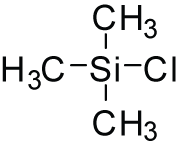In chemistry, a disulfide is a compound containing a R−S−S−R′ functional group or the S2−
2 anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drugs. This kind of conversion is in fact so common that a comprehensive overview is challenging. This article mainly deals with halogenation using elemental halogens. Halides are also commonly introduced using salts of the halides and halogen acids. Many specialized reagents exist for and introducing halogens into diverse substrates, e.g. thionyl chloride.

In organic chemistry, an acyl halide is a chemical compound derived from an oxoacid by replacing a hydroxyl group with a halide group.

Allyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCH2Cl. This colorless liquid is insoluble in water but soluble in common organic solvents. It is mainly converted to epichlorohydrin, used in the production of plastics. It is a chlorinated derivative of propylene. It is an alkylating agent, which makes it both useful and hazardous to handle.
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.

Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula AlCl3. It forms a hexahydrate with the formula [Al(H2O)6]Cl3, containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are colourless crystals, but samples are often contaminated with iron(III) chloride, giving them a yellow colour.

Acetyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

In chemistry, the term phosphonium describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Sulfuryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula SO2Cl2. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Sulfuryl chloride is not found in nature, as can be inferred from its rapid hydrolysis.
Geminal halide hydrolysis is an organic reaction. The reactants are geminal dihalides with a water molecule or a hydroxide ion. The reaction yields ketones from secondary halides or aldehydes from primary halides.
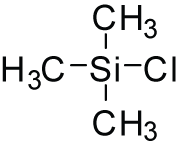
Trimethylsilyl chloride, also known as chlorotrimethylsilane is an organosilicon compound, with the formula (CH3)3SiCl, often abbreviated Me3SiCl or TMSCl. It is a colourless volatile liquid that is stable in the absence of water. It is widely used in organic chemistry.

The Finkelstein reaction, named after the German chemist Hans Finkelstein, is an SN2 reaction that involves the exchange of one halogen atom for another. It is an equilibrium reaction, but the reaction can be driven to completion by exploiting the differential solubility of halide salts, or by using a large excess of the halide salt.

Thiophosgene is a red liquid with the formula CSCl2. It is a molecule with trigonal planar geometry. There are two reactive C–Cl bonds that allow it to be used in diverse organic syntheses.
In chemistry, dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction which removes a hydrogen halide from a substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications.
In inorganic chemistry, sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X, where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.

Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PSCl3. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.

Sulfinyl halide have the general formula R−S(O)−X, where X is a halogen. They are intermediate in oxidation level between sulfenyl halides, R−S−X, and sulfonyl halides, R−SO2−X. The best known examples are sulfinyl chlorides, thermolabile, moisture-sensitive compounds, which are useful intermediates for preparation of other sufinyl derivatives such as sulfinamides, sulfinates, sulfoxides, and thiosulfinates. Unlike the sulfur atom in sulfonyl halides and sulfenyl halides, the sulfur atom in sulfinyl halides is chiral, as shown for methanesulfinyl chloride.

Imidoyl chlorides are organic compounds that contain the functional group RC(NR')Cl. A double bond exist between the R'N and the carbon centre. These compounds are analogues of acyl chloride. Imidoyl chlorides tend to be highly reactive and are more commonly found as intermediates in a wide variety of synthetic procedures. Such procedures include Gattermann aldehyde synthesis, Houben-Hoesch ketone synthesis, and the Beckmann rearrangement. Their chemistry is related to that of enamines and their tautomers when the α hydrogen is next to the C=N bond. Many chlorinated N-heterocycles are formally imidoyl chlorides, e.g. 2-chloropyridine, 2, 4, and 6-chloropyrimidines.