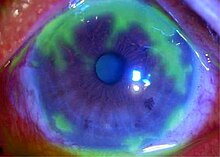
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired eyesight, photophobia, red eye and a 'gritty' sensation.

Aciclovir (ACV), also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection. It can be taken by mouth, applied as a cream, or injected.

A herpetic whitlow is a lesion (whitlow), typically on a finger or thumb, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). Occasionally infection occurs on the toes or on the nail cuticle. Herpes whitlow can be caused by infection by HSV-1 or HSV-2. HSV-1 whitlow is often contracted by health care workers that come in contact with the virus; it is most commonly contracted by dental workers and medical workers exposed to oral secretions. It is also often observed in thumb-sucking children with primary HSV-1 oral infection (autoinoculation) prior to seroconversion, and in adults aged 20 to 30 following contact with HSV-2-infected genitals.

Gingivostomatitis is a combination of gingivitis and stomatitis, or an inflammation of the oral mucosa and gingiva. Herpetic gingivostomatitis is often the initial presentation during the first ("primary") herpes simplex infection. It is of greater severity than herpes labialis which is often the subsequent presentations. Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis is the most common viral infection of the mouth.

A corneal ulcer, or ulcerative keratitis, is an inflammatory condition of the cornea involving loss of its outer layer. It is very common in dogs and is sometimes seen in cats. In veterinary medicine, the term corneal ulcer is a generic name for any condition involving the loss of the outer layer of the cornea, and as such is used to describe conditions with both inflammatory and traumatic causes.

Genital herpes is an infection by the herpes simplex virus (HSV) of the genitals. Most people either have no or mild symptoms and thus do not know they are infected. When symptoms do occur, they typically include small blisters that break open to form painful ulcers. Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, aching, or swollen lymph nodes, may also occur. Onset is typically around 4 days after exposure with symptoms lasting up to 4 weeks. Once infected further outbreaks may occur but are generally milder.

Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK) is a rare disease in which amoebae of the genus Acanthamoeba invade the clear portion of the front (cornea) of the eye. It affects roughly 100 people in the United States each year. Acanthamoeba are protozoa found nearly ubiquitously in soil and water and can cause infections of the skin, eyes, and central nervous system.

Idoxuridine is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug.
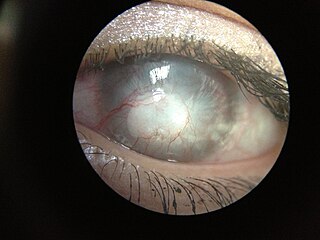
Corneal neovascularization (CNV) is the in-growth of new blood vessels from the pericorneal plexus into avascular corneal tissue as a result of oxygen deprivation. Maintaining avascularity of the corneal stroma is an important aspect of corneal pathophysiology as it is required for corneal transparency and optimal vision. A decrease in corneal transparency causes visual acuity deterioration. Corneal tissue is avascular in nature and the presence of vascularization, which can be deep or superficial, is always pathologically related.

Corneal ulcer, also called keratitis, is an inflammatory or, more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and in farming. In developing countries, children afflicted by vitamin A deficiency are at high risk for corneal ulcer and may become blind in both eyes persisting throughout life. In ophthalmology, a corneal ulcer usually refers to having an infection, while the term corneal abrasion refers more to a scratch injury.
Herpes gladiatorum is one of the most infectious of herpes-caused diseases, and is transmissible by skin-to-skin contact. The disease was first described in the 1960s in the New England Journal of Medicine. It is caused by contagious infection with human herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), which more commonly causes oral herpes. Another strain, HSV-2 usually causes genital herpes, although the strains are very similar and either can cause herpes in any location.

Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected.

A cold sore, also known as a fever blister and herpes labialis, is a type of infection by the herpes simplex virus that affects primarily the lip. Symptoms typically include a burning pain followed by small blisters or sores. The first attack may also be accompanied by fever, sore throat, and enlarged lymph nodes. The rash usually heals within ten days, but the virus remains dormant in the trigeminal ganglion. The virus may periodically reactivate to create another outbreak of sores in the mouth or lip.

Herpes esophagitis is a viral infection of the esophagus caused by Herpes simplex virus (HSV).
Deepak Shukla is an American molecular virologist with expertise in herpesviruses. He contributed to the discovery of HSV-1 entry receptors and establishing a link between the receptors and HSV-1 induced ocular diseases such as keratitis and retinitis. He has authored over 100 published papers and several book chapters on herpes viruses.
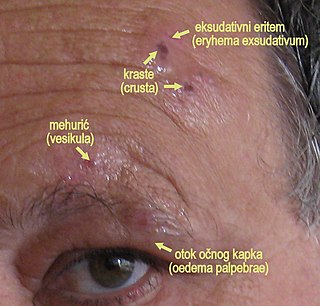
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO), also known as ophthalmic zoster, is shingles involving the eye or the surrounding area. Common signs include a rash of the forehead with swelling of the eyelid. There may also be eye pain and redness, inflammation of the conjunctiva, cornea or uvea, and sensitivity to light. Fever and tingling of the skin and allodynia near the eye may precede the rash. Complications may include visual impairment, increased pressure within the eye, chronic pain, and stroke.
Mooren's ulcer is a rare idiopathic ocular disorder that may lead to blindness due to progressive destruction of the peripheral cornea. Although the etiology of Mooren's ulcer is poorly understood, recent evidence suggests that the pathogenesis of this disease appears to be the result of an autoimmune process directed against molecules expressed in the corneal stroma.
Neurotrophic keratitis (NK) is a degenerative disease of the cornea caused by damage of the trigeminal nerve, which results in impairment of corneal sensitivity, spontaneous corneal epithelium breakdown, poor corneal healing and development of corneal ulceration, melting and perforation. This is because, in addition to the primary sensory role, the nerve also plays a role maintaining the integrity of the cornea by supplying it with trophic factors and regulating tissue metabolism.
Exposure keratopathy is medical condition affecting the cornea of eyes. It can lead to corneal ulceration and permanent loss of vision due to corneal opacity.
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis (PUK) is a group of destructive inflammatory diseases involving the peripheral cornea in human eyes. The symptoms of PUK include pain, redness of the eyeball, photophobia, and decreased vision accompanied by distinctive signs of crescent-shaped damage of the cornea. The causes of this disease are broad, ranging from injuries, contamination of contact lenses, to association with other systemic conditions. PUK is associated with different ocular and systemic diseases. Mooren's ulcer is a common form of PUK. The majority of PUK is mediated by local or systemic immunological processes, which can lead to inflammation and eventually tissue damage. Standard PUK diagnostic test involves reviewing the medical history and a completing physical examinations. Two major treatments are the use of medications such as corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive agents and surgical resection of the conjunctiva. The prognosis of PUK is unclear with one study providing potential complications. PUK is a rare condition with an estimated incidence of 3 per million annually.