Related Research Articles

Maritime archaeology is a discipline within archaeology as a whole that specifically studies human interaction with the sea, lakes and rivers through the study of associated physical remains, be they vessels, shore-side facilities, port-related structures, cargoes, human remains and submerged landscapes. A specialty within maritime archaeology is nautical archaeology, which studies ship construction and use.
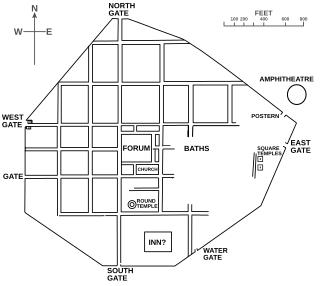
Calleva Atrebatum was an Iron Age oppidum, the capital of the Atrebates tribe. It then became a walled town in the Roman province of Britannia, at a major crossroads of the roads of southern Britain.

The archaeology of Israel is the study of the archaeology of the present-day Israel, stretching from prehistory through three millennia of documented history. The ancient Land of Israel was a geographical bridge between the political and cultural centers of Mesopotamia and Egypt.

Tusculum is a ruined Roman city in the Alban Hills, in the Latium region of Italy. Tusculum was most famous in Roman times for the many great and luxurious patrician country villas sited close to the city, yet a comfortable distance from Rome, notably the villas of Cicero and Lucullus.

Dion is a village and municipal unit in the municipality of Dion-Olympos in the Pieria regional unit, Greece. It is located at the foot of Mount Olympus at a distance of 17 km from the capital city of Katerini.

Kyrenia is a 4th-century BC ancient Greek merchant ship that sank c. 294 BC.
The year 1985 in archaeology involved some significant events.

Vishnu Shridhar Wakankar was an Indian archaeologist. Wakankar is credited with the discovery of the Bhimbetka rock caves in 1957 and the Kayatha culture in 1964, among others. In 2003, UNESCO inscribed the Bhimbetka rock caves as a World Heritage Site. The Bhimbetka rock caves exhibit one of the earliest traces of human life in India.

Phoenice or Phoenike was an ancient Greek city in Epirus and capital of the Chaonians. It is located high on an almost impregnable hill commanding the fertile valley below and near the modern town of the same name, Finiq, in southern Albania. It was the wealthiest city in Epirus and had the strongest walls until the Roman conquest. It was the location of the Treaty of Phoenice which ended the First Macedonian War. The city is part of an archaeological park.

George Emmanuel Mylonas was a Greek archaeologist of ancient Greece and of Aegean prehistory. He excavated widely, particularly at Olynthus, Eleusis and Mycenae, where he made the first archaeological study and publication of Grave Circle B, the earliest known monumentalized burials at the site.
This page lists major events of 2007 in archaeology.

Pompeii was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and many surrounding villas, the city was buried under 4 to 6 m of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD.

Desilo is an underwater archaeological site in southern Bosnia and Herzegovina, located near the Neretva river and the Croatian border. The site was first discovered in the late 20th century, but Desilo's history can be traced as far back as ancient times. Investigations by a University of Mostar archaeological team in 2007 uncovered many sunken boats at the bottom of the small lake in Desilo valley. The archaeologists believe these boats to be Illyrian ships, dating back to the first and second centuries B.C. Further excavations in 2008 by University of Oslo archaeologists found evidence suggesting that Desilo was an Illyrian trading post. These archaeological findings are significant because they are the first known discovery of Illyrian ships. Additionally, Desilo functioning as a trading centre suggests there were peaceful interactions between the Illyrians and the Romans.

The Ma'agan Michael Ship is a well-preserved 5th-century BCE boat discovered off the coast of Kibbutz Ma'agan Michael, Israel, in 1985. The ship was excavated and its timber immersed in preservation tanks at the University of Haifa, undergoing a seven-year process of impregnation by heated polyethylene glycol (PEG). In March 1999, the boat was reassembled and transferred to a dedicated wing built at the Hecht Museum, on the grounds of the university. The boat has provided researchers with insights into ancient methods of shipbuilding and the evolution of anchors.
This page lists major archaeological events of 2016.
This page lists major archaeological events of 2017.
This page lists major events of 2019 in archaeology.
This page lists major events of 2020 in archaeology.
This page lists major events of 2021 in archaeology.
This page lists significant events of 2022 in archaeology.
References
- ↑ "The Shipwreck at Ma'agan Mikhael (ca. 400 B.C.)". ΣΑΜΑΙΝΑ. Archived from the original on 2012-03-30. Retrieved 2011-08-13.
- ↑ Suro, Roberto (10 June 1988). "Newly Found Wall May Give Clue To Origin of Rome, Scientist Says". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 June 2017.
- ↑ "London Roman Amphitheatre". Historvius. Retrieved 2018-03-24.
- ↑ "Dr Lisa Lodwick (1988-2022) | All Souls College". www.asc.ox.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-02-06.
- ↑ "Dr. V. S. Wakankar". Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts. Retrieved 14 July 2024.
- ↑ G. E. Mylonas, 89, Archeologist Who Led Greek Excavations, Dies