 |
|---|
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 9 June 1875, electing members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg City, Redange, and Vianden. [1] [2]
 |
|---|
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 9 June 1875, electing members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg City, Redange, and Vianden. [1] [2]
Candidates who were successful are in bold.
The electoral system provided for run-off votes, but in this case all successful candidates were elected after only one round with an absolute majority.
| Canton | Seats | Candidate | Votes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capellen | 3 | Norbert Metz | 427 |
| Funck | 395 | ||
| Kirpach | 381 | ||
| Turnout | 471 | ||
| Clervaux | 3 | Joseph Conzemius | 363 |
| Théodore-Arthur Bouvier | 335 | ||
| Urbin | 325 | ||
| Hamelius | 143 | ||
| Toutsch | 23 | ||
| Turnout | 406 | ||
| Diekirch | 4 | Pierre Toussaint | 341 |
| Victor Tschiderer | 308 | ||
| Jean-Pierre Salentiny | 301 | ||
| Mergen | 291 | ||
| Steichen | 228 | ||
| Schmit | 172 | ||
| Turnout | 535 | ||
| Grevenmacher | 3 | Victor Schoren | 339 |
| Félix Putz | 337 | ||
| Zénon de Muyser | 313 | ||
| Turnout | 361 | ||
| Luxembourg-Ville | 3 | Charles-Jean Simons | 361 |
| Antoine Pescatore | 311 | ||
| Simonis | 309 | ||
| Mersch-Wittenauer | 212 | ||
| Turnout | 541 | ||
| Redange | 3 | Berger | 359 |
| Rénilde-Guillaume Jacques | 355 | ||
| Jean Orianne | 327 | ||
| Bian | 291 | ||
| Turnout | 580 | ||
| Vianden | 1 | Adolphe Pauly | 65 |
| Tibesar | 20 | ||
| Turnout | 86 | ||
A by-election in Grevenmacher was soon organised for 27 July, as Victor Schoren, one of the Grevenmacher Deputies, had been appointed commissioner of the district of Grevenmacher. [3]
Another by-election had to be organised for Vianden, as Adolphe Pauly soon resigned; the election date was set for 15 November. This resulted in the election of Camille Dumont, who was supported by the Blochausen government. [4]
Luxembourg is a parliamentary representative democratic monarchy, whereby the prime minister is the head of government, and the multi-party system. Executive power is under the constitution of 1868, as amended, exercised by the government, by the grand duke and the Council of Government (cabinet), which consists of a prime minister and several other ministers. Usually, the prime minister is the leader of the political party or coalition of parties having the most seats in parliament. Legislative power is vested in both the government and parliament. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The National Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral French Parliament under the Fifth Republic, the upper house being the Senate. The National Assembly's legislators are known as députés, meaning "delegate" or "envoy" in English; etymologically, it is a cognate of the English word deputy, the standard term for legislators in many parliamentary systems.
The 12 cantons of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg are subdivisions at the first level of local administrative unit (LAU-1) in the European Union's Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics for Eurostat purposes. They were subdivisions of the three districts of Luxembourg until 2015, when the district level of government was abolished. The cantons are in turn subdivided into 100 communes.
Elections in Luxembourg are held to determine the political composition of the representative institutions of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Luxembourg is a liberal representative democracy, with universal suffrage guaranteed under its constitution. Elections are held regularly, and are considered to be fair and free.

South is one of the four multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Deputies, the national legislature of Luxembourg. The constituency was established in 1919 following the introduction of proportional representation for elections to the Chamber of Deputies. It consists of the cantons of Capellen and Esch-sur-Alzette. The constituency currently elects 23 of the 60 members of the Chamber of Deputies using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 general election it had 111,884 registered electors.

East is one of the four multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Deputies, the national legislature of Luxembourg. The constituency was established in 1919 following the introduction of proportional representation for elections to the Chamber of Deputies. It consists of the cantons of Echternach, Grevenmacher and Remich. The constituency currently elects seven of the 60 members of the Chamber of Deputies using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 general election it had 40,246 registered electors.

North is one of the four multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Deputies, the national legislature of Luxembourg. The constituency was established in 1919 following the introduction of proportional representation for elections to the Chamber of Deputies. It consists of the cantons of Clervaux, Diekirch, Redange, Vianden and Wiltz. The constituency currently elects nine of the 60 members of the Chamber of Deputies using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 general election it had 52,922 registered electors.
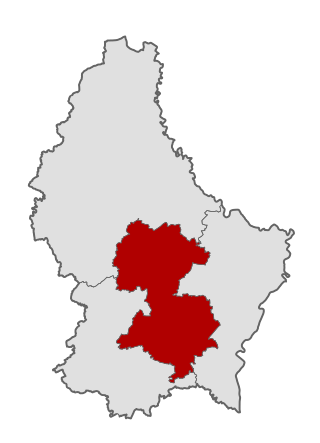
Centre is one of the four multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Deputies, the national legislature of Luxembourg. The constituency was established in 1919 following the introduction of proportional representation for elections to the Chamber of Deputies. It consists of the cantons of Luxembourg and Mersch. The constituency currently elects 21 of the 60 members of the Chamber of Deputies using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2023 general election it had 81,687 registered electors.

Constituencies are used to elect representatives ('deputies') to Luxembourg's unicameral national legislature, the Chamber of Deputies.
The Party of the Right, abbreviated to PD, was a political party in Luxembourg between 1914 and 1944. It was the direct predecessor of the Christian Social People's Party (CSV), which has ruled Luxembourg for all but fifteen years since.

The first French legislative constituency for citizens abroad is one of eleven constituencies representing French people living outside France. It was created by the 2010 redistricting of French legislative constituencies and elects, since 2012, one representative to the National Assembly.

The president of France is elected by direct popular vote to a five-year term. If the office falls vacant before the end of five years, an election to a new five-year term is held, generally within 20 to 35 days of the vacancy.
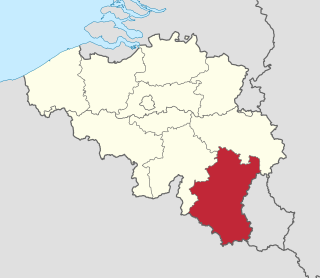
Luxembourg is one of the 11 multi-member constituencies of the Chamber of Representatives, the lower house of the Belgian Federal Parliament, the national legislature of Belgium. The constituency was established as Arlon-Marche-Bastogne-Neufchâteau-Virton in 1995 following the fourth Belgian state reform. It was renamed Luxembourg in 2003 following the re-organisation of constituencies across Belgium along provincial lines. It is conterminous with the province of Luxembourg. The constituency currently elects four of the 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives using the open party-list proportional representation electoral system. At the 2019 federal election the constituency had 212,441 registered electors.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 13 and 20 June 1893, electing 20 members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg-Ville, Redange and Vianden.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 14 June 1887, electing 21 members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Esch-sur-Alzette, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg-Ville, Redange, and Vianden.
General elections were held in Luxembourg on 14 June 1854, electing members of the Chamber of Deputies from all the cantons of Luxembourg.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 30 July 1860, electing 15 members of the Assembly of Estates. The elections took place in Echternach, Esch-sur-Alzette, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg-Campagne, Mersch, Redange, Remich, and Wiltz.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 14 June 1881, electing members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Esch-sur-Alzette, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg-Ville, Redange, and Vianden.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 8 June 1869, electing 20 members of the Chamber of Deputies. The elections took place in Capellen, Clervaux, Diekirch, Grevenmacher, Luxembourg City, Redange, and Vianden.
Partial general elections were held in Luxembourg on 9 June 1863, electing members of the Assembly of Estates. The elections took place in Luxembourg-City, Capellen, Diekirch, Grevenmacher, Redange, Clervaux, and Vianden.