| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events from the year 1889 in Italy
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events from the year 1889 in Italy
The total population of Italy in 1889 (within the current borders) was 31.325 million. [1] Life expectancy in 1889 was 39.1 years. [2]

Due to the tariff war with France, business confidence was undermined and in 1889, a real estate boom burst. Three banks in Turin, seriously involved in building speculation in Rome, failed. Small savers lost several hundred million lire and 80,000 building workers in Rome — mainly immigrants — found themselves out of a job. In February 1889 some of them rioted. [3] [4]


Giovanni Giolitti was an Italian statesman. He was the prime minister of Italy five times between 1892 and 1921. He is the longest-serving democratically elected prime minister in Italian history, and the second-longest serving overall after Benito Mussolini. A prominent leader of the Historical Left and the Liberal Union, he is widely considered one of the most wealthy, powerful and important politicians in Italian history; due to his dominant position in Italian politics, Giolitti was accused by critics of being an authoritarian leader and a parliamentary dictator.

Giuseppe Zanardelli was an Italian jurist and political figure. He served as the Prime Minister of Italy from 15 February 1901 to 3 November 1903. An eloquent orator, he was also a Grand Master freemason. Zanardelli, representing the bourgeoisie from Lombardy, personified the classical 19th-century liberalism, committed to suffrage expansion, anticlericalism, civil liberties, free trade and laissez-faire economics. Throughout his long political career, he was among the most ardent advocates of freedom of conscience and divorce.
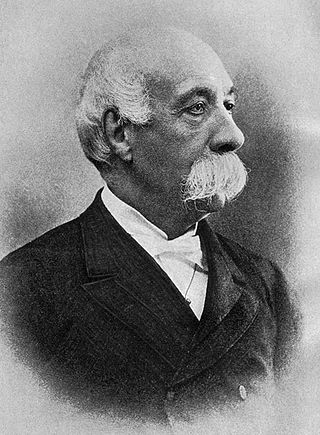
Francesco Crispi was an Italian patriot and statesman. He was among the main protagonists of the Risorgimento, a close friend and supporter of Giuseppe Mazzini and Giuseppe Garibaldi, and one of the architects of Italian unification in 1860. Crispi served as Prime Minister of Italy for six years, from 1887 to 1891, and again from 1893 to 1896, and was the first prime minister from Southern Italy. Crispi was internationally famous and often mentioned along with world statesmen such as Otto von Bismarck, William Ewart Gladstone, and Lord Salisbury.

Antonio Starrabba, Marquess of Rudinì was an Italian statesman, Prime Minister of Italy between 1891 and 1892 and from 1896 until 1898.

Luigi Gerolamo Pelloux was an Italian general and politician, born of parents who retained their Italian citizenship when Savoy was annexed to France. He was the Prime Minister of Italy from 29 June 1898 to 24 June 1900, his rule was considered by historians as conservative and militarist.

Napoleone Colajanni was an Italian writer, journalist, criminologist, socialist, and politician. In the 1880s, he abandoned republicanism for socialism, and became Italy's leading theoretical writer on the issue for a time. He has been called the father of Sicilian socialism. Due to the Italian Socialist Party's discourse of Marxist class struggle, he reverted in 1894 to his original republicanism and joined the Italian Republican Party. Colajanni was an ardent critic of the Lombrosian school in criminology. In 1890, he was elected in the national Chamber of Deputies and was re-elected in all subsequent parliaments until his death in September 1921.

The Banca Romana scandal surfaced in January 1893 in Italy over the bankruptcy of the Banca Romana, one of the six national banks authorised at the time to issue currency. The scandal was the first of many Italian corruption scandals, and discredited both ministers and parliamentarians, in particular those of the Historical Left and was comparable to the Panama Canal Scandal that was shaking France at the time, threatening the constitutional order. The crisis prompted a new banking law, tarnished the prestige of the Prime Ministers Francesco Crispi and Giovanni Giolitti and prompted the collapse of the latter's government in November 1893. The scandal led also to the creation of one central bank, the Bank of Italy.
General elections were held in Italy on 23 November 1890, with a second round of voting on 30 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 401 of the 508 seats. As in 1886, the elections were held using small multi-member constituencies with between two and five seats.
General elections were held in Italy on 6 November 1892, with a second round of voting on 13 November. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc emerged as the largest in Parliament, winning 323 of the 508 seats. The electoral system reverted to the pre-1882 method of using single-member constituencies with second round run-offs.
Events from the year 1893 in Italy.
Events from the year 1894 in Italy.
Events from the year 1895 in Italy.
Events from the year 1896 in Italy.
Events from the year 1899 in Italy.
The Left group, later called Historical Left by historians to distinguish it from the left-wing groups of the 20th century, was a liberal and reformist parliamentary group in Italy during the second half of the 19th century. The members of the Left were also known as Democrats or Ministerials. The Left was the dominant political group in the Kingdom of Italy from the 1870s until its dissolution in the early 1910s.
The Italian Penal Code of 1889, commonly known as the Zanardelli Code, was the penal code in effect in the Kingdom of Italy from 1890 to 1930, and it is still in effect in Vatican City. The Zanardelli code gets its name from Giuseppe Zanardelli, then Minister of Justice, who lobbied for the code's approval. It unified penal legislation in Italy, abolished capital punishment and recognised the right to strike.
Events from the year 1890 in Italy.
Events from the year 1888 in Italy
Events from the year 1887 in Italy
Events from the year 1884 in Italy