| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1939 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1939 in Taiwan, Empire of Japan.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1939 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1939 in Taiwan, Empire of Japan.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. It is located at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands with a combined area of 36,193 square kilometres. The main island of Taiwan, also known as Formosa, has an area of 35,808 square kilometres, with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanized population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.

Taiwan, officially known as the Republic of China (ROC), is governed in a framework of a representative democratic republic under a five-power system first envisioned by Sun Yat-sen in 1906, whereby under the constitutional amendments, the President is head of state and the Premier (President of the Executive Yuan) is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Executive Yuan. Legislative power is vested primarily in the Legislative Yuan. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. In addition, the Examination Yuan is in charge of validating the qualification of civil servants, and the Control Yuan inspects, reviews, and audits the policies and operations of the government. The party system is currently dominated by two major parties: the Kuomintang (KMT), which broadly favors maintaining the constitutional framework of the Republic of China Constitution and deepened economical cooperation with mainland China, and the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), which broadly favors de jure Taiwanese Independence, and the eventual abolition of the ROC Constitution in favor of creating a "Taiwanese Republic."

The president of the Republic of China, commonly known as the president of Taiwan, is the head of state of the Republic of China (Taiwan) as well as the commander-in-chief of the Republic of China Armed Forces. The position once had authority of ruling over Mainland China, but its remaining jurisdictions has been limited to Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and other smaller islands since the conclusion of the Chinese Civil War.

The Legislative Yuan is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of China (Taiwan) located in Taipei. The Legislative Yuan is composed of 113 members, who are directly elected for four-year terms by people of the Taiwan Area through a parallel voting system.

The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fifth and current constitution of the Republic of China (ROC), ratified by the Kuomintang during the Constituent National Assembly session on 25 December 1946, in Nanjing, and adopted on 25 December 1947. The constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.

Yuan Tseh Lee is a Taiwanese chemist. He is a Professor Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley. He was the first Taiwanese Nobel Prize laureate who, along with the Hungarian-Canadian John C. Polanyi and American Dudley R. Herschbach, won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1986 "for their contributions to the dynamics of chemical elementary processes".
The history of the Republic of China begins after the Qing dynasty in 1912, when the Xinhai Revolution and the formation of the Republic of China put an end to 2,000 years of imperial rule. The Republic experienced many trials and tribulations after its founding which included being dominated by elements as disparate as warlord generals and foreign powers.
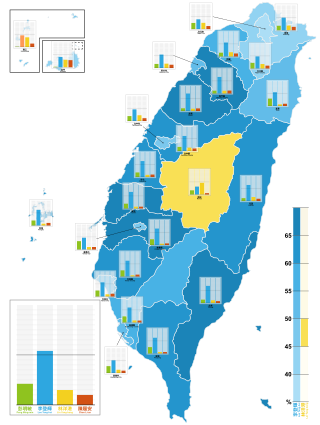
Presidential elections were held in Taiwan on 23 March 1996. It was the first direct presidential election in Taiwan, officially the Republic of China. In the previous eight elections the president and vice president had been chosen in a ballot of the deputies of the National Assembly, in accordance with the 1947 constitution. These were the first free and direct elections in the History of Taiwan.
The Executive Yuan is the executive branch of the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Its leader is premier, who is appointed by the president of the Republic of China (ROC) and serves as the head of government.

The Control Yuan is the supervisory and auditory branch of the government of the Republic of China, both during its time in mainland China and Taiwan.
The elections in Taiwan each held every four years, typically in January and November. Since 2012 the previously eleven types of elections in Taiwan have been unified into general and local elections. There may also be by-elections. Electoral systems include first-past-the-post, proportional representation, single non-transferable voting, and a parallel mixture of the above.
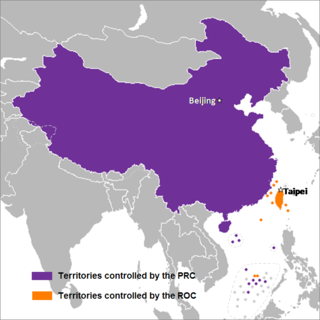
The term "Two Chinas" refers to the geopolitical situation where two political entities exist under the name "China".
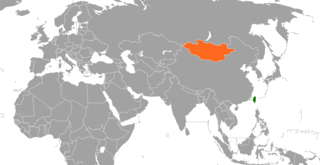
At its establishment in 1912, the Republic of China claimed to be the successor state to the entirety of the Qing empire, which included Outer Mongolia. The Republic of China did not recognize Outer Mongolia until 1945; neither country exchanged diplomats between 1946 and 1949. At the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, Mongolia recognized the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China retreated to the island of Taiwan. The Republic of China continued to show Mongolia as part of its territory on official maps until 2002 when they recognized Mongolia as an independent country, and informal relations were established between the two sides.
Referendums in Taiwan at both the national and local level are governed by the Referendum Act of Taiwan, which was enacted by the Legislative Yuan in December 2003. Citizens can propose laws via referendums at the national and local levels. The Referendum Act also allowed people to make changes or abolish laws by referendums.
Tuan Tuan and Yuan Yuan were two giant pandas that were gifted by the People's Republic of China to the Republic of China in 2008 as part of a cultural exchange program. The idea was first proposed in 2005, but the previous ROC administration in Taipei had initially refused to accept the pandas.
The Consumer Protection Committee is the agency of the Executive Yuan of Taiwan (ROC) which is responsible for consultation, discussion, and review of important consumer protection policies, laws and regulations, mechanisms, and enforcement outcomes, as well as cross-agency coordination in Taiwan.
Events from the year 1951 in Taiwan, Republic of China. This year is numbered Minguo 40 according to the official Republic of China calendar.
Events from the year 1953 in Taiwan, Republic of China. This year is numbered Minguo 42 according to the official Republic of China calendar.
Events from the year 1959 in Taiwan, Republic of China. This year is numbered Minguo 48 according to the official Republic of China calendar.

Fan Kuang-chun is a Taiwanese lawyer and politician.