| |||||||||||||
| Registered | 29,479,386 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 57.68% | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
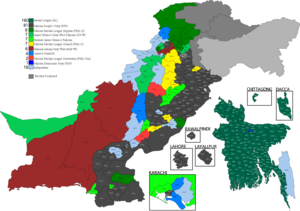 Map of Pakistan showing National Assembly Constituencies and winning partes | |||||||||||||
| History of Bangladesh |
|---|
 |
General Elections were held in East Pakistan province on Monday 7 December 1970 to elect 169 Members of 5th National Assembly of Pakistan. Out of 169 National Assembly seats 162 were General seats and 7 were reserved for women. Awami League won 167 out of 169 seats belonging to East Pakistan in the National Assembly of Pakistan, as well as a landslide in the East Pakistan Provincial Assembly. [1] [2] [3]

