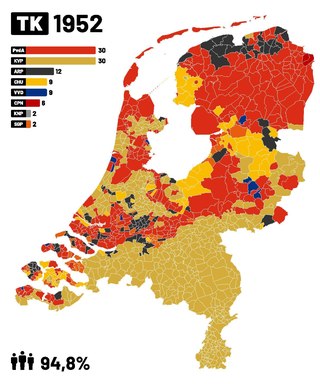
General elections were held in the Netherlands on 25 June 1952. The Catholic People's Party and the Labour Party both won 30 of the 100 seats in the House of Representatives. It was the first time since 1913 that the Catholic People's Party and its predecessors had not received a plurality of the vote.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 13 June 1956. For the first time, the Labour Party (PvdA) emerged as the largest party, winning 50 of the 150 seats in the House of Representatives.
The Greens of Andorra is a green political party in Andorra.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 28 October 1884. The Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag, with 99 of the 397 seats. Voter turnout was 60.5%.
The Democratic Party is a centre-right political party in Bulgaria led by Alexander Pramatarski. The party was a member of the European People's Party (EPP).
Parliamentary elections were held in Greece on 11 December [O.S. 28 November] 1910, following elections in August. The Liberal Party won 307 of the 362 seats. Eleftherios Venizelos remained Prime Minister, having assumed office on 18 October.

Folketing elections were held in Denmark on 28 October 1947, except in the Faroe Islands where they were held on 18 February 1948. The Social Democratic Party remained the largest in the Folketing, with 57 of the 150 seats. Voter turnout was 86% in Denmark proper and 60% in the Faroes.

General elections were held in Belgium on 17 April 1977. The result was a victory for the Christian People's Party, which won 56 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 28 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 95.1%. Elections were also held for the nine provincial councils and for the Council of the German Cultural Community.

General elections were held in Malta between 12 and 14 June 1971. The Malta Labour Party emerged as the largest party, winning 28 of the 55 seats.
Federal elections were held in Switzerland on 28 October 1928. Although the Social Democratic Party received the most votes, the Free Democratic Party remained the largest party in the National Council, winning 58 of the 198 seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary between 28 and 30 June 1931. The result was a victory for the Unity Party, which won 149 of the 245 seats in Parliament. István Bethlen remained Prime Minister, but resigned on 24 August due to the effects of the Great Depression and was replaced by Gyula Károlyi.
Parliamentary elections were held in Hungary on 28 and 29 May 1939. The result was a victory for the Party of Hungarian Life, which won 181 of the 260 seats in Parliament and won 49 percent of the popular vote in the election. Pál Teleki remained Prime Minister. This was a major breakthrough for the far-right in Hungary; between them, far-right parties were officially credited with 49 seats and 25 percent of the vote.
General elections were held in Italy on 23 May 1886, with a second round of voting on 30 May. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 292 of the 508 seats. As in 1882, the elections were held using small multi-member constituencies of between two and five seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 27 October 1923. Voters elected all 28 seats in the Lower House of the Althing and eight of the fourteen seats in Upper House. The Citizens' Party, a loose collection of conservatives, emerged as the largest party in the Lower House, winning 16 of the 28 seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 9 July 1927. Voters elected all 28 seats in the Lower House of the Althing and eight of the fourteen seats in Upper House. The Progressive Party emerged as the largest party in the Lower House, winning 13 of the 28 seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 16 July 1933. Voters elected all 28 seats in the Lower House of the Althing and eight of the fourteen seats in Upper House. The Independence Party emerged as the largest party in the Lower House, winning 13 of the 28 seats.
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 24 June 1934. They were the first held after reforms to the electoral system that increased the number of seats in the Lower House from 28 to 33 and ensured that all members of the Althing were elected at the same election. The Independence Party emerged as the largest party in the Lower House, winning 14 of the 33 seats.

Constituent Assembly elections were held in Portugal on 28 May 1911, following a coup in October 1910. The result was a victory for the Portuguese Republican Party, which won 229 of the 234 seats.

General elections were held in Portugal on 28 April 1918, following a coup by Sidónio Pais in December 1917. The elections were boycotted by the Democratic Party, the Evolutionist Party and the Republican Union, who had won over 90% of the seats in the 1915 elections.

The People's Party was a political party in Bulgaria between 1894 and 1920.










