 | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
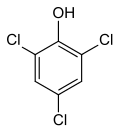
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 776729 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.633 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 3766 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2020 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H2Cl3OH/C6H3Cl3O | |||
| Molar mass | 197.45 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | yellow-whitish lumps or powder | ||
| Density | 1.4901 g/cm3 at 75 °C [1] | ||
| Melting point | 69.5 °C (157.1 °F; 342.6 K) [1] | ||
| Boiling point | 249 °C (480 °F; 522 K) [1] | ||
| 0.069 g/100 g H2O [2] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| Warning | |||
| H302, H315, H319, H351, H410 | |||
| P201, P202, P264, P270, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, also known as TCP, phenaclor, Dowicide 2S, Dowcide 2S, omal, is a chlorinated phenol that has been used as a fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, antiseptic, [3] defoliant, and glue preservative. [4] It is a clear to yellowish crystalline solid with a strong, phenolic odor. It decomposes on heating to produce toxic and corrosive fumes including hydrogen chloride and chlorine.


