| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1895 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1895 in Taiwan.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1895 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1895 in Taiwan.

Taiwan Province is a nominal administrative division of the Republic of China (ROC). The province remains a titular division as a part of the Constitution of the Republic of China, but it is no longer considered to have any administrative function practically.
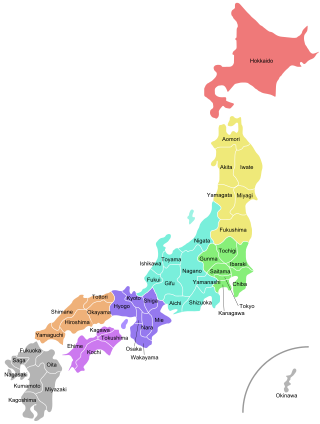
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one regional prefecture and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.

The February 28 incident was an anti-government uprising in Taiwan that was violently suppressed by the Kuomintang–led nationalist government of the Republic of China (ROC). Directed by provincial governor Chen Yi and president Chiang Kai-shek, thousands of civilians were killed beginning on February 28, 1947. The incident is considered to be one of the most important events in Taiwan's modern history and was a critical impetus for the Taiwan independence movement.

Provinces are the most numerous type of province-level divisions in China. There are currently 22 provinces administered by China and 1 province that is claimed, but not administered (Taiwan). The government of Chinese provinces consists of a Provincial People's Government headed by a governor that acts as the executive, a Provincial People's Congress with legislative powers, and a parallel provincial branch of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) that elects a Party Secretary and a Provincial Standing Committee.

The Republic of Formosa was a short-lived republic that existed on the island of Taiwan in 1895 between the formal cession of Taiwan by the Qing dynasty of China to the Empire of Japan by the Treaty of Shimonoseki and its being taken over by Japanese troops. The Republic lasted 151 days; it was proclaimed on 23 May 1895 and extinguished on 21 October, when the Republican capital Tainan was taken over by the Japanese. Though sometimes claimed as the first East Asian republic to have been proclaimed, it was predated by the Lanfang Republic in Borneo, established in 1777, as well as by the Republic of Ezo in Japan, established in 1869.
Sangokujin is a Japanese term referring to the various former colonial subjects of the Empire of Japan in the aftermath of World War II. This term particularly applied to Koreans and Taiwanese people, although it also sometimes was used for Ryukyuan people. The term is now generally considered antiquated and offensive.
There are eleven types of elections in Taiwan which, since 2012, have been unified into general and local elections, each held every four years, typically in January and November respectively. There may also be by-elections. Electoral systems include first-past-the-post, proportional representation, single non-transferable voting, and a parallel mixture of the above.

The governor-general of Taiwan was the head of the Government-General of Taiwan in the Japanese era when they were part of the Empire of Japan, from 1895 to 1945.

The Presidential Office Building is the work place of the President of the Republic of China on Taiwan. The building, located in the Zhongzheng District in the national capital — Taipei, was designed by architect Uheiji Nagano during the period of Japanese rule of Taiwan (1895–1945). The structure originally housed the Office of the Governor-General of Taiwan. Damaged in Allied bombing during World War II, the building was restored after the war by Chen Yi, the governor-general of Taiwan Province. It became the Presidential Office in 1950 after the government of the Republic of China lost control of mainland China and relocated the nation's capital to Taipei at the end of the Chinese Civil War. At present, this Baroque-style building is a symbol of the government and a famous historical landmark in downtown Taipei.

Retrocession Day is the name given to the annual observance and a former public holiday in Taiwan to commemorate the end of Japanese rule of Taiwan and Penghu, and the claimed retrocession ("return") of Taiwan to the Republic of China on 25 October 1945. However, the idea of "Taiwan retrocession" is in dispute.

The island of Taiwan, together with the Penghu Islands, became a dependency of Japan in 1895, when the Qing dynasty ceded Fujian-Taiwan Province in the Treaty of Shimonoseki after the Japanese victory in the First Sino-Japanese War. The short-lived Republic of Formosa resistance movement was suppressed by Japanese troops and quickly defeated in the Capitulation of Tainan, ending organized resistance to Japanese occupation and inaugurating five decades of Japanese rule over Taiwan. The entity, historically known in English as Formosa, had an administrative capital located in Taihoku (Taipei) led by the Governor-General of Taiwan.

Taiwanese kana is a katakana-based writing system that was used to write Taiwanese Hokkien when the island of Taiwan was under Japanese rule. It functioned as a phonetic guide to hanzi, much like furigana in Japanese or Zhuyin fuhao in Chinese. There were similar systems for other languages in Taiwan as well, including Hakka and Formosan languages.

Shinchiku Prefecture was one of the administrative divisions of Taiwan during the Japanese era. The prefecture consisted of modern-day Hsinchu City, Hsinchu County, Taoyuan City, and Miaoli County.

The Taihoku Air Raid that took place on 31 May 1945 was the largest Allied air raid on the city of Taihoku, then under Japanese colonial rule, during World War II. Many residents were killed in the raid and tens of thousands wounded or displaced.

The Ministry of Colonial Affairs was a cabinet-level government ministry of the Empire of Japan from 1929 to 1942.
Japanization or Japanisation is the process by which Japanese culture dominates, assimilates, or influences other cultures. According to The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, "To japanize" means "To make or become Japanese in form, idiom, style, or character".

The recordkeeping and development of the economic history of Taiwan started in the Age of Discovery. In the 17th century, the Europeans realized that Taiwan is located on the strategic cusp between the Far East and Southeast Asia. Two main European empires that competed to colonize it were the Dutch and Spanish Empires. Taiwan also became an intermediate destination for trade between Western European empires and East Asia states. The history of Taiwan as a colony of the Dutch Empire, Kingdom of Tungning, Qing China, and Empire of Japan between 1630 and 1945 was based heavily on economics.

The Taiwan Army of Japan was an army of the Imperial Japanese Army stationed on the island of Taiwan as a garrison force. Taiwanese were relegated to non-combatant civilian work work as manual labourers, porters and Chinese language interpreters. Taiwanese were not allowed as combatants until 1942 when volunteers were permitted to enlist and all combatant soldiers from the Taiwan army of Japan before 1942 were ethnic Japanese. Japan only conscripted Taiwanese in 1945 in a last ditch attempt for manpower.

The Truku War, is series of events happened between May and August 1914, involving the Truku indigenous group uprising against colonial Japanese forces in Japanese Taiwan.
The Second Prefectural Assembly Elections(Japanese: 第二囘州會議員選擧) were held on 20 November 1940 in Taiwan under Japanese rule. According to the Japanese law, half members of prefectural assembly shall be elected by the members of local assembly and the other half shall be appointed by the Governor-General (Japanese: 總督). In this time, 82 seats from five prefectural assemblies were open for election. Voting was done by Electoral colleges (EC) formed by the more than 3,600 members of local assemblies. Around half of them were directly elected in the previous year, the other half were appointed by the prefectural governor (Japanese: 州知事).