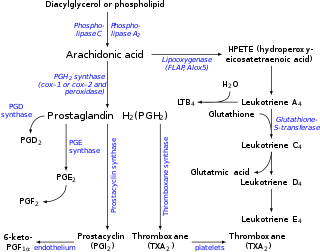
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, around 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a sub-category of oxylipins, i.e. oxidized fatty acids of diverse carbon units in length, and are distinguished from other oxylipins by their overwhelming importance as cell signaling molecules. Eicosanoids function in diverse physiological systems and pathological processes such as: mounting or inhibiting inflammation, allergy, fever and other immune responses; regulating the abortion of pregnancy and normal childbirth; contributing to the perception of pain; regulating cell growth; controlling blood pressure; and modulating the regional flow of blood to tissues. In performing these roles, eicosanoids most often act as autocrine signaling agents to impact their cells of origin or as paracrine signaling agents to impact cells in the proximity of their cells of origin. Eicosanoids may also act as endocrine agents to control the function of distant cells.

5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), also known as oxitriptan, is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor as well as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin.

4-Hydroxynonenal, or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal or 4-HNE or HNE,, is an α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal that is produced by lipid peroxidation in cells. 4-HNE is the primary α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal formed in this process. It is a colorless oil. It is found throughout animal tissues, and in higher quantities during oxidative stress due to the increase in the lipid peroxidation chain reaction, due to the increase in stress events. 4-HNE has been hypothesized to play a key role in cell signal transduction, in a variety of pathways from cell cycle events to cellular adhesion.

Synephrine, or, more specifically, p-synephrine, is an alkaloid, occurring naturally in some plants and animals, and also in approved drugs products as its m-substituted analog known as neo-synephrine. p-Synephrine and m-synephrine are known for their longer acting adrenergic effects compared to epinephrine and norepinephrine. This substance is present at very low concentrations in common foodstuffs such as orange juice and other orange products, both of the "sweet" and "bitter" variety. The preparations used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), also known as Zhi Shi (枳实), are the immature and dried whole oranges from Citrus aurantium. Extracts of the same material or purified synephrine are also marketed in the US, sometimes in combination with caffeine, as a weight-loss-promoting dietary supplement for oral consumption. While the traditional preparations have been in use for millennia as a component of TCM-formulas, synephrine itself is not an approved over the counter drug. As a pharmaceutical, m-synephrine (phenylephrine) is still used as a sympathomimetic, mostly by injection for the treatment of emergencies such as shock, and rarely orally for the treatment of bronchial problems associated with asthma and hay-fever.
Thailand's Psychotropic Substances Act is a law designed to regulate certain mind-altering drugs. According to the Office of the Narcotics Control Board, "The Act directly resulted from the Convention on Psychotropic Substances 1971 of which Thailand is a party." The Act divides psychotropic drugs into four Schedules. Offenses involving Schedule I and II drugs carry heavier penalties than those involving Schedule III and IV drugs. Note that this statute does not regulate most opioids, cocaine, or some amphetamines. The vast majority of narcotic painkillers, along with cocaine and most amphetamines are regulated under the Narcotics Act.

The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is the ester of caffeic acid and (−)-quinic acid, functioning as an intermediate in lignin biosynthesis. The term "chlorogenic acids" refers to a related polyphenol family of esters, including hydroxycinnamic acids with quinic acid.
The Reformatsky reaction is an organic reaction which condenses aldehydes or ketones with α-halo esters using metallic zinc to form β-hydroxy-esters:
Alpha hydroxy acids, or α-hydroxy acids, are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group substituent on the adjacent (alpha) carbon. Prominent examples are glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic acid and citric acid.
The Rubottom oxidation is a useful, high-yielding chemical reaction between silyl enol ethers and peroxyacids to give the corresponding α-hydroxy carbonyl product. The mechanism of the reaction was proposed in its original disclosure by A.G. Brook with further evidence later supplied by George M. Rubottom. After a Prilezhaev-type oxidation of the silyl enol ether with the peroxyacid to form the siloxy oxirane intermediate, acid-catalyzed ring-opening yields an oxocarbenium ion. This intermediate then participates in a 1,4-silyl migration to give an α-siloxy carbonyl derivative that can be readily converted to the α-hydroxy carbonyl compound in the presence of acid, base, or a fluoride source.

γ-Amino-β-hydroxybutyric acid (GABOB), also known as β-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (β-hydroxy-GABA), and sold under the brand name Gamibetal among others, is an anticonvulsant which is used for the treatment of epilepsy in Europe, Japan, and Mexico. It is a GABA analogue, or an analogue of the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and has been found to be an endogenous metabolite of GABA.
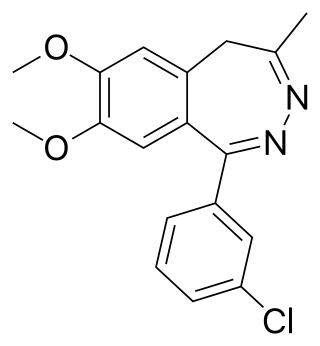
Girisopam is a drug which is a 2,3-benzodiazepine derivative, related to tofisopam and zometapine. It has selective anxiolytic action with no sedative, anticonvulsant or muscle relaxant effects.

Oxoeicosanoid receptor 1 (OXER1) also known as G-protein coupled receptor 170 (GPR170) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OXER1 gene located on human chromosome 2p21; it is the principal receptor for the 5-Hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid family of carboxy fatty acid metabolites derived from arachidonic acid. The receptor has also been termed hGPCR48, HGPCR48, and R527 but OXER1 is now its preferred designation. OXER1 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is structurally related to the hydroxy-carboxylic acid (HCA) family of G protein-coupled receptors whose three members are HCA1 (GPR81), HCA2, and HCA3 ; OXER1 has 30.3%, 30.7%, and 30.7% amino acid sequence identity with these GPCRs, respectively. It is also related to the recently defined receptor, GPR31, for the hydroxyl-carboxy fatty acid 12-HETE.

The γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) receptor (GHBR), originally identified as GPR172A, is an excitatory G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds the neurotransmitter and psychoactive drug γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). As solute carrier family 52 member 2 (SLC52A2), it is also a transporter for riboflavin.
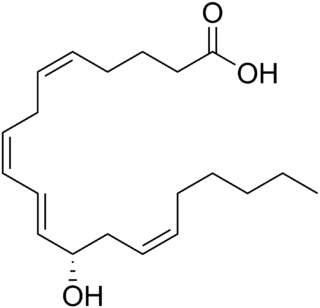
12-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) is a derivative of the 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid, containing a hydroxyl residue at carbon 12 and a 5Z,8Z,10E,14Z Cis–trans isomerism configuration (Z=cis, E=trans) in its four double bonds. It was first found as a product of arachidonic acid metabolism made by human and bovine platelets through their 12S-lipoxygenase (i.e. ALOX12) enzyme(s). However, the term 12-HETE is ambiguous in that it has been used to indicate not only the initially detected "S" stereoisomer, 12S-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid (12(S)-HETE or 12S-HETE), made by platelets, but also the later detected "R" stereoisomer, 12(R)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E,14Z-eicosatetraenoic acid (also termed 12(R)-HETE or 12R-HETE) made by other tissues through their 12R-lipoxygenase enzyme, ALOX12B. The two isomers, either directly or after being further metabolized, have been suggested to be involved in a variety of human physiological and pathological reactions. Unlike hormones which are secreted by cells, travel in the circulation to alter the behavior of distant cells, and thereby act as Endocrine signalling agents, these arachidonic acid metabolites act locally as Autocrine signalling and/or Paracrine signaling agents to regulate the behavior of their cells of origin or of nearby cells, respectively. In these roles, they may amplify or dampen, expand or contract cellular and tissue responses to disturbances.
A hydroxynaphthoquinone is any of several organic compounds that can be viewed as derivatives of a naphthoquinone through replacement of one hydrogen atom (H) by a hydroxyl group (-OH).

Oxendolone, sold under the brand names Prostetin and Roxenone, is an antiandrogen and progestin medication which is used in Japan in the treatment of enlarged prostate. However, this use is controversial due to concerns about its clinical efficacy. Oxendolone is not effective by mouth and must be given by injection into muscle.
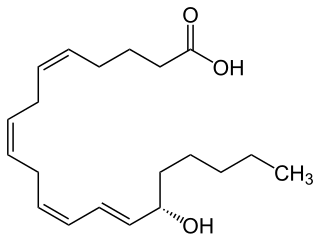
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (also termed 15-HETE, 15(S)-HETE, and 15S-HETE) is an eicosanoid, i.e. a metabolite of arachidonic acid. Various cell types metabolize arachidonic acid to 15(S)-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15(S)-HpETE). This initial hydroperoxide product is extremely short-lived in cells: if not otherwise metabolized, it is rapidly reduced to 15(S)-HETE. Both of these metabolites, depending on the cell type which forms them, can be further metabolized to 15-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid (15-oxo-ETE), 5S,15S-dihydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (5(S),15(S)-diHETE), 5-oxo-15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-15(S)-HETE, a subset of specialized pro-resolving mediators viz., the lipoxins, a class of pro-inflammatory mediators, the eoxins, and other products that have less well-defined activities and functions. Thus, 15(S)-HETE and 15(S)-HpETE, in addition to having intrinsic biological activities, are key precursors to numerous biologically active derivatives.

12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid (also termed 12-HHT, 12(S)-hydroxyheptadeca-5Z,8E,10E-trienoic acid, or 12(S)-HHTrE) is a 17 carbon metabolite of the 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid, arachidonic acid. It was first detected and structurally defined by P. Wlodawer, Bengt I. Samuelsson, and M. Hamberg as a product of arachidonic acid metabolism made by microsomes (i.e. endoplasmic reticulum) isolated from sheep seminal vesicle glands and by intact human platelets. 12-HHT is less ambiguously termed 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid to indicate the S stereoisomerism of its 12-hydroxyl residue and the Z, E, and E cis-trans isomerism of its three double bonds. The metabolite was for many years thought to be merely a biologically inactive byproduct of prostaglandin synthesis. More recent studies, however, have attached potentially important activity to it.
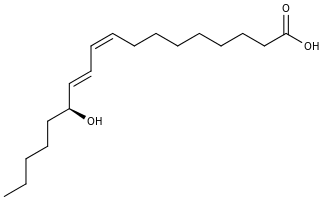
13-Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE) is the commonly used term for 13(S)-hydroxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid (13(S)-HODE). The production of 13(S)-HODE is often accompanied by the production of its stereoisomer, 13(R)-hydroxy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid (13(R)-HODE). The adjacent figure gives the structure for the (S) stereoisomer of 13-HODE. Two other naturally occurring 13-HODEs that may accompany the production of 13(S)-HODE are its cis-trans (i.e., 9E,11E) isomers viz., 13(S)-hydroxy-9E,11E-octadecadienoic acid (13(S)-EE-HODE) and 13(R)-hydroxy-9E,11E-octadecadienoic acid (13(R)-EE-HODE). Studies credit 13(S)-HODE with a range of clinically relevant bioactivities; recent studies have assigned activities to 13(R)-HODE that differ from those of 13(S)-HODE; and other studies have proposed that one or more of these HODEs mediate physiological and pathological responses, are markers of various human diseases, and/or contribute to the progression of certain diseases in humans. Since, however, many studies on the identification, quantification, and actions of 13(S)-HODE in cells and tissues have employed methods that did not distinguish between these isomers, 13-HODE is used here when the actual isomer studied is unclear.

















