Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly.

Diabetic coma is a life-threatening but reversible form of coma found in people with diabetes mellitus.

Glimepiride is an antidiabetic medication within the sulfonylurea class, primarily prescribed for the management of type 2 diabetes. It is regarded as a second-line option compared to metformin, due to metformin's well-established safety and efficacy. Use of glimepiride is recommended in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth, reaching a peak effect within three hours and lasting for about a day.
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by decreasing the glucose level in the blood. With the exception of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists, and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of hypoglycemic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of diabetes, age, and situation of the person, as well as other factors.

The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia, is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Atenolol, however, does not seem to improve mortality in those with high blood pressure. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats. It is taken orally or by intravenous injection. It can also be used with other blood pressure medications.
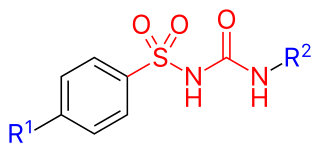
Sulfonylureas or sulphonylureas are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture. The functional group consists of a sulfonyl group (-S(=O)2) with its sulphur atom bonded to a nitrogen atom of a ureylene group (N,N-dehydrourea, a dehydrogenated derivative of urea). The side chains R1 and R2 distinguish various sulfonylureas. Sulfonylureas as the most widely used herbicide.
Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia describes the condition and effects of low blood glucose caused by excessive insulin. Hypoglycemia due to excess insulin is the most common type of serious hypoglycemia. It can be due to endogenous or injected insulin.

Diabetic hypoglycemia is a low blood glucose level occurring in a person with diabetes mellitus. It is one of the most common types of hypoglycemia seen in emergency departments and hospitals. According to the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System-All Injury Program (NEISS-AIP), and based on a sample examined between 2004 and 2005, an estimated 55,819 cases involved insulin, and severe hypoglycemia is likely the single most common event.

Tolbutamide is a first-generation potassium channel blocker, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medication. This drug may be used in the management of type 2 diabetes if diet alone is not effective. Tolbutamide stimulates the secretion of insulin by the pancreas.

Exenatide, sold under the brand name Byetta and Bydureon among others, is a medication used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. It is used together with diet, exercise, and potentially other antidiabetic medication. It is a treatment option after metformin and sulfonylureas. It is given by injection under the skin twice daily or once weekly.
Repaglinide is an antidiabetic drug in the class of medications known as meglitinides, and was invented in 1983. Repaglinide is a medication used in addition to diet and exercise for blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes. The mechanism of action of repaglinide involves promoting insulin release from β-islet cells of the pancreas; like other antidiabetic drugs, a main side effect concern is hypoglycemia. It is sold by Novo Nordisk under the name of Prandin in the United States, Gluconorm in Canada, Surepost in Japan, Repaglinide in Egypt, and Novonorm elsewhere. In Japan it is produced by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.

Meglitinides or glinides are a class of drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes.
Gliclazide, sold under the brand name Diamicron among others, is a sulfonylurea type of anti-diabetic medication, used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is used when dietary changes, exercise, and weight loss are not enough. It is taken by mouth.

Delorazepam, also known as chlordesmethyldiazepam and nordiclazepam, is a drug which is a benzodiazepine and a derivative of desmethyldiazepam. It is marketed in Italy, where it is available under the trade name EN and Dadumir. Delorazepam (chlordesmethyldiazepam) is also an active metabolite of the benzodiazepine drugs diclazepam and cloxazolam. Adverse effects may include hangover type effects, drowsiness, behavioural impairments and short-term memory impairments. Similar to other benzodiazepines delorazepam has anxiolytic, skeletal muscle relaxant, hypnotic and anticonvulsant properties.
Complications of diabetes are secondary diseases that are a result of elevated blood glucose levels that occur in diabetic patients. These complications can be divided into two types: acute and chronic. Acute complications are complications that develop rapidly and can be exemplified as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), lactic acidosis (LA), and hypoglycemia. Chronic complications develop over time and are generally classified in two categories: microvascular and macrovascular. Microvascular complications include neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy; while cardiovascular disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease are included in the macrovascular complications.
Dysglycemia is a general definition for any abnormalities in blood glucose levels. They include hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance test, impaired fasting glucose, among others.

Gemigliptin (rINN), sold under the brand name Zemiglo, is an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor class of drugs. Glucose lowering effects of DPP-4 inhibitors are mainly mediated by GLP-1 and gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) incretin hormones which are inactivated by DPP-4.

Dulaglutide, sold under the brand name Trulicity among others, is a medication used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with diet and exercise. It is also approved in the United States for the reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes who have established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors. It is a once-weekly injection.