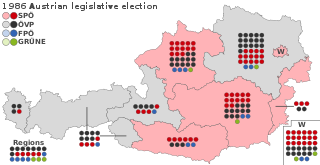
Early parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 23 November 1986. They were called by Chancellor Franz Vranitzky of the Socialist Party (SPÖ), as he was not prepared to continue the coalition government with new Freedom Party (FPÖ) leader Jörg Haider, who had ousted Norbert Steger at the party convention.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 24 April 1983. The result was a victory for the Socialist Party, which won 90 of the 183 seats. However, the Socialists lost the outright majority they had held since 1971, prompting Bruno Kreisky to stand down as SPÖ leader and Chancellor in favour of Fred Sinowatz. The SPÖ stayed in office by entering into a coalition government with the Freedom Party of Austria, which at this point was a liberal party. Voter turnout was 93%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 6 May 1979. The Socialist Party won a fourth term in government, taking 95 of the 183 seats. Voter turnout was 92.2%. As of the 2017 elections, this is the most seats that an Austrian party has won in a free election, as well as the last time that an Austrian party has won an outright majority.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 5 October 1975. The result was a victory for the Socialist Party (SPÖ), which won 93 of the 183 seats. Voter turnout was 93%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 1 March 1970. The Socialist Party (SPÖ) emerged as the largest party in the National Council, winning 81 of the 165 seats, just three seats short of an absolute majority and the first time it had become the largest party during the Second Republic. Voter turnout was 92%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 6 March 1966. The result was a victory for the Austrian People's Party (ÖVP), which won 85 of the 165 seats. Voter turnout was 94%.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 18 November 1962. The result was a victory for the Austrian People's Party, which won 81 of the 165 seats. Voter turnout was 94%. Although the People's Party had come up only two seats short of an outright majority, Chancellor Alfons Gorbach retained the grand coalition with the Socialists under Vice-Chancellor Bruno Pittermann.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 10 May 1959. Although the Socialist Party (SPÖ) received the most votes, the Austrian People's Party won one more seat than the SPÖ. The Communist Party of Austria lost its remaining three seats and has not returned to the National Council since. Voter turnout was 94%. The grand coalition that had governed the country since 1945 remained in office, with People's Party leader Julius Raab as chancellor and Socialist leader Bruno Pittermann as vice-chancellor.
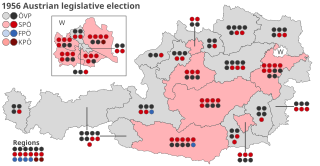
Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 13 May 1956. The result was a victory for the Austrian People's Party, which won 82 of the 165 seats in the National Council. Voter turnout was 96%. Although the ÖVP had come up one seat short of an absolute majority, ÖVP leader and Chancellor Julius Raab retained the grand coalition with the Socialists, with the SPÖ leader Adolf Schärf as Vice-Chancellor.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 22 February 1953. They were the elections in which the Socialist Party received the most votes since 1920. However, the Austrian People's Party won the most seats. The grand coalition between the two parties was continued with Julius Raab replacing Leopold Figl as Chancellor of Austria, who had had to resign after facing criticism from his own party, and Adolf Schärf of the Socialist Party remaining Vice Chancellor.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 9 October 1949. About 500,000 registered Nazis, who were not allowed to vote in 1945, regained their voting rights. A newly created party, the Electoral Party of Independents (WdU) specifically targeted this group of voters and immediately won a large share of votes. The Austrian People's Party remained strongest party, although losing their absolute majority of seats. Leopold Figl stayed as Chancellor, leading a coalition with the Socialist Party of Austria as junior partner.

Parliamentary elections were held in Austria on 25 November 1945, the first after World War II. The elections were held according to the Austrian election law of 1929, with all citizens at least 21 years old eligible to vote, however former Nazis were banned from voting, official sources putting their numbers at around 200,000.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 20 February 1890. The Centre Party regained its position as the largest party in the Reichstag by winning 107 of the 397 seats, whilst the National Liberal Party, formerly the largest party, was reduced to 38 seats.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 15 June 1893. Despite the Social Democratic Party (SPD) receiving a plurality of votes, the Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 96 of the 397 seats, whilst the SPD won just 44. Voter turnout was 72.4%.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 25 January 1907. Despite the Social Democratic Party (SPD) receiving a clear plurality of votes, they were hampered by the unequal constituency sizes that favoured rural seats. As a result, the Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 101 of the 397 seats, whilst the SPD won only 43. Voter turnout was 84.7%.

General elections were held in Sweden on 16 September 1956. The Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 106 of the 231 seats in the Andra kammaren of the Riksdag. A Social Democratic-Farmers' League coalition government was formed by Prime Minister Tage Erlander after the election with 125 of the total of 231 seats. Although the non-socialist parties held a majority in the Second Chamber, the Social Democrats held a majority in the First Chamber, so a non-socialist government could not be formed.

General elections were held in Sweden on 16 September 1979. Although the Swedish Social Democratic Party remained the largest party, winning 154 of the 349 seats in the Riksdag, the liberal interim government of Ola Ullsten was succeeded by another centre-right coalition government composed of the People's Party, the Moderate Party and the Centre Party, led by Centre Party leader Thorbjörn Fälldin. The three parties together won 175 seats, compared to the 174 won by the Social Democrats and Communists. It was the only time that non-socialist parties retained power in an election between 1928 and 2010. The Moderates dramatically increased their representation in the Riksdag, becoming the largest party of the non-socialist bloc, a position they maintained until 2022.

General elections were held in Belgium on 11 April 1954. The dominant Christian Social Party won 95 of the 212 seats in the Chamber of Representatives and 49 of the 106 seats in the Senate. Voter turnout was 93.2%. Elections for the nine provincial councils were also held.

Legislative elections were held in Cisleithania, the northern and western ("Austrian") crown lands of Austria-Hungary, on 14 and 23 May 1907 to elect the members of the 11th Imperial Council. They were the first elections held under universal male suffrage, after an electoral reform abolishing tax paying requirements for voters had been adopted by the Council and was endorsed by Emperor Franz Joseph earlier in the year. However, seat allocations were based on tax revenues from the States.

General elections were held in Macedonia on 16 October 1994 to elect a President and Assembly, with a second round of Assembly elections on 30 October. The presidential election was won by Kiro Gligorov of the Alliance for Macedonia, whilst the parties forming Alliance for Macedonia also won the Assembly elections with 95 of the 120 seats. However, the second round of the Assembly elections were boycotted by VMRO-DPMNE and the Democratic Party, as they claimed there had been irregularities in the first round.



























