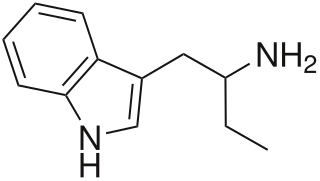
α-Ethyltryptamine, also known as etryptamine, is a psychedelic, stimulant, and entactogenic drug of the tryptamine class. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s.
United States Adopted Names are unique nonproprietary names assigned to pharmaceuticals marketed in the United States. Each name is assigned by the USAN Council, which is co-sponsored by the American Medical Association (AMA), the United States Pharmacopeial Convention (USP), and the American Pharmacists Association (APhA).

Ritanserin is a serotonin receptor antagonist which was never marketed for clinical use but has been used in scientific research.
The beta-2 adrenergic receptor, also known as ADRB2, is a cell membrane-spanning beta-adrenergic receptor that binds epinephrine (adrenaline), a hormone and neurotransmitter whose signaling, via adenylate cyclase stimulation through trimeric Gs proteins, increased cAMP, and downstream L-type calcium channel interaction, mediates physiologic responses such as smooth muscle relaxation and bronchodilation.

Nalfurafine is an antipruritic that is marketed in Japan for the treatment of uremic pruritus in individuals with chronic kidney disease undergoing hemodialysis. It acts as a potent, selective, centrally-penetrant κ-opioid receptor (KOR) agonist, and is the first and currently the only selective KOR agonist to have been approved for clinical use. It has also been dubiously referred to as the "first non-narcotic opioid drug" in history.

Procaterol is an intermediate-acting β2 adrenoreceptor agonist used for the treatment of asthma. It has never been filed for FDA evaluation in the United States, where it is not marketed. The drug is readily oxidized in the presence of moisture and air, making it unsuitable for therapeutic use by inhalation. Pharmaceutical company Parke-Davis/Warner-Lambert researched a stabilizer to prevent oxidation, but an effective one was never developed.

Melengestrol acetate (MLGA), sold under the brand names Heifermax and MGA among others, is a progestin medication which is used in animal reproduction. It is not approved for use in humans, and is instead used as an implantable contraceptive for captive animals in zoos and other refuges, and is also used as a feed additive to promote growth in cattle, a purpose it is licensed for in the United States and Canada.

Nalmexone (INN), or nalmexone hydrochloride (USAN), is a semisynthetic, opioid partial agonist or mixed agonist-antagonist with both analgesic and narcotic antagonist properties that was never marketed. In clinical studies it was found to have comparable analgesic efficacy to morphine, though with several-fold reduced potency. In addition, nalmexone's side effects, the most common of which were sleepiness and sweating, were reported to be similar to those of morphine, albeit with a noticeably higher degree of incidence.

Drug nomenclature is the systematic naming of drugs, especially pharmaceutical drugs. In the majority of circumstances, drugs have 3 types of names: chemical names, the most important of which is the IUPAC name; generic or nonproprietary names, the most important of which are the International Nonproprietary Names (INNs); and trade names, which are brand names. Generic names for drugs are nowadays constructed out of affixes and stems that classify the drugs into different categories and also separate drugs within categories. A marketed drug might also have a company code or compound code.

Tofogliflozin is an experimental drug for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and is being developed by Chugai Pharma in collaboration with Kowa and Sanofi. It is an inhibitor of subtype 2 sodium-glucose transport protein (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. As of September 2012, the drug is in Phase III clinical trials.
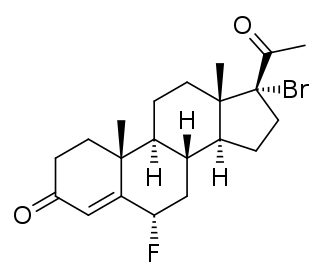
Haloprogesterone, sold under the brand name Prohalone, is a progestin medication which was previously marketed by Ayerst but is now no longer available.

Tigestol, also known as 17α-ethynylestr-5(10)-en-17β-ol, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group that was developed by Organon in the 1960s but was never marketed. It is an isomer of the related 19-nortestosterone derivative progestins lynestrenol and cingestol.

Taleranol, or teranol, also known as β-zearalanol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in Fusarium spp which was never marketed. It is the β epimer of zeranol (α-zearalanol) and is a major metabolite of zeranol but with less biological activity.

Stercuronium iodide is an aminosteroid neuromuscular blocking agent which was never marketed. It acts as a competitive antagonist of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), and is also reported to be an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.













