Related Research Articles
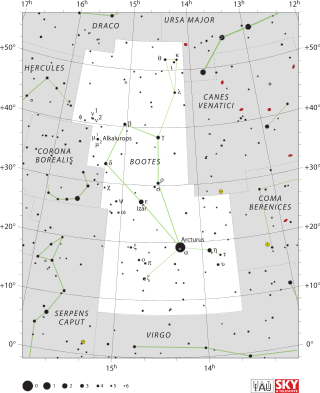
Zeta Boötis, Latinized from ζ Boötis, is a binary star system in the constellation of Boötes. They have the Flamsteed designation 30 Boötis; Zeta Boötis is the Bayer designation. This system is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent magnitude of +3.78. The individual magnitudes differ slightly, with component A having a magnitude of 4.46 and component B at the slightly dimmer magnitude 4.55. It is located at a distance of approximately 180 light years from the Sun based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −9 km/s.
45 Aurigae or PLX 1468.2 is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.34, making it visible to the naked eye under suitable viewing conditions. An annual parallax shift of 16.89 mas as seen from Earth's orbit indicates the system is located about 193 light years from the Sun.
46 Boötis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Boötes, located mid-way between α Coronae Borealis and ε Boötis. It has the Bayer designation b Boötis; 46 Boötis is the Flamsteed designation. The system lies 478 light-years away from the Sun based on parallax, and is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.67. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +19 km/s. The light from this system displays an unusually high level of polarization due to interstellar dust.
14 Boötis is a possible binary star system located 110 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, yellow-white hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.53. This system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −40 km/s. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 0.260 arc seconds per annum.
39 Boötis is a triple star system located around 224 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with a combined apparent magnitude of 5.68. The system is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −31 km/s.
29 Arietis is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Aries. 29 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. Its annual parallax shift of 34.86±0.13 mas indicates a distance of about 94 light-years from Earth. The system is barely visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 6.0; it is 0.02 degree north of the ecliptic. It is moving further from Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 9 km/s.
HD 129132 is a triple star system in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is dimly visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 6.13. The distance to this system is approximately 382 light years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +1.7 km/s.

Epsilon Herculis, Latinized from ε Herculis, is a fourth-magnitude multiple star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. The combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.9111 is bright enough to make this system visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 21.04 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 155 light years from the Sun. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −25 km/s.

Theta Draconis, a name Latinized from θ Draconis, is a binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. It is faintly visible to the naked eye at night with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.12. Parallax measurements place it at an estimated distance of 68.6 light-years from the Sun, and it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −8 km/s. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 0.464″ per year. O. J. Eggen included this star as a member of the NGC 1901 supercluster based on its space motion.
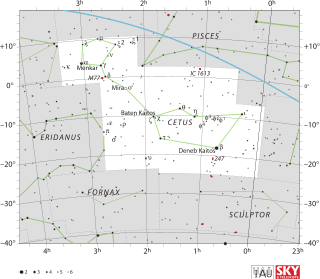
Xi1 Ceti , Latinized from ξ1 Ceti, is a binary star system located in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.36. The distance to this system is approximately 340 light years based on parallax measurements, and it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −4 km/s. The proximity of the star to the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations.
μ Cygni, Latinised as Mu Cygni, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Cygnus. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.49. The system is located 72 light years distant from the Sun, based on parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +17 km/s.
HD 151613 is a binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.84. The distance to this star, as estimated from its annual parallax shift of 39.3 mas, is 83 light years. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −2 km/s.
Theta Hydrae, Latinized from θ Hydrae, is a binary star system in the constellation Hydra. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.9. The star system has a high proper motion with an annual parallax shift of 28.4 mas, indicating a distance of about 115 light years. Theta Hydrae forms a double with a magnitude 9.9 star located at an angular separation of 29 arcseconds.

43 Persei is a binary star system in the northern constellation Perseus. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.28. The system is located around 38.5 parsecs (125.4 ly) distant from the Sun, based on parallax.
49 Librae is the Flamsteed designation for a binary star system in the Zodiac constellation of Libra. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.47, making it faintly visible to the naked eye from dark suburban skies as a dim, yellow-white hued star. The system is located 95 light years away from the Sun, based on parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −20 km/s.
38 Leonis Minoris is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Leo Minor. It shines with a combined light of apparent magnitude 5.84, which indicates it a dimly visible to the naked eye under good viewing conditions. An annual parallax shift of 19.11 mas provides a distance estimate of around 171 light years. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at a rate of 0.226 arcseconds per year, and is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +31 km/s.

ZZ Boötis is a star system in the constellation Boötes. It varies from magnitude 6.79 to 7.44 over five days. Based on its parallax, measured by the Gaia spacecraft, it is about 350 light-years away.
HD 60803 is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Canis Minor, located less than a degree to the northwest of the prominent star Procyon. It has a yellow hue and is visible to the naked eye as a dim point of light with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.904. The distance to this system is 135 light years as determined using parallax measurements, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +4.6 km/s.
HD 72945 and HD 72946 form a co-moving star system in the northern constellation of Cancer. HD 72945 is a binary star that is dimly visible to the naked eye as a point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.91. At an angular separation of 10.10″ is the fainter companion star HD 72946 at magnitude 7.25. It is being orbited by a brown dwarf. The system as a whole is located at a distance of approximately 84 light years from the Sun based on parallax measurements.

19 Leonis Minoris is a spectroscopic binary located in the northern constellation Leo Minor. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.1, making it one of the brighter members of the constellation. The system is relatively close at a distance of 94 light years but is drifitng closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of 8.6 km/s.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv: 1108.4971 , Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Eggleton, Peter P.; Yakut, Kadri (July 2017), "Models for 60 double-lined binaries containing giants", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 468 (3): 3533−3556, arXiv: 1611.05041 , Bibcode:2017MNRAS.468.3533E, doi: 10.1093/mnras/stx598 , S2CID 119476544.
- ↑ Abt, Helmut A. (January 2009), "MK Classifications of Spectroscopic Binaries", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement, 180 (1): 117–118, Bibcode:2009ApJS..180..117A, doi:10.1088/0067-0049/180/1/117, S2CID 122811461.
- ↑ Cowley, A. P.; Bidelman, W. P. (February 1979), "MK spectral types for some F and G stars", Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 91: 83–86, Bibcode:1979PASP...91...83C, doi: 10.1086/130446 .
- 1 2 "3 Boo". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2019-04-10.