| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
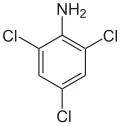
| Preferred IUPAC name 2,4,6-Trichloroaniline | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.200 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2811 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H4Cl3N | |||
| Molar mass | 196.46 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Long needles or fine, light purple fibers [1] | ||
| Melting point | 78.5 °C (173.3 °F; 351.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 262 °C (504 °F; 535 K) | ||
| 40 mg/L | |||
| Solubility | chloroform, ether, ethanol [2] | ||
| log P | 3.69 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 1.47×10−7 mmHg | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.07 (for the conjugate acid) | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 13.93 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards | Harmful, corrosive, toxic | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
    | |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H311, H317, H331, H373, H410, H411 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P340, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P333+P313, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) | ||
| Decomposes | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) | 2400 mg/kg (rat, oral) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
2,4,6-Trichloroaniline is a chemical compound with a formula of C6H4Cl3N. It is useful as an intermediate in chemical reactions. [2]