
Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) are a class of drugs that selectively activate the androgen receptor in certain tissues like muscle and bone over other tissues like the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.

BMS-564,929 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is being developed by Bristol-Myers Squibb for treatment of the symptoms of age-related decline in androgen levels in men ("andropause"). These symptoms may include depression, loss of muscle mass and strength, reduction in libido and osteoporosis. Treatment with exogenous testosterone is effective in counteracting these symptoms but is associated with a range of side effects, the most serious of which is enlargement of the prostate gland, which can lead to benign prostatic hypertrophy and even prostate cancer. This means there is a clinical need for selective androgen receptor modulators, which produce anabolic effects in some tissues such as muscle and bone, but without stimulating androgen receptors in the prostate.

S-40503 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by the Japanese company Kaken Pharmaceuticals, which was developed for the treatment of osteoporosis. SARMs are a new class of drugs which produce tissue-specific anabolic effects in some tissues such as muscle and bone, but without stimulating androgen receptors in other tissues such as in the prostate gland, thus avoiding side effects such as benign prostatic hypertrophy which can occur following treatment with unselective androgens like testosterone or anabolic steroids.

LGD-2226 is an investigational selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), which is being developed for treatment of muscle wasting and osteoporosis.

Enobosarm, also formerly known as ostarine and by the developmental code names GTx-024, MK-2866, and S-22, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of androgen receptor-positive breast cancer. It was also under development for a variety of other indications, including treatment of cachexia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, muscle atrophy or sarcopenia, and stress urinary incontinence, but development for all other uses has been discontinued. Enobosarm was evaluated for the treatment of muscle wasting related to cancer in late-stage clinical trials, and the drug improved lean body mass in these trials, but it was not effective in improving muscle strength. As a result, enobosarm was not approved and development for this use was terminated. Enobosarm is taken by mouth.
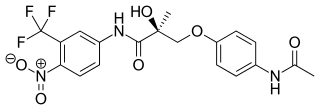
Andarine is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was developed by GTX, Inc for the treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting, osteoporosis, and benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH), using the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide as a lead compound. Development of andarine for all indications has been discontinued, in favor of the structurally related and improved compound enobosarm.

AC-262536 is a drug developed by Acadia Pharmaceuticals which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). Chemically it possesses endo-exo isomerism, with the endo form being the active form. It acts as a partial agonist for the androgen receptor with a Ki of 5nM, and no significant affinity for any other receptors tested. In animal studies it produced a maximal effect of around 66% of the anabolic action of testosterone, but only around 27% of its potency as an androgen.
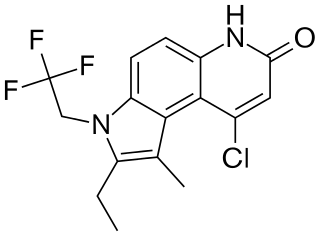
LGD-3303 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM), with good oral bioavailability. It is a selective agonist for the androgen receptor, producing functional selectivity with effective dissociation of anabolic and androgenic effects, acting as a partial agonist for androgenic effects, but a full agonist for anabolic effects. It has been investigated as a possible treatment for osteoporosis, and was shown in animal studies to enhance the effectiveness of a bisphosphonate drug.

Ligandrol, also known by the developmental code names VK5211 and LGD-4033, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of muscle atrophy in people with hip fracture. It was also under development for the treatment of cachexia, hypogonadism, and osteoporosis, but development for these indications was discontinued. Ligandrol has been reported to dose-dependently improve lean body mass and muscle strength in preliminary clinical trials, but is still being developed and has not been approved for medical use. The drug is taken by mouth.

Vosilasarm, also known by the development codes RAD140 and EP0062 and by the black-market name Testolone or Testalone, is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which is under development for the treatment of hormone-sensitive breast cancer. It is specifically under development for the treatment of androgen receptor-positive, estrogen receptor-negative, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Vosilasarm was also previously under development for the treatment of sarcopenia, osteoporosis, and weight loss due to cancer cachexia, but development for these indications was discontinued. The drug is taken by mouth.

Acetothiolutamide is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) derived from the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide that was described in 2002 and was one of the first SARMs to be discovered and developed. It is a high-affinity, selective ligand of the androgen receptor (AR), where it acts as a full agonist in vitro, and has in vitro potency comparable to that of testosterone. However, in vivo, acetothiolutamide displayed overall negligible androgenic effects, though significant anabolic effects were observed at high doses. In addition, notable antiandrogen effects were observed in castrated male rats treated with testosterone propionate. The discrepancy between the in vitro and in vivo actions of acetothiolutamide was determined to be related to rapid plasma clearance and extensive hepatic metabolism into a variety of metabolites with differing pharmacological activity, including AR partial agonism and antagonism. In accordance with its poor metabolic stability, acetothiolutamide is not orally bioavailable, and shows activity only via injected routes such as subcutaneous and intravenous.

LG121071 is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals that was first described in 1999 and was the first orally active nonsteroidal androgen to be discovered. It is a tricyclic quinolone derivative, structurally distinct from other nonsteroidal AR agonists like andarine and enobosarm (ostarine). The drug acts as a high-affinity full agonist of the androgen receptor (AR), with a potency and efficacy that is said to be equivalent to that of dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Unlike testosterone, but similarly to DHT, LG121071 and other nonsteroidal androgens cannot be potentiated by 5α-reductase in androgenic tissues, and for this reason, show tissue-selective androgenic effects. In accordance, they are said to possess full anabolic activity with reduced androgenic activity, similarly to anabolic-androgenic steroids.

TFM-4AS-1 is a dual selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) and 5α-reductase inhibitor. It is a potent and selective partial agonist (Emax = 55%) of the androgen receptor (IC50 = 30 nM) and inhibitor of 5α-reductase types I and II (IC50 = 2 and 3 nM, respectively). TFM-4AS-1 shows tissue-selective androgenic effects; it promotes the accumulation of bone and muscle mass and has reduced effects in reproductive tissues and sebaceous glands. In an animal study, TFM-4AS-1 stimulated sebaceous gland formation only 31% as much as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) at doses that were as anabolic or more so than DHT. In addition, TFM-4AS-1 only weakly promoted growth of the prostate gland and it partially antagonized the actions of DHT in the seminal vesicles and endogenous androgens in the prostate gland. Structurally, TFM-4AS-1 is a 4-azasteroid. A structurally related and more advanced version of TFM-4AS-1, MK-0773, was developed and pursued for potential pharmaceutical use.

LG-120907 is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) of the quinoline group which was developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals along with selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) like LG-121071 and was never marketed. The drug is a high-affinity antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR) with a Ki value of 26 nM and has been found to inhibit growth of the ventral prostate and seminal vesicles in male rats without increasing circulating levels of luteinizing hormone or testosterone. However, this tissue selectivity has not been assessed in humans. LG-120907 is orally active and shows greater oral potency than the arylpropionamide NSAA flutamide.

RU-59063 is a nonsteroidal androgen or selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was first described in 1994 and was never marketed. It was originally thought to be a potent antiandrogen, but subsequent research found that it actually possesses dose-dependent androgenic activity, albeit with lower efficacy than dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The drug is an N-substituted arylthiohydantoin and was derived from the first-generation nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) nilutamide. The second-generation NSAAs enzalutamide, RD-162, and apalutamide were derived from RU-59063.
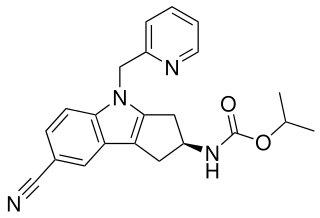
OPK-88004 is a non-steroidal indole derivative which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It has been investigated by OPKO Health for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and symptoms associated with benign prostate hyperplasia.

GSK2881078 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It was developed for the prevention of muscle wasting and sarcopenia in elderly people.

JNJ-28330835 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). In studies on rats it was found to enhance muscle growth and sexual behavior but with minimal effects on prostate gland size. A number of related compounds are known, though JNJ-28330835 has progressed furthest through development.
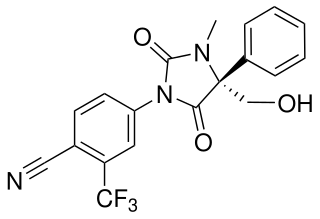
GLPG-0492 (DT-200) is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It has been investigated for the treatment of cachexia and muscular dystrophy.

ACP-105 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It has been investigated for the treatment of age-related cognitive decline.



















