| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events from the year 1896 in Italy.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | |||||
Events from the year 1896 in Italy.

In 1896, the Banco Ambrosiano was founded in Milan by Giuseppe Tovini, a Catholic advocate, and was named after Saint Ambrose, the 4th century archbishop of the city. Tovini's purpose was to create a Catholic bank as a counterbalance to Italy's "lay" banks, and its goals were "serving moral organisations, pious works, and religious bodies set up for charitable aims." The bank came to be known as the "priests' bank."

The Battle of Adwa was the climactic battle of the First Italo-Ethiopian War. Ethiopia managed to defeat the invading Italian force led by Oreste Baratieri on Sunday, March 1, 1896, near the town of Adwa. The decisive victory thwarted the campaign of the Kingdom of Italy to expand its colonial empire in the Horn of Africa. By the end of the 19th century, European powers had carved up almost all of Africa after the Berlin Conference; only Ethiopia and Liberia still maintained their independence. Adwa became a pre-eminent symbol of pan-Africanism and secured Ethiopian sovereignty until the Second Italo-Ethiopian War forty years later.

The First Italo-Ethiopian War, also referred to as the First Italo-Abyssinian War, or simply in Italy as the Abyssinian War, was a war fought between Italy and Ethiopia from 1895 to 1896. It originated from the disputed Treaty of Wuchale, which the Italians claimed turned Ethiopia into an Italian protectorate. Full-scale war broke out in 1895, with Italian troops from Italian Eritrea achieving initial successes against Tigrayan warlords at Coatit, Senafe and Debra Ailà, until they were reinforced by a large Ethiopian army led by Emperor Menelik II. The Italian defeat came about after the Battle of Adwa, where the Ethiopian army dealt the heavily outnumbered Italian soldiers and Eritrean askaris a decisive blow and forced their retreat back into Eritrea. The war concluded with the Treaty of Addis Ababa. Because this was one of the first decisive victories by African forces over a European colonial power, this war became a preeminent symbol of pan-Africanism and secured Ethiopia's sovereignty until the Second Italo-Ethiopian War of 1935–37.
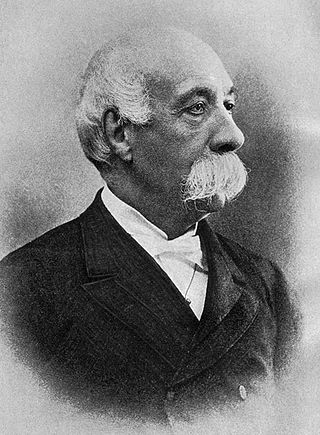
Francesco Crispi was an Italian patriot and statesman. He was among the main protagonists of the Risorgimento, a close friend and supporter of Giuseppe Mazzini and Giuseppe Garibaldi, and one of the architects of Italian unification in 1860. Crispi served as Prime Minister of Italy for six years, from 1887 to 1891, and again from 1893 to 1896, and was the first prime minister from Southern Italy. Crispi was internationally famous and often mentioned along with world statesmen such as Otto von Bismarck, William Ewart Gladstone, and Lord Salisbury.

Antonio Starrabba, Marquess of Rudinì was an Italian statesman, Prime Minister of Italy between 1891 and 1892 and from 1896 until 1898.

Luigi Gerolamo Pelloux was an Italian general and politician, born of parents who retained their Italian citizenship when Savoy was annexed to France. He was the Prime Minister of Italy from 29 June 1898 to 24 June 1900, his rule was considered by historians as conservative and militarist.

The Fasci Siciliani, short for Fasci Siciliani dei Lavoratori, were a popular movement of democratic and socialist inspiration that arose in Sicily in the years between 1889 and 1894. The Fasci gained the support of the poorest and most exploited classes of the island by channeling their frustration and discontent into a coherent programme based on the establishment of new rights. Consisting of a jumble of traditionalist sentiment, religiosity, and socialist consciousness, the movement reached its apex in the summer of 1893, when new conditions were presented to the landowners and mine owners of Sicily concerning the renewal of sharecropping and rental contracts.

Giuseppe Galliano was an officer of the Royal Italian Army, mostly known for his role during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. He perished in the Battle of Adwa and was posthumously awarded the Gold Medal of Military Valour.

Umberto I was King of Italy from 9 January 1878 until his assassination in 1900. His reign saw Italy's expansion into the Horn of Africa, as well as the creation of the Triple Alliance among Italy, Germany and Austria-Hungary.
General elections were held in Italy on 26 May 1895, with a second round of voting on 2 June. The "ministerial" left-wing bloc remained the largest in Parliament, winning 334 of the 508 seats.
General elections were held in Italy on 21 March 1897, with a second round of voting on 28 March. The "Ministerial" left-wing bloc, led by Giovanni Giolitti remained the largest in Parliament, winning 327 of the 508 seats.
Events from the year 1895 in Italy.
Events from the year 1891 in Italy.
Events from the year 1898 in Italy.
The Right group, later called Historical Right by historians to distinguish it from the right-wing groups of the 20th century, was an Italian conservative parliamentary group during the second half of the 19th century. After 1876, the Historical Right constituted the Constitutional opposition toward the left governments. It originated in the convergence of the most liberal faction of the moderate right and the moderate wing of the democratic left. The party included men from heterogeneous cultural, class, and ideological backgrounds, ranging from British-American individualist liberalism to Neo-Hegelian liberalism as well as liberal-conservatives, from strict secularists to more religiously-oriented reformists. Few prime ministers after 1852 were party men; instead they accepted support where they could find it, and even the governments of the Historical Right during the 1860s included leftists in some capacity.

The Siege of Mekelle, sometimes known as the battle of Mekelle, took place in January 1896 during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. Italian forces surrendered a partially completed fort at Mekelle, a city in the northern Tigray Region of Ethiopia which they had occupied since 1895, to Ethiopian forces.
The Liberal Constitutional Party was a political party in Italy, born to represent the liberal-conservative and anti-Transformist wing of the Historical Right. Their members were usually labeled as Constitutionals or Liberal-Conservatives, especially during the leadership of Rudinì and Sonnino.
Events from the year 1897 in Italy
Events from the year 1890 in Italy.

Giuseppe Edoardo Arimondi, OSML, OMS, OCI was an Italian general, mostly known for his role during the First Italo-Ethiopian War. He was one of the few European commanders who gained a victory over the Mahdists before Kitchener's Expedition, soundly defeating them at Agordat in 1893. After a long and successful colonial service, he died in combat at Adwa, and was posthumously awarded the Gold Medal of Military Valour.
Events from the year 1887 in Italy