| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 460 seats in the Sejm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 21 March 1976. [1]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 460 seats in the Sejm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 21 March 1976. [1]
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party or alliance | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |||
| Front of National Unity | Polish United Workers' Party | 23,502,983 | 99.43 | 261 | +6 | ||
| United People's Party | 113 | –4 | |||||
| Democratic Party | 37 | –2 | |||||
| Independents | 49 | 0 | |||||
| Blank ballots | 134,350 | 0.57 | – | – | |||
| Total | 23,637,333 | 100.00 | 460 | 0 | |||
| Valid votes | 23,637,333 | 99.94 | |||||
| Invalid votes | 14,923 | 0.06 | |||||
| Total votes | 23,652,256 | 100.00 | |||||
| Registered voters/turnout | 24,069,579 | 98.27 | |||||
| Source: Nohlen & Stöver | |||||||
As the other parties and "independents" were subordinate to PZPR, its control of the Sejm was total. [2] [3]

Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an area of 207,600 square kilometres (80,200 sq mi) with a population of 9.1 million. The country has a hemiboreal climate and is administratively divided into six regions. Minsk is the capital and largest city; it is administered separately as a city with special status.

Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and temperate transitional climate. Poland is composed of sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the fifth largest EU country by land area, covering a combined area of 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi). The capital and largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin.

Solidarity, full name Independent Self-Governing Trade Union "Solidarity", is a Polish trade union founded in August 1980 at the Lenin Shipyard in Gdańsk, Poland. Subsequently, it was the first independent trade union in a Warsaw Pact country to be recognised by the state.

The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and also referred to as Poland–Lithuania or the First Polish Republic, was a federative real union between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, existing from 1569 to 1795. This state was among the largest and most populated countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its peak in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth spanned nearly 1,000,000 km2 (390,000 sq mi) and supported a multi-ethnic population of approximately 12 million as of 1618. The official languages of the Commonwealth were Polish and Latin, with Catholicism as the state religion.
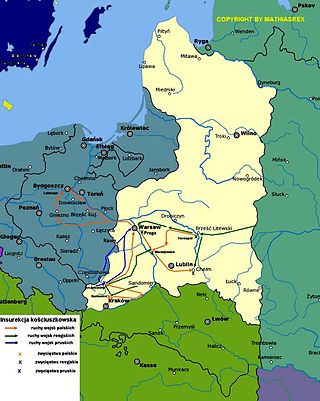
The Kościuszko Uprising, also known as the Polish Uprising of 1794, Second Polish War, Polish Campaign of 1794, and the Polish Revolution of 1794, was an uprising against the Russian and Prussian influence on the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, led by Tadeusz Kościuszko in Poland-Lithuania and the Prussian partition in 1794. It was a failed attempt to liberate the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from external influence after the Second Partition of Poland (1793) and the creation of the Targowica Confederation.

The Polish–Russian War of 1792 was fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on one side, and the Targowica Confederation and the Russian Empire under Catherine the Great on the other.

The Constitution of 3 May 1791, titled the Government Act, was a written constitution for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was adopted by the Great Sejm that met between 1788 and 1792. The Commonwealth was a dual monarchy comprising the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania; the new constitution was intended to address political questions following a period of political agitation and gradual reform that began with the Convocation Sejm of 1764 and the election that year of the Commonwealth's last king, Stanisław August Poniatowski. It was the first codified, modern constitution in Europe and the second in the world, after that of the United States.

National Rebirth of Poland, abbreviated to NOP, is an ultranationalist far-right political party in Poland registered by the District Court in Warsaw and National Electoral Commission. As of the 2015 election, the party had no seats in the Polish parliament. It was a member of the European National Front.

The Great Sejm, also known as the Four-Year Sejm was a Sejm (parliament) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that was held in Warsaw between 1788 and 1792. Its principal aim became to restore sovereignty to, and reform, the Commonwealth politically and economically.

Royal elections in Poland were the elections of individual kings, rather than dynasties, to the Polish throne. Based on traditions dating to the very beginning of the Polish statehood, strengthened during the Piast and Jagiellon dynasties, they reached their final form in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth period between 1572 and 1791. The "free election" was abolished by the Constitution of 3 May 1791, which established a constitutional-parliamentary monarchy.

The General Sejm was the bicameral legislature of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was established by the Union of Lublin in 1569 following the merger of the legislatures of the two states, the Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland and the Seimas of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It was one of the primary elements of the democratic governance in the Commonwealth. The sejm was a powerful political institution. The king could not pass laws without its approval.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 4 June 1989 to elect members of the Sejm and the recreated Senate, with a second round on 18 June. They were the first elections in the country since the communist government abandoned its monopoly of power in April 1989 and the first elections in the Eastern Bloc that resulted in the communist government losing power.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 16 November 1930, with Senate elections held a week later on 23 November. In what became known as the Brest elections, the pro-Sanation Nonpartisan Bloc for Cooperation with the Government took 47% of the vote and 249 of the 444 seats in Sejm and 77 of the 111 seats in the Senate. The elections are known as the least free elections in the Second Polish Republic due to the Brest trial controversy.
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 20 January 1957. They were the second election to the Sejm – the unicameral parliament of the People's Republic of Poland, and the third ever in the history of Communist Poland. It took place during the liberalization period, following Władysław Gomułka's ascension to power. Although conducted in a more liberal atmosphere than previous elections, they were far from free. Voters had the option of voting against some official candidates; de facto having a small chance to express a vote of no confidence against the government and the ruling Communist Polish United Workers Party. However, as in all Communist countries, there was no opportunity to elect any true opposition members to the Sejm. The elections resulted in a predictable victory for the Front of National Unity, dominated by the PZPR.
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 16 April 1961. They were the third elections to the Sejm, the parliament of the People's Republic of Poland, and fourth in Communist Poland.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 30 May 1965. They were the fourth elections to the Sejm of the People's Republic of Poland, and fifth in Communist Poland. They took place on 30 May. The lists admitted were controlled by the Front of National Unity (FJN), in turn controlled by the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR).
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 13 October 1985. According to the Constitution of 1952 the elections should have been held every 4 years, that is in the spring of 1984, but since the internal political situation was still considered "unstable" even after the repealing in 1983 of the Martial Law, the Sejm voted to extend its own term at first indefinitely and then until August 31, 1985, fixing the elections to be held not beyond the end of 1985. As was the case in previous elections, only candidates approved by the Communist regime were permitted on the ballot. The outcome was thus not in doubt, nevertheless the regime was hoping for a high turnout, which it could then claim as evidence of strong support for the government among the population. The opposition from the Solidarity movement called for a boycott of the elections. According to official figures 78.9% of the electorate turned out to vote. This turnout, while relatively high, was much lower than the nearly 100% turnout which was reported in previous elections.
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 1 June 1969. The results, like with the other elections in communist Poland, were controlled by the communist government. The results of the 1969 election were identical to the 1965 elections and were repeated in 1972.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 19 March 1972. The results, like with the other elections in communist Poland, were controlled by the communist government. The results of the 1965 election would be duplicated, exactly, by the 1969 and 1972 elections. The results of the next, 1976 election, would be only marginally different.

Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 23 March 1980. The results, like with the other elections in communist Poland, were controlled by the communist government. The results of the 1980 election exactly duplicated the 1976 elections, which were only marginally different from those of the preceding years.