| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1935 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1935 in Taiwan, Empire of Japan.
| |||||
| Decades: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See also: | Other events of 1935 History of Taiwan • Timeline • Years | ||||
Events from the year 1935 in Taiwan, Empire of Japan.

A colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, the rule remains separate to the original country of the colonizers, the metropolitan state, within the shared imperialist administration. This colonial administrative separation, though often blurred, makes colonies neither annexed or incorporated territories nor client states. Colonies contemporarily are identified and organized as not sufficiently self-governed dependent territories. Other past colonies have become either sufficiently incorporated and self-governed, or independent, with some to a varying degree dominated by remaining colonial settler societies or neocolonialism.

The Constitution of the Republic of China is the fifth and current constitution of the Republic of China (ROC), ratified by the Kuomintang during the Constituent National Assembly session on 25 December 1946, in Nanjing, and adopted on 25 December 1947. The constitution, along with its Additional Articles, remains effective in ROC-controlled territories.

Chen Yi was the chief executive and garrison commander of Taiwan Province after the Empire of Japan surrendered to the Republic of China. He acted on behalf of the Allied Powers to accept the Japanese Instrument of Surrender in Taipei Zhongshan Hall on October 25, 1945. He is considered to have mismanaged the tension between the Taiwanese and Mainland Chinese which resulted in the February 28 Incident in 1947, and was dismissed. In June 1948 he was appointed Chairman of Zhejiang Province, but was dismissed and arrested when his plan to surrender to the Chinese Communist Party was discovered. He was sentenced to death and executed by shooting in Taipei in 1950.

Dadaocheng is an area in Datong District, Taipei, Taiwan. It was also known as Twatutia, Daitōtei during Japanese rule, and Tataocheng (Mandarin) during the Kuomintang era.

Expo 58, also known as the 1958 Brussels World's Fair, was a world's fair held on the Heysel/Heizel Plateau in Brussels, Belgium, from 17 April to 19 October 1958. It was the first major world's fair registered under the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE) after World War II.

Jamestown 2007 is the name of the organization which planned the events commemorating the 400th anniversary (quadricentennial) of the founding of Jamestown, Virginia in 1607, the first permanent English-speaking settlement in what is now the United States of America. America's 400th Anniversary was an 18-month-long commemoration including 10 Signature Events, hundreds of community programs and dozens of partner and programs and events. Activities took place throughout Virginia, in major cities along the East Coast, and in the United Kingdom.

Chiang Wei-shui was a Taiwanese physician and activist. He was a founding member of the Taiwanese Cultural Association and the Taiwanese People's Party. He is seen as one of the most important figures in Taiwan's resistance movement against Japanese rule.

A colonial exhibition was a type of international exhibition that was held to boost trade. During the 1880s and beyond, colonial exhibitions had the additional aim of bolstering popular support for the various colonial empires during the New Imperialism period, which included the scramble for Africa.

The island of Taiwan, together with the Penghu Islands, became a dependency of Japan in 1895, when the Qing dynasty ceded Fujian-Taiwan Province in the Treaty of Shimonoseki after the Japanese victory in the First Sino-Japanese War. The short-lived Republic of Formosa resistance movement was suppressed by Japanese troops and quickly defeated in the Capitulation of Tainan, ending organized resistance to Japanese occupation and inaugurating five decades of Japanese rule over Taiwan. The entity, historically known in English as Formosa, had an administrative capital located in Taihoku (Taipei) led by the Governor-General of Taiwan.

The National Taiwan Museum, established in 1908, is the oldest museum in the Republic of China (Taiwan). It was founded by the colonial government during Taiwan's period of Japanese rule. The museum is located in Zhongzheng District, Taipei.

The recordkeeping and development of the economic history of Taiwan started in the Age of Discovery. In the 17th century, the Europeans realized that Taiwan is located on the strategic cusp between the Far East and Southeast Asia. Two main European empires that competed to colonize it were the Dutch and Spanish Empires. Taiwan also became an intermediate destination for trade between Western European empires and East Asia states. The history of Taiwan as a colony of the Dutch Empire, Kingdom of Tungning, Qing China, and Empire of Japan between 1630 and 1945 was based heavily on economics.

Local elections were held for the first time in Taiwan by the Japanese colonial government on 22 November 1935, electing half of the city and township councillors. The other half were appointed by the prefectural governors.

The Colonial Exhibition, Dutch: Koloniale Tentoonstelling, took place in Semarang, Dutch East Indies in from 20 August through 22 November 1914. Colonial exhibitions were trade expositions. It was designed to "give a comprehensive picture of the Dutch Indies in their present prosperous condition." It was the first large scale exposition in the Dutch East Indies, and financed by the participating corporations with a subsidy from the Dutch East Indies government.

Nakagawa Kenzō was a Japanese bureaucrat and political figure.
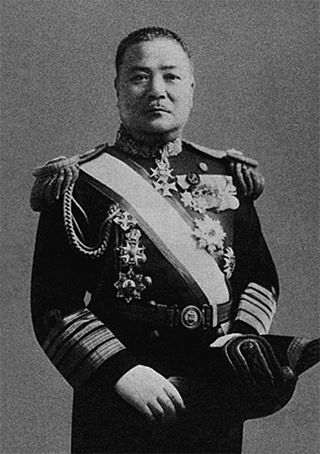
Admiral Seizō Kobayashi was a Japanese naval commander, commander of the Combined Fleet of the Imperial Japanese Navy (1931–1933) and the 17th Governor-General of Taiwan (1936–1940).

The Taiwan Exposition: In Commemoration of the First Forty Years of Colonial Rule was an exhibition held in Taihoku Prefecture in 1935, the 10th year of Hirohito's reign, to mark 40 years of the establishment of Japanese Formosa.
The Fifth National Industrial Exhibition was held in Osaka, Japan in 1903. It was the first to be open to foreign exhibitors, and twice the size of previous National Industrial Exhibitions. It was the fifth and final of the centrally planned National Industrial Exhibitions though exhibitions such as the one in 1907 in Tokyo followed.

In 1861, Prussia and the Qing dynasty signed the first Sino-German treaty during the Eulenburg Expedition. West Germany established diplomatic relations with the Republic of China in 1955. After recognizing the People's Republic of China in 1972, the two countries maintain unofficial diplomatic relations.