics that act on the Na-K-Cl cotransporter along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in nephrons of the kidneys. They are primarily used in medicine to treat hypertension and edema often due to congestive heart failure or chronic kidney disease. While thiazide diuretics are more effective in patients with normal kidney function, loop diuretics are more effective in patients with impaired kidney function.

Amiloride, sold under the trade name Midamor among others, is a medication typically used with other medications to treat high blood pressure or swelling due to heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver. Amiloride is classified as a potassium-sparing diuretic. Amiloride is often used together with another diuretic, such as a thiazide or loop diuretic. It is taken by mouth. Onset of action is about two hours and it lasts for about a day.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Long-term treatment with chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.

Potassium-sparing diuretics refers to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine. They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure. The steroidal aldosterone antagonists can also be used for treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism. Spironolactone, a steroidal aldosterone antagonist, is also used in management of female hirsutism and acne from PCOS or other causes.

Triamterene is a potassium-sparing diuretic often used in combination with thiazide diuretics for the treatment of high blood pressure or swelling. The combination with hydrochlorothiazide, is known as hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene.

Losartan, sold under the brand name Cozaar among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It is in the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) family of medication, and is considered protective of the kidneys. Besides hypertension, it is also used in diabetic kidney disease, heart failure, and left ventricular enlargement. It comes as a tablet that is taken by mouth. It may be used alone or in addition to other blood pressure medication. Up to six weeks may be required for the full effects to occur.

Tizanidine, sold under the brand name Zanaflex among others, is an alpha-2 (α2) adrenergic receptor agonist, similar to clonidine, that is used to treat muscle spasticity due to spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis, and spastic cerebral palsy. Effectiveness appears similar to baclofen or diazepam. It is taken by mouth.
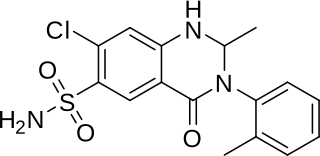
Metolazone is a thiazide-like diuretic marketed under the brand names Zytanix, Metoz, Zaroxolyn, and Mykrox. It is primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure. Metolazone indirectly decreases the amount of water reabsorbed into the bloodstream by the kidney, so that blood volume decreases and urine volume increases. This lowers blood pressure and prevents excess fluid accumulation in heart failure. Metolazone is sometimes used together with loop diuretics such as furosemide or bumetanide, but these highly effective combinations can lead to dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.
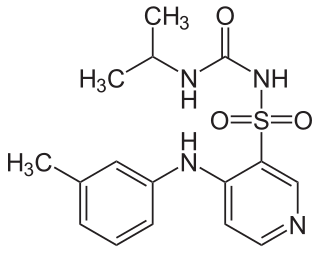
Torasemide, also known as torsemide, is a diuretic medication used to treat fluid overload due to heart failure, kidney disease, and liver disease. It is a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
The Na–K–Cl cotransporter (NKCC) is a transport protein that aids in the secondary active transport of sodium, potassium, and chloride into cells. In humans there are two isoforms of this membrane transport protein, NKCC1 and NKCC2, encoded by two different genes. Two isoforms of the NKCC1/Slc12a2 gene result from keeping or skipping exon 21 in the final gene product.

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.

In the United States the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA), has since the 1970s been patrolling the usage of illegal drugs and substances for student-athletes attending universities and colleges. In 1999, NCAA Drug Committee published a list containing substances banned for the usage to student-athletes. Year after year it is updated and given to those students participating in college sports. If any student is caught taking any of the substances, they are subjected to suspension or even banned from participating in NCAA sports and possibly attending the university.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.

Ototoxicity is defined as the toxic effect on the functioning of the inner ear, which may lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss (cochleotoxic) and balancing problems (vestibulotoxic). Drugs or pharmaceutical agents inducing ototoxicity are regarded as ototoxic medications.


















