Related Research Articles

Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for animals. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most notably beta-carotene. Vitamin A has multiple functions: it is essential for embryo development and growth, for maintenance of the immune system, and for vision, where it combines with the protein opsin to form rhodopsin – the light-absorbing molecule necessary for both low-light and color vision.

Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes, immune function and reproductive development. Dietary sources include fish, dairy products, and meat. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. As an ingredient in skin-care products, it is used to reduce wrinkles and other effects of skin aging.

In the field of molecular biology, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes. PPARs play essential roles in the regulation of cellular differentiation, development, and metabolism, and tumorigenesis of higher organisms.

Retinoic acid (used simplified here for all-trans-retinoic acid) is a metabolite of vitamin A1 (all-trans-retinol) that mediates the functions of vitamin A1 required for growth and development. All-trans-retinoic acid is required in chordate animals, which includes all higher animals from fish to humans. During early embryonic development, all-trans-retinoic acid generated in a specific region of the embryo helps determine position along the embryonic anterior/posterior axis by serving as an intercellular signaling molecule that guides development of the posterior portion of the embryo. It acts through Hox genes, which ultimately control anterior/posterior patterning in early developmental stages.
The thyroid hormone receptor (TR) is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding thyroid hormone. TRs act as transcription factors, ultimately affecting the regulation of gene transcription and translation. These receptors also have non-genomic effects that lead to second messenger activation, and corresponding cellular response.
The retinoic acid receptor (RAR) is a type of nuclear receptor which can also act as a ligand-activated transcription factor that is activated by both all-trans retinoic acid and 9-cis retinoic acid, retinoid active derivatives of Vitamin A. They are typically found within the nucleus. There are three retinoic acid receptors (RAR), RAR-alpha, RAR-beta, and RAR-gamma, encoded by the RARA, RARB, RARG genes, respectively. Within each RAR subtype there are various isoforms differing in their N-terminal region A. Multiple splice variants have been identified in human RARs: four for RARA, five for RARB, and two for RARG. As with other type II nuclear receptors, RAR heterodimerizes with RXR and in the absence of ligand, the RAR/RXR dimer binds to hormone response elements known as retinoic acid response elements (RAREs) complexed with corepressor protein. Binding of agonist ligands to RAR results in dissociation of corepressor and recruitment of coactivator protein that, in turn, promotes transcription of the downstream target gene into mRNA and eventually protein. In addition, the expression of RAR genes is under epigenetic regulation by promoter methylation. Both the length and magnitude of the retinoid response is dependent of the degradation of RARs and RXRs through the ubiquitin-proteasome. This degradation can lead to elongation of the DNA transcription through disruption of the initiation complex or to end the response to facilitate further transcriptional programs. Due to RAR/RXR heterodimers acting as subtrates to the non steroid hormone ligand retinoid they are extensively involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis.

The liver X receptor (LXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors and is closely related to nuclear receptors such as the PPARs, FXR and RXR. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are important regulators of cholesterol, fatty acid, and glucose homeostasis. LXRs were earlier classified as orphan nuclear receptors, however, upon discovery of endogenous oxysterols as ligands they were subsequently deorphanized.
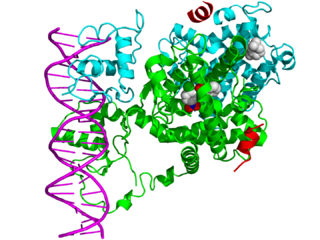
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism.
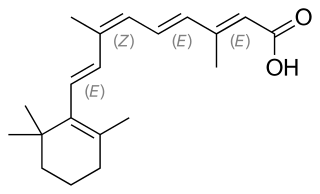
Alitretinoin, or 9-cis-retinoic acid, is a form of vitamin A. It is also used in medicine as an antineoplastic (anti-cancer) agent developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals. It is a first generation retinoid. Ligand gained Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for alitretinoin in February 1999.
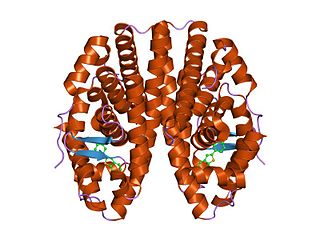
The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 also known as NCoA-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA2 gene. NCoA-2 is also frequently called glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2), or transcriptional mediators/intermediary factor 2 (TIF2).

Retinoid X receptor alpha (RXR-alpha), also known as NR2B1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRA gene.

Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RAR-α), also known as NR1B1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RARA gene.

Retinoid X receptor gamma (RXR-gamma), also known as NR2B3 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRG gene.

Retinoid X receptor beta (RXR-beta), also known as NR2B2 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRB gene.

Retinoic acid receptor beta (RAR-beta), also known as NR1B2 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RARB gene.

Retinoic acid receptor gamma (RAR-γ), also known as NR1B3 is a nuclear receptor encoded by the RARG gene. Adapalene selectively targets retinoic acid receptor beta and retinoic acid receptor gamma and its agonism of the gamma subtype is largely responsible for adapalene's observed effects.
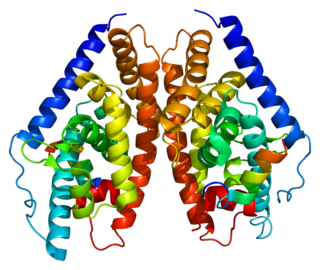
Liver X receptor beta (LXR-β) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. LXR-β is encoded by the NR1H2 gene.

Retinol binding protein 1, cellular, also known as RBP1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBP1 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) also known as transcriptional intermediary factor 1α (TIF1α) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRIM24 gene.
Dino Moras, born on 23 November 1944, is a French biochemist, research director at the CNRS and co-director of the Institute of Genetics and Molecular and Cellular Biology (IGBMC) in Illkirch-Graffenstaden until 2010.
References
- ↑ Germain P, Chambon P, Eichele G, Evans RM, Lazar MA, Leid M, De Lera AR, Lotan R, Mangelsdorf DJ, Gronemeyer H (2006). "International Union of Pharmacology. LXIII. Retinoid X receptors". Pharmacol Rev. 58 (4): 760–72. doi:10.1124/pr.58.4.7. PMID 17132853. S2CID 1476000.
- ↑ de Lera AR, Krezel W, Rühl R (2016). "An Endogenous Mammalian Retinoid X Receptor Ligand, At Last!". ChemMedChem. 11 (10): 1–12. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201600105. PMID 27151148. S2CID 269196.
- ↑ Allenby G, Bocquel MT, Saunders M, Kazmer S, Speck J, Rosenberger M, Lovey A, Kastner P, Grippo JF, Chambon P, Levin AA (1993). "Retinoic acid receptors and retinoid X receptors: interactions with endogenous retinoic acids". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90 (1): 30–4. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90...30A. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.30 . PMC 45593 . PMID 8380496.
- ↑ Rühl R, Krzyżosiak A, Niewiadomska-Cimicka A, Rochel N, Szeles L, Vaz B, Wietrzych-Schindler M, Álvarez S, Szklenar M, Nagy L, de Lera AR, Krężel W (2015). "9-cis-13,14-Dihydroretinoic Acid Is an Endogenous Retinoid Acting as RXR Ligand in Mice". PLOS Genetics. 11 (6): e1005213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005213 . PMC 4451509 . PMID 26030625.
- 1 2 Rühl R, Krężel W, de Lera AR (2018). "9-cis-13,14-Dihydroretinol, a new endogenous mammalian ligand of the retinood X receptor and the active ligand of a potential new vitamin category: vitamin A5". Nutr. Rev. 76 (12): 929–941. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuy057 . PMID 30358857.
- ↑ Plutzky J (April 2011). "The PPAR-RXR transcriptional complex in the vasculature: energy in the balance". Circ. Res. 108 (8): 1002–16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.226860 . PMID 21493923.