
General elections were held in Guatemala on 9 November 2003, with a second round of the presidential election held on 28 December. Óscar Berger won the presidential election, representing the Grand National Alliance, a coalition of alliance of the Patriotic Party, the Reform Movement and the National Solidarity Party. The Alliance were also victorious in the Congressional elections, winning 47 of the 158 seats. Voter turnout was 57.9% in the Congressional elections, 58.9% in the first round of the presidential elections and 46.8% in the second.

General elections were held in the Netherlands on 5 July 1922. They were the first elections held under universal suffrage, which became reality after the acceptance of a proposal by Henri Marchant in 1919 that gave women full voting rights. Almost all major parties had a woman elected. The number of female representatives increased from one to seven. Only the Anti-Revolutionary Party principally excluded women from the House of Representatives. Another amendment to the electoral law increased the electoral threshold from 0.5% to 0.75%, after six parties had won seats with less than 0.75% of the vote in the previous elections.
The 1971 Turkish military memorandum, issued on 12 March that year, was the second military intervention to take place in Turkey, coming 11 years after its 1960 predecessor. It is known as the "coup by memorandum", which the military delivered in lieu of sending out tanks, as it had done previously. The event came amid worsening domestic strife, but ultimately did little to halt this phenomenon.

The People's Party is a Panamanian Christian democratic political party. Founded in 1956, it was made up of middle-class professionals, intellectuals and students, with support from trade unions, particularly the Federation of Christian Workers. It went on to become one of Latin America's most conservative and anti-communist Christian democratic parties. The ideological foundation of the party is based on the social doctrine of the Catholic Church. The PP is a full member of the Christian Democrat International and Christian Democratic Organization of America.

Elections in Guyana take place within the framework of a multi-party representative democracy and a presidential system. The National Assembly is directly elected, with the nominee of the party or alliance that receives the most votes becoming President.

Osmín Aguirre y Salinas was a Salvadoran military officer and politician who served as the provisional president of El Salvador from 21 October 1944 until 1 March 1945. A Colonel in the Salvadoran Army, Aguirre y Salinas led two successful coups against the Salvadoran government: once in 1931 and once more in 1944. He left office in 1945, with the assurance that his successor in the next election would be Salvador Castaneda Castro. Aguirre y Salinas was later assassinated by left-wing guerrillas near his home in San Salvador at the age of 87.

Federal elections were held in Germany on 15 June 1893. Despite the Social Democratic Party (SPD) receiving a plurality of votes, the Centre Party remained the largest party in the Reichstag after winning 96 of the 397 seats, whilst the SPD won just 44. Voter turnout was 72.4%.
Parliamentary elections were held in Finland on 15 and 16 March 1970.

General elections were held in Belgium on 26 June 1949. Several reforms took effect prior to the elections; they were the first after the introduction of universal women's suffrage; the number of seats in the Chamber of Representatives was increased from 202 to 212, and from now on, elections for the nine provincial councils were held simultaneously with parliamentary elections. The number of Chamber seats and the simultaneous provincial and parliamentary elections would remain unchanged until state reforms in 1993.

A constitutional referendum was held in France on 8 May 1870. Voters were asked whether they approved of the liberal reforms made to the constitution since 1860 and passed by the Sénatus-consulte on 20 April 1870. The changes were approved by 82.7% of voters with an 81.3% turnout. However, France's defeat in the Franco-Prussian War caused the Empire to be abolished later that year. Although this was the ninth constitutional referendum in French history, it was the first to have more than 8% oppose the motion; four of the previous seven had officially gained 99% approval.
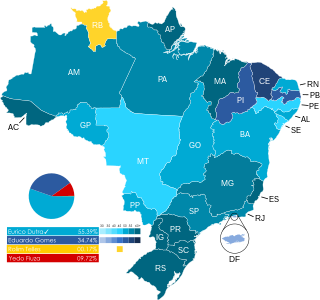
General elections were held in Brazil on 2 December 1945, the first since the establishment of Getúlio Vargas' Estado Novo. The presidential elections were won by Eurico Gaspar Dutra of the Social Democratic Party (PSD), whilst the PSD also won a majority of seats in both the Chamber of Deputies and the Senate. Voter turnout was 83% in the presidential election, 81% in the Chamber elections and 73% in the Senate elections.
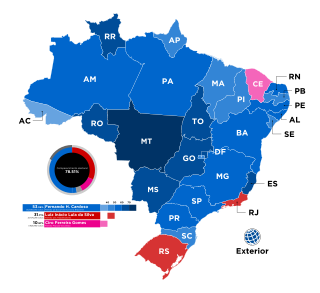
General elections were held in Brazil on 4 October 1998 to elect the President, National Congress and state governorships. If no candidate in the presidential election received more than 50% of the vote in the first round, a second-round runoff would have been held on 25 October. The election saw voting machines used for the first time in Brazilian history.

General elections were held in Costa Rica on 1 April 1917. Federico Tinoco Granados had seized power in a military coup in January and was the only candidate in the presidential election. The elections were considered to be fraudulent, with Tinoco as the only formal candidate.

General elections were held in Costa Rica on 4 February 1962. Francisco Orlich Bolmarcich of the National Liberation Party won the presidential election, whilst his party also won the parliamentary election. Voter turnout was 81%.

General elections were held in the Dominican Republic on 16 May 1990. Following a long vote count, Joaquín Balaguer of the Social Christian Reformist Party (PSRC) was declared winner of the presidential election, whilst in the Congressional elections the PSRC received the most votes and won a majority in the Senate, although the Dominican Liberation Party won the most seats in the House of Representatives.

General elections were held in the Dominican Republic on 16 May 1994. Joaquín Balaguer of the Social Christian Reformist Party won the presidential election, whilst the Dominican Revolutionary Party-led alliance won the Congressional elections. Voter turnout was 87.6%.

Legislative elections were held in Cisleithania, the northern and western ("Austrian") crown lands of Austria-Hungary, on 14 and 23 May 1907 to elect the members of the 11th Imperial Council. They were the first elections held under universal male suffrage, after an electoral reform abolishing tax paying requirements for voters had been adopted by the Council and was endorsed by Emperor Franz Joseph earlier in the year. However, seat allocations were based on tax revenues from the States.

Parliamentary elections were held in Brazil on 15 November 1982. The elections were conducted under the military dictatorship. Massive popular street demonstrations led the military dictatorship to stage the elections.
General elections were held in Colombia on 21 April 1974 to elect the President, Senate and Chamber of Representatives. They were the first elections after the end of the National Front agreement, which had restricted electoral participation to the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party, with each party allocated 50% of the seats in both houses, whilst the presidency alternated between the two parties.
Fifteen referendums were held in Switzerland during 2000. The first five were held on 12 March on reforming the judiciary and four popular initiatives; "for speeding up direct democracy ", "for a just representation of women in federal authorities", "for the protection of men against manipulations in procreation technology" and one to reduce motorised road by 50%. Whilst the judiciary reform was approved, all four popular initiatives were rejected. The next referendum was held on 21 May to authorise sectoral agreements between Switzerland and the European Union, and was approved by around two-thirds of voters.
















