General anaesthetics are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awareness to painful stimuli, sufficient to facilitate surgical applications in clinical and veterinary practice. General anaesthetics do not act as analgesics and should also not be confused with sedatives. General anaesthetics are a structurally diverse group of compounds whose mechanisms encompasses multiple biological targets involved in the control of neuronal pathways. The precise workings are the subject of some debate and ongoing research.

Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. A person under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.

Halothane, sold under the brand name Fluothane among others, is a general anaesthetic. It can be used to induce or maintain anaesthesia. One of its benefits is that it does not increase the production of saliva, which can be particularly useful in those who are difficult to intubate. It is given by inhalation.

A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways, paralysis also can be achieved.

Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is most commonly used in dental procedures to numb the area around a tooth and is also used to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, in some regions, procaine is referred to generically as novocaine. It acts mainly as a sodium channel blocker. Today it is used therapeutically in some countries due to its sympatholytic, anti-inflammatory, perfusion-enhancing, and mood-enhancing effects.

Sevoflurane is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflurane, it is the volatile anesthetic with the fastest onset. While its offset may be faster than agents other than desflurane in a few circumstances, its offset is more often similar to that of the much older agent isoflurane. While sevoflurane is only half as soluble as isoflurane in blood, the tissue blood partition coefficients of isoflurane and sevoflurane are quite similar. For example, in the muscle group: isoflurane 2.62 vs. sevoflurane 2.57. In the fat group: isoflurane 52 vs. sevoflurane 50. As a result, the longer the case, the more similar will be the emergence times for sevoflurane and isoflurane.

An anesthetic or anaesthetic is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.

Desflurane is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (R) and (S) optical isomers (enantiomers). Together with sevoflurane, it is gradually replacing isoflurane for human use, except in economically undeveloped areas, where its high cost precludes its use. It has the most rapid onset and offset of the volatile anesthetic drugs used for general anesthesia due to its low solubility in blood.
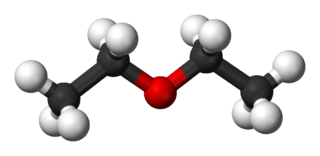
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound in the ether class with the formula (C
2H
5)
2O, sometimes abbreviated as Et
2O. It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling, extremely flammable liquid. It is commonly used as a solvent in laboratories and as a starting fluid for some engines. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic, until non-flammable drugs were developed, such as halothane. It has been used as a recreational drug to cause intoxication.

An inhalational anesthetic is a chemical compound possessing general anesthetic properties that can be delivered via inhalation. They are administered through a face mask, laryngeal mask airway or tracheal tube connected to an anesthetic vaporiser and an anesthetic delivery system. Agents of significant contemporary clinical interest include volatile anesthetic agents such as isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane, as well as certain anesthetic gases such as nitrous oxide and xenon.
A topical anesthetic is a local anesthetic that is used to numb the surface of a body part. They can be used to numb any area of the skin as well as the front of the eyeball, the inside of the nose, ear or throat, the anus and the genital area. Topical anesthetics are available in creams, ointments, aerosols, sprays, lotions, and jellies. Examples include benzocaine, butamben, dibucaine, lidocaine, oxybuprocaine, pramoxine, proxymetacaine (proparacaine), and tetracaine.

Articaine is a dental amide-type local anesthetic. It is the most widely used local anesthetic in a number of European countries and is available in many countries. It is the only local anaesthetic to contain a thiophene ring, meaning it can be described as 'thiophenic'; this conveys lipid solubility.
Alfaxolone/alfadolone (brand names Althesin, Saffan is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic agent. It was withdrawn from the market due to severe drug reactions. It is composed of a 3:1 mixture of alfaxalone and alfadolone, two neurosteroids.

An anesthetic technician is an allied healthcare worker who performs a patient care role predominantly assisting with the administration and monitoring of anesthesia and has an extensive knowledge of anesthesia techniques, instruments, supplies and technology.

Minaxolone (CCI-12923) is a neuroactive steroid which was developed as a general anesthetic but was withdrawn before registration due to toxicity seen with long-term administration in rats, and hence was never marketed. It is a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor, as well as, less potently, a positive allosteric modulator of the glycine receptor.

Alfaxalone, also known as alphaxalone or alphaxolone and sold under the brand name Alfaxan, is a neuroactive steroid and general anesthetic which is used currently in veterinary practice as an induction agent for anesthesia and as an injectable anesthetic. Though it is more expensive than other induction agents, it often preferred due to the lack of depressive effects on the cardiovascular system. The most common side effect seen in current veterinary practice is respiratory depression when Alfaxan is administered concurrently with other sedative and anesthetic drugs; when premedications aren't given, veterinary patients also become agitated and hypersensitive when waking up.
Divinyl ether is the organic compound with the formula O(CH=CH2)2. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that has mainly been of interest as an inhalation anesthetic. It is prepared by treating bis(chloroethyl) ether with base.
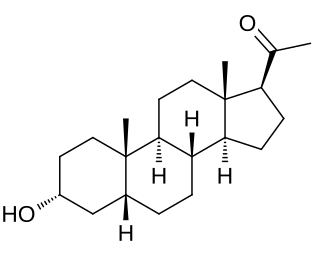
Pregnanolone, also known as eltanolone, is an endogenous inhibitory neurosteroid which is produced in the body from progesterone. It is closely related to allopregnanolone, which has similar properties.

Hydroxydione, as hydroxydione sodium succinate, also known as 21-Hydroxy-5β-pregnane-3,20-dione, is a neuroactive steroid which was formerly used as a general anesthetic, but was discontinued due to incidence of thrombophlebitis in patients. It was introduced in 1957, and was the first neuroactive steroid general anesthetic to be introduced for clinical use, an event which was shortly preceded by the observation in 1954 of the sedative properties of progesterone in mice.
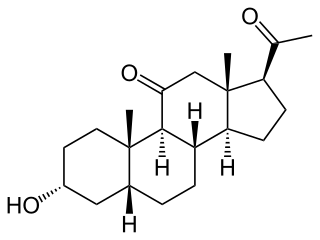
Renanolone (INN), or 11-ketopregnanolone, also known as 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-dione, is a synthetic neuroactive steroid which is described as a general anesthetic but was never introduced for clinical use. Its isomers, alfaxolone and alfadolone, are also general anesthetics, and are known to act as positive allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor, a property which is likely the case for renanolone as well.
















