
In organic chemistry, isothiocyanate is a functional group as found in compounds with the formula R−N=C=S. Isothiocyanates are the more common isomers of thiocyanates, which have the formula R−S−C≡N.

In organic chemistry, isothiocyanate is a functional group as found in compounds with the formula R−N=C=S. Isothiocyanates are the more common isomers of thiocyanates, which have the formula R−S−C≡N.
Many isothiocyanates from plants are produced by enzymatic conversion of metabolites called glucosinolates. A prominent natural isothiocyanate is allyl isothiocyanate, also known as mustard oils.
Cruciferous vegetables, such as bok choy, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, and others, are rich sources of glucosinolate precursors of isothiocyanates. [1]
The N=C and C=S distances are 117 and 158 pm. [2] By contrast, in methyl thiocyanate, N≡C and C−S distances are 116 and 176 pm.
Typical bond angles for C−N=C in aryl isothiocyanates are near 165°. Again, the thiocyanate isomers are quite different with C−S−C angle near 100°. [3] In both isomers the SCN angle approaches 180°.
Allyl thiocyanate isomerizes to the isothiocyanate: [4]
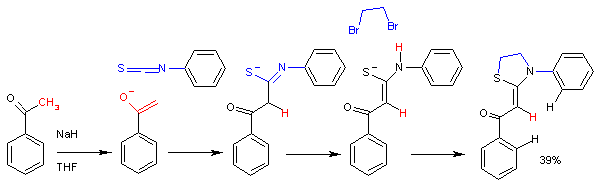
Isothiocyanates can be prepared by degradation of dithiocarbamate salts, e.g. induced with lead nitrate. [5] A related method is tosyl chloride-mediated decomposition of dithiocarbamate salts. [6]

Isothiocyanates may also be accessed by the fragmentation reactions of 1,4,2-oxathiazoles. [7] This methodology has been applied to a polymer-supported synthesis of isothiocyanates. [8]
Isothiocyanates are weak electrophiles, susceptible to hydrolysis. In general, nucleophiles attack at carbon:
Isothiocyanates occur widely in nature and are of interest in food science and medical research. [1] Vegetable foods with characteristic flavors due to isothiocyanates include bok choy, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, kale, wasabi, horseradish, mustard, radish, Brussels sprouts, watercress, papaya seeds, nasturtiums, and capers. [1] These species generate isothiocyanates in different proportions, and so have different, but recognizably related, flavors. They are all members of the order Brassicales, which is characterized by the production of glucosinolates, and of the enzyme myrosinase, which acts on glucosinolates to release isothiocyanates. [1]
Phenyl isothiocyanate, is used for amino acid sequencing in the Edman degradation.
Isothiocyanate and its linkage isomer thiocyanate are ligands in coordination chemistry. Thiocyanate is a more common ligand.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
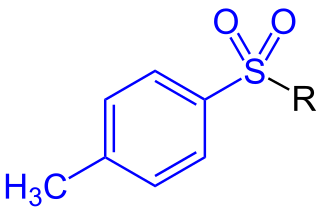
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula −SO2−C6H4−CH3. It consists of a tolyl group, −C6H4−CH3, joined to a sulfonyl group, −SO2−, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, CH3C6H4SO2OH (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.

In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−HC=CH2. It consists of a methylene bridge attached to a vinyl group. The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, Allium sativum. In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "Schwefelallyl". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to H2C=CH−CH2, some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride.
Cyclopropene is an organic compound with the formula C3H4. It is the simplest cycloalkene. Because the ring is highly strained, cyclopropene is difficult to prepare and highly reactive. This colorless gas has been the subject for many fundamental studies of bonding and reactivity. It does not occur naturally, but derivatives are known in some fatty acids. Derivatives of cyclopropene are used commercially to control ripening of some fruit.

Allyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCH2Cl. This colorless liquid is insoluble in water but soluble in common organic solvents. It is mainly converted to epichlorohydrin, used in the production of plastics. It is a chlorinated derivative of propylene. It is an alkylating agent, which makes it both useful and hazardous to handle.
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resultant aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and pharmaceuticals. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.

Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) is a naturally occurring unsaturated isothiocyanate. The colorless oil is responsible for the pungent taste of Cruciferous vegetables such as mustard, radish, horseradish, and wasabi. This pungency and the lachrymatory effect of AITC are mediated through the TRPA1 and TRPV1 ion channels. It is slightly soluble in water, but more soluble in most organic solvents.
In chemistry, linkage isomerism or ambidentate isomerism is a form of isomerism in which certain coordination compounds have the same composition but differ in their metal atom's connectivity to a ligand.

Sulforaphane is a compound within the isothiocyanate group of organosulfur compounds. It is produced when the enzyme myrosinase transforms glucoraphanin, a glucosinolate, into sulforaphane upon damage to the plant, which allows the two compounds to mix and react.

In organic chemistry, a sulfoxide, also called a sulphoxide, is an organosulfur compound containing a sulfinyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.

Glucosinolates are natural components of many pungent plants such as mustard, cabbage, and horseradish. The pungency of those plants is due to mustard oils produced from glucosinolates when the plant material is chewed, cut, or otherwise damaged. These natural chemicals most likely contribute to plant defence against pests and diseases, and impart a characteristic bitter flavor property to cruciferous vegetables.
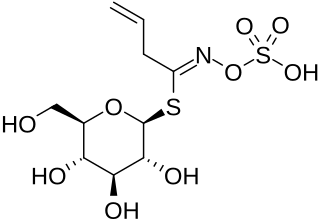
Sinigrin or allyl glucosinolate is a glucosinolate that belongs to the family of glucosides found in some plants of the family Brassicaceae such as Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and the seeds of black mustard. Whenever sinigrin-containing plant tissue is crushed or otherwise damaged, the enzyme myrosinase degrades sinigrin to a mustard oil, which is responsible for the pungent taste of mustard and horseradish. Seeds of white mustard, Sinapis alba, give a less pungent mustard because this species contains a different glucosinolate, sinalbin.

Methyl isothiocyanate is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3N=C=S. This low melting colorless solid is a powerful lachrymator. As a precursor to a variety of valuable bioactive compounds, it is the most important organic isothiocyanate in industry.

Myrosinase is a family of enzymes involved in plant defense against herbivores, specifically the mustard oil bomb. The three-dimensional structure has been elucidated and is available in the PDB.

Phenyl isothiocyanate (PITC) is a reagent used in reversed phase HPLC. PITC is less sensitive than o-phthaldehyde (OPA) and cannot be fully automated. PITC can be used for analysing secondary amines, unlike OPA. It is also known as Edman's reagent and is used in Edman degradation.

Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. The simplest member of the organic thiocyanates, it is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).

Allyl cyanide is an organic compound with the formula CH2CHCH2CN. Like other small alkyl nitriles, allyl cyanide is colorless and soluble in organic solvents. Allyl cyanide occurs naturally as an antifeedant and is used as a cross-linking agent in some polymers.
In organic chemistry, the oxy-Cope rearrangement is a chemical reaction. It involves reorganization of the skeleton of certain unsaturated alcohols. It is a variation of the Cope rearrangement in which 1,5-dien-3-ols are converted to unsaturated carbonyl compounds by a mechanism typical for such a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement.
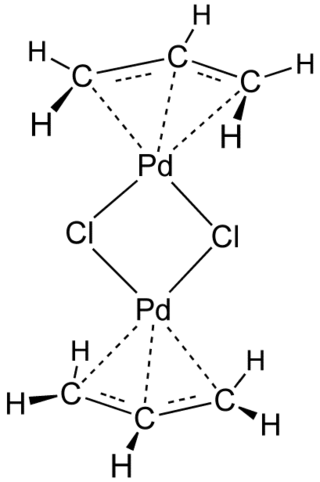
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures.

Organic thiocyanates are organic compounds containing the functional group RSCN. the organic group is attached to sulfur: R−S−C≡N has a S–C single bond and a C≡N triple bond.