
γ-Aminobutyric acid, or GABA, is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.

The GABA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. There are two classes of GABA receptors: GABAA and GABAB. GABAA receptors are ligand-gated ion channels ; whereas GABAB receptors are G protein-coupled receptors, also called metabotropic receptors.

Aniracetam, also known as N-anisoyl-2-pyrrolidinone, is a racetam which is sold in Europe as a prescription drug. It is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States as a prescription medication or dietary supplement. Despite the FDA's lack of approval, the drug is readily available over-the-counter in the US as a dietary supplement.
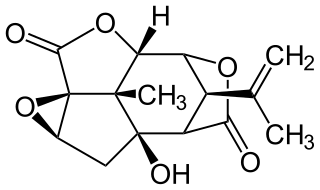
Picrotoxin, also known as cocculin, is a poisonous crystalline plant compound. It was first isolated by the French pharmacist and chemist Pierre François Guillaume Boullay (1777–1869) in 1812. The name "picrotoxin" is a combination of the Greek words "picros" (bitter) and "toxicon" (poison). A mixture of two different compounds, picrotoxin occurs naturally in the fruit of the Anamirta cocculus plant, although it can also be synthesized chemically.

The GABAA receptor (GABAAR) is an ionotropic receptor and ligand-gated ion channel. Its endogenous ligand is γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Upon opening, the GABAA receptor on the postsynaptic cell is selectively permeable to chloride ions (Cl−) and, to a lesser extent, bicarbonate ions (HCO3−). Depending on the membrane potential and the ionic concentration difference, this can result in ionic fluxes across the pore. If the membrane potential is higher than the equilibrium potential (also known as the reversal potential) for chloride ions, when the receptor is activated Cl− will flow into the cell. This causes an inhibitory effect on neurotransmission by diminishing the chance of a successful action potential occurring at the postsynaptic cell. The reversal potential of the GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) in normal solution is −70 mV, contrasting the GABAB IPSP (-100 mV).
The GABAA-rho receptor is a subclass of GABAA receptors composed entirely of rho (ρ) subunits. GABAA receptors including those of the ρ-subclass are ligand-gated ion channels responsible for mediating the effects of gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. The GABAA-ρ receptor, like other GABAA receptors, is expressed in many areas of the brain, but in contrast to other GABAA receptors, the GABAA-ρ receptor has especially high expression in the retina.

Gabazine (SR-95531) is a drug that acts as an antagonist at GABAA receptors. It is used in scientific research and has no role in medicine, as it would be expected to produce convulsions if used in humans.

Hexobarbital or hexobarbitone, sold both in acid and sodium salt forms as Citopan, Evipan, and Tobinal, is a barbiturate derivative having hypnotic and sedative effects. It was used in the 1940s and 1950s as an agent for inducing anesthesia for surgery, as well as a rapid-acting, short-lasting hypnotic for general use, and has a relatively fast onset of effects and short duration of action. It was also used to murder women prisoners at Ravensbrück concentration camp. Modern barbiturates have largely supplanted the use of hexobarbital as an anesthetic, as they allow for better control of the depth of anesthesia. Hexobarbital is still used in some scientific research.

NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induce is referred to as dissociative anesthesia.

Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum depression. It is used by injection into a vein over a 60-hour period under medical supervision.
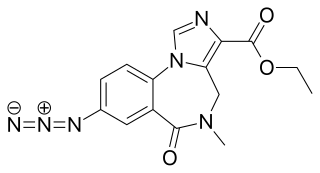
Ro15-4513(IUPAC: Ethyl-8-azido-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo-1,4-benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate) is a weak partial inverse agonist of the benzodiazepine class of drugs, developed by Hoffmann–La Roche in the 1980s. It acts as a inverse agonist, and can therefore be an antidote to the acute impairment caused by alcohols, including ethanol, isopropanol, tert-butyl alcohol, tert-amyl alcohol, 3-methyl-3-pentanol, methylpentynol and ethchlorvynol.

Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA3 gene.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-2 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the GABRA2 gene.

A channel blocker is the biological mechanism in which a particular molecule is used to prevent the opening of ion channels in order to produce a physiological response in a cell. Channel blocking is conducted by different types of molecules, such as cations, anions, amino acids, and other chemicals. These blockers act as ion channel antagonists, preventing the response that is normally provided by the opening of the channel.
A convulsant is a drug which induces convulsions and/or epileptic seizures, the opposite of an anticonvulsant. These drugs generally act as stimulants at low doses, but are not used for this purpose due to the risk of convulsions and consequent excitotoxicity. Most convulsants are antagonists at either the GABAA or glycine receptors, or ionotropic glutamate receptor agonists. Many other drugs may cause convulsions as a side effect at high doses but only drugs whose primary action is to cause convulsions are known as convulsants. Nerve agents such as sarin, which were developed as chemical weapons, produce convulsions as a major part of their toxidrome, but also produce a number of other effects in the body and are usually classified separately. Dieldrin which was developed as an insecticide blocks chloride influx into the neurons causing hyperexcitability of the CNS and convulsions. The Irwin observation test and other studies that record clinical signs are used to test the potential for a drug to induce convulsions. Camphor, and other terpenes given to children with colds can act as convulsants in children who have had febrile seizures.

In pharmacology, GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators are positive allosteric modulator (PAM) molecules that increase the activity of the GABAA receptor protein in the vertebrate central nervous system.
A channel modulator, or ion channel modulator, is a type of drug which modulates ion channels. They include channel blockers and channel openers.

A chloride channel opener is a type of drug which facilitates ion transmission through chloride channels.
A chloride channel blocker is a type of drug which inhibits the transmission of ions (Cl−) through chloride channels.
Ionotropic GABA receptors (iGABARs) are ligand-gated ion channel of the GABA receptors class which are activated by gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and include:















